Unveiling the Earth’s Surface: A Comprehensive Exploration of World Terrain Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Earth’s Surface: A Comprehensive Exploration of World Terrain Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Earth’s Surface: A Comprehensive Exploration of World Terrain Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Earth’s Surface: A Comprehensive Exploration of World Terrain Maps
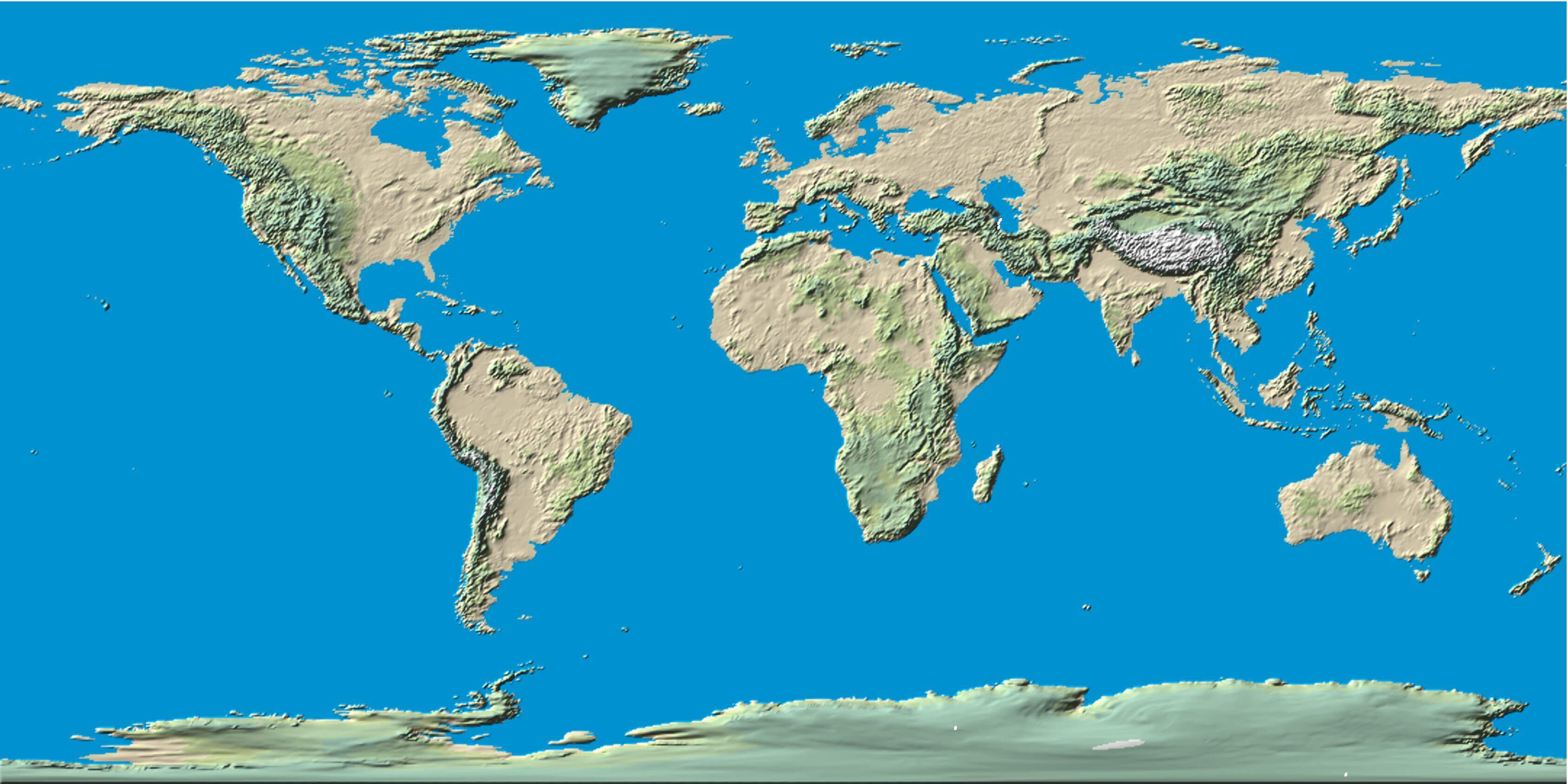
The Earth’s surface, a tapestry of diverse landscapes, presents a visually stunning and geographically intricate panorama. Understanding the intricacies of this terrain is crucial for a multitude of applications, from navigating vast oceans to planning infrastructure projects, from predicting natural disasters to guiding ecological conservation efforts. This intricate understanding is made possible through the creation of world terrain maps, which serve as invaluable tools for visualizing and analyzing the Earth’s topography.
A Visual Representation of Earth’s Topography
World terrain maps, often referred to as topographic maps, provide a visual representation of the Earth’s surface, capturing its elevation, relief, and other significant geographical features. These maps utilize a range of techniques to depict the varied heights and forms of the land, effectively translating three-dimensional landscapes onto a two-dimensional surface.
Key Elements of a World Terrain Map
A comprehensive world terrain map typically incorporates several key elements, each contributing to its effectiveness in conveying geographical information:
- Contour Lines: These lines connect points of equal elevation, providing a visual representation of the slope and shape of the land. Closely spaced contour lines indicate steep terrain, while widely spaced lines suggest gentle slopes.
- Elevation Points: Numerical values indicate the precise height of specific points on the map, offering a quantitative understanding of the terrain.
- Relief Shading: This technique uses shading to simulate the effect of light and shadow, emphasizing the three-dimensional nature of the landscape.
- Water Features: Rivers, lakes, and oceans are depicted accurately, providing context for the surrounding terrain and highlighting the influence of water on the landscape.
- Geographic Features: Mountains, valleys, plateaus, and other prominent features are clearly marked, providing a comprehensive overview of the major landforms present.
- Color Coding: Different colors are often used to represent various elevation ranges, further enhancing the visual clarity of the map.
The Significance of World Terrain Maps
The significance of world terrain maps extends beyond their visual appeal. They serve as indispensable tools in a wide range of fields, contributing to our understanding of the Earth’s surface and its dynamic processes.
1. Navigation and Exploration:
World terrain maps have long been essential tools for explorers, navigators, and travelers. By providing a clear understanding of the landscape, they facilitate safe and efficient movement across varied terrains. From navigating treacherous mountain passes to charting the course of a ship across vast oceans, these maps guide exploration and ensure safe passage.
2. Infrastructure Planning and Development:
Terrain maps play a crucial role in the planning and development of infrastructure projects. Engineers and architects rely on these maps to assess the feasibility of construction projects, considering factors such as elevation, slope, and soil conditions. This information is vital for determining the optimal location for roads, bridges, dams, and other infrastructure, minimizing environmental impact and ensuring project success.
3. Disaster Management and Mitigation:
Understanding the terrain is crucial for preparing for and mitigating natural disasters. Terrain maps help identify areas prone to landslides, floods, earthquakes, and other hazards. This information allows for effective disaster planning, evacuation routes, and early warning systems, minimizing potential damage and saving lives.
4. Ecological Conservation and Management:
World terrain maps provide valuable insights into the distribution of ecosystems and the impact of human activities on the environment. They help identify sensitive areas requiring protection, such as endangered habitats and fragile ecosystems. This information informs conservation efforts, ensuring the preservation of biodiversity and the sustainable management of natural resources.
5. Scientific Research and Analysis:
Terrain maps are invaluable tools for a wide range of scientific research. Geographers, geologists, climatologists, and other researchers use these maps to analyze geological formations, study climate patterns, and understand the distribution of plant and animal life. They provide a foundation for understanding the Earth’s dynamic processes and the interconnectedness of various environmental factors.
6. Education and Public Awareness:
World terrain maps serve as powerful educational tools, fostering an appreciation for the Earth’s diverse landscapes and promoting geographical literacy. They provide a visual and accessible way to learn about the planet’s topography, fostering a deeper understanding of the world around us.
Frequently Asked Questions about World Terrain Maps:
1. What are the different types of world terrain maps?
World terrain maps can be classified based on their scale, projection, and intended use.
- Small-scale maps: These maps cover vast areas with a lower level of detail, suitable for general overview and global analysis.
- Large-scale maps: These maps focus on specific regions, providing greater detail and accuracy for local planning and navigation.
- Planar maps: These maps use a flat projection, often suitable for depicting specific regions with minimal distortion.
- Conical maps: These maps project the Earth’s surface onto a cone, providing a balance between accuracy and visual representation.
- Cylindrical maps: These maps project the Earth’s surface onto a cylinder, useful for depicting the entire globe but with significant distortion at higher latitudes.
2. How are world terrain maps created?
World terrain maps are created using a combination of data sources and mapping techniques.
- Traditional Surveying: This method involves physically measuring the elevation of points on the ground using instruments such as theodolites and levels.
- Remote Sensing: This technique utilizes satellite imagery and aerial photography to capture data about the Earth’s surface.
- Digital Elevation Models (DEMs): These models are created using data from multiple sources, including remote sensing, surveys, and existing maps. They provide a digital representation of the terrain, facilitating analysis and visualization.
3. How accurate are world terrain maps?
The accuracy of world terrain maps varies depending on the data sources, mapping techniques, and the scale of the map. Generally, maps based on recent data and advanced technologies offer greater accuracy.
4. What are the limitations of world terrain maps?
World terrain maps, despite their usefulness, have some limitations.
- Distortion: All maps project a three-dimensional surface onto a two-dimensional plane, inevitably introducing some distortion. This distortion is more pronounced in maps covering large areas.
- Data Availability: The accuracy of terrain maps is dependent on the availability of data, which may be limited in remote or sparsely populated areas.
- Dynamic Nature: The Earth’s surface is constantly changing due to natural processes such as erosion, tectonic activity, and climate change. Terrain maps represent a snapshot in time and may not reflect the most up-to-date information.
Tips for Utilizing World Terrain Maps Effectively:
- Choose the appropriate map scale and projection: Consider the specific purpose and area of interest to select the map that provides the necessary level of detail and accuracy.
- Understand the map’s legend and symbols: Familiarize yourself with the map’s key, which explains the symbols and colors used to represent different features.
- Use multiple maps and data sources: Combine information from various maps and data sources to obtain a comprehensive understanding of the terrain.
- Consider the limitations of the map: Be aware of the potential for distortion and data limitations, and interpret the information accordingly.
Conclusion
World terrain maps provide an invaluable window into the Earth’s diverse and intricate surface. They serve as essential tools for navigation, infrastructure planning, disaster management, ecological conservation, scientific research, and public education. By understanding the elements, significance, and limitations of these maps, we can effectively utilize them to navigate the world, manage its resources, and protect its fragile ecosystems. As technology advances and data availability increases, world terrain maps will continue to evolve, offering increasingly accurate and comprehensive representations of our planet’s remarkable topography.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Earth’s Surface: A Comprehensive Exploration of World Terrain Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!