Unraveling Virginia’s Topography: A Comprehensive Look at the State’s Elevation Map
Related Articles: Unraveling Virginia’s Topography: A Comprehensive Look at the State’s Elevation Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling Virginia’s Topography: A Comprehensive Look at the State’s Elevation Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling Virginia’s Topography: A Comprehensive Look at the State’s Elevation Map
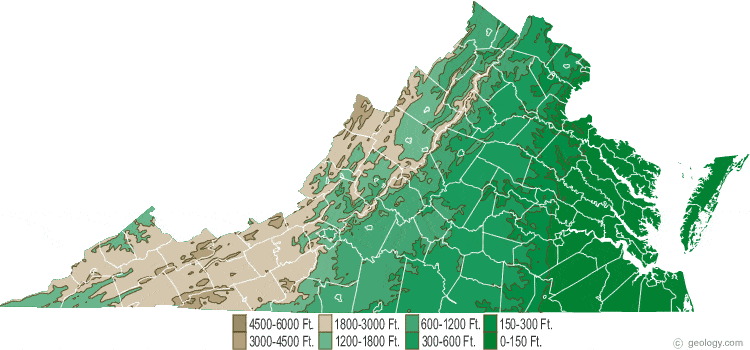
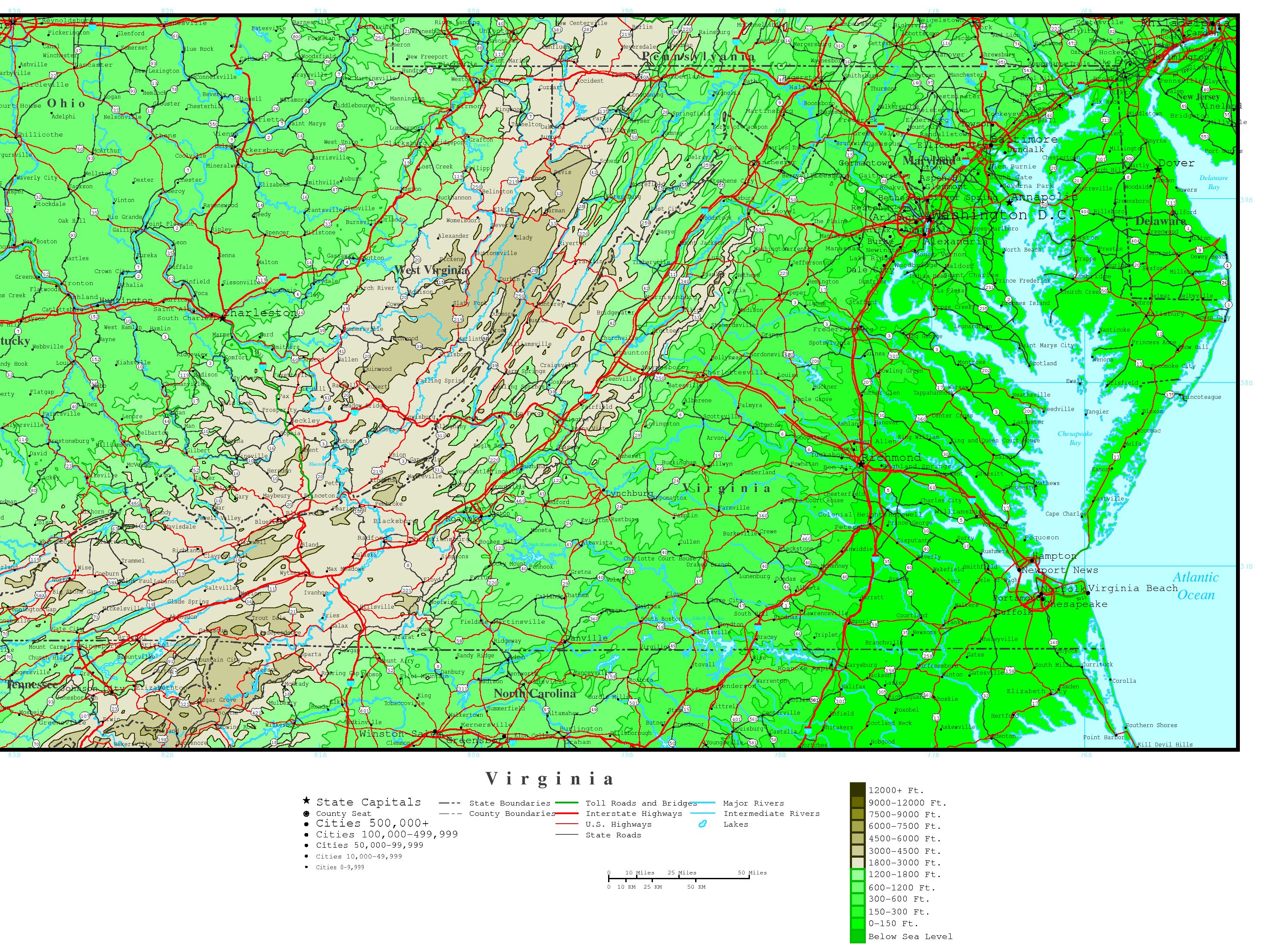
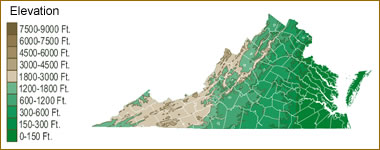
Virginia, a state steeped in history and natural beauty, boasts a diverse landscape shaped by geological forces over millennia. The state’s elevation map, a visual representation of its topography, offers a fascinating glimpse into these forces and their impact on the environment, infrastructure, and human activity.
Understanding the Landscape Through Elevation:
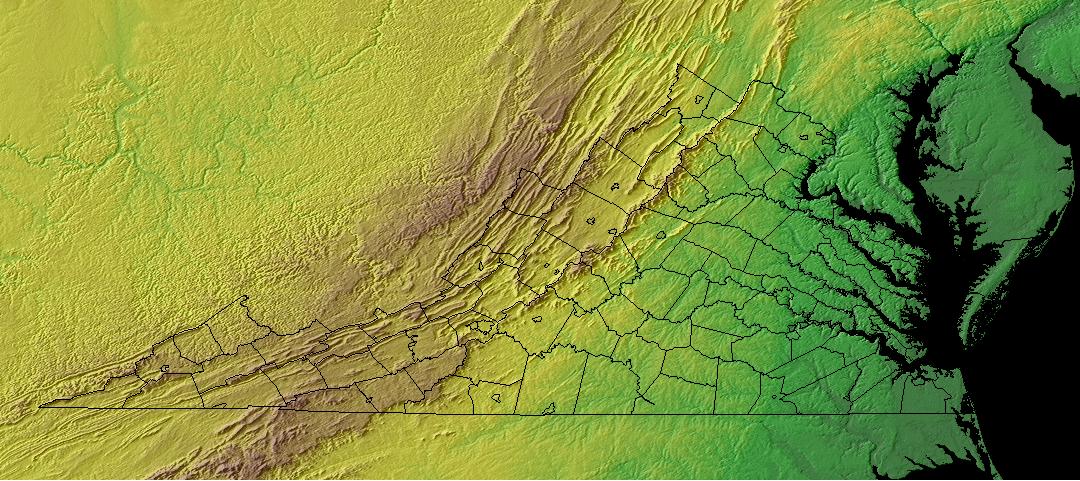
The Virginia elevation map reveals a dramatic tapestry of elevation, ranging from the coastal plains along the Atlantic Ocean to the majestic peaks of the Blue Ridge Mountains. This diverse topography is a result of several geological processes:
- The Appalachian Orogeny: This ancient mountain-building event, spanning millions of years, created the Appalachian Mountains, including the Blue Ridge, which dominate the western part of Virginia.
- Erosion and Sedimentation: Over time, the forces of erosion and weathering sculpted the mountains, carrying sediment to lower elevations, forming the Piedmont Plateau and the Coastal Plain.
- Faulting and Uplift: Geological faults and uplift events further shaped the landscape, creating distinct topographic features like the Shenandoah Valley and the Blue Ridge Escarpment.
Key Features of the Virginia Elevation Map:
-
The Blue Ridge Mountains: These iconic mountains, part of the larger Appalachian chain, rise to impressive heights, with peaks exceeding 5,000 feet. Mount Rogers, at 5,729 feet, is Virginia’s highest point. The Blue Ridge is a major geological feature, influencing weather patterns, water flow, and the distribution of plant and animal life.
-
The Piedmont Plateau: This gently rolling region lies between the Blue Ridge Mountains and the Coastal Plain. It features a mosaic of rolling hills, valleys, and streams, characterized by moderate elevations ranging from 200 to 1,500 feet. The Piedmont is home to numerous forests, agricultural lands, and urban centers.
-
The Coastal Plain: This flat, low-lying region stretches along the Atlantic coast, extending inland from the Chesapeake Bay. Elevations are generally below 200 feet, making it susceptible to flooding and sea-level rise. The Coastal Plain is a vital agricultural region, known for its fertile soils and proximity to the ocean.
-
The Shenandoah Valley: This fertile valley, nestled between the Blue Ridge Mountains and the Allegheny Mountains, is a unique geological feature. It formed due to faulting and erosion, creating a narrow, elongated basin with elevations ranging from 500 to 1,500 feet. The Shenandoah Valley is renowned for its scenic beauty, agricultural productivity, and rich history.
The Significance of the Virginia Elevation Map:
The Virginia elevation map holds significant value for various fields, including:
-
Environmental Management: It helps understand the distribution of natural resources, including water resources, forests, and wildlife habitats. This knowledge is crucial for sustainable resource management, conservation efforts, and mitigating the effects of climate change.
-
Infrastructure Development: The elevation map informs the design and construction of roads, bridges, pipelines, and other infrastructure projects. It helps engineers identify potential challenges related to terrain, soil stability, and water drainage.
-
Land-Use Planning: Understanding the elevation and topography allows for informed land-use planning, ensuring appropriate zoning, development, and agricultural practices. This helps prevent environmental degradation and promotes sustainable land management.
-
Disaster Preparedness: The elevation map is essential for disaster preparedness and mitigation. It helps identify areas prone to flooding, landslides, and other natural hazards, allowing for effective response planning and community resilience.
-
Tourism and Recreation: The elevation map highlights the state’s diverse landscapes, attracting tourists and outdoor enthusiasts. It provides information for hiking, camping, skiing, and other recreational activities, contributing to the tourism industry.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q: What is the average elevation of Virginia?
A: The average elevation of Virginia is approximately 600 feet above sea level.
Q: What are the highest and lowest points in Virginia?
A: Mount Rogers, located in the Blue Ridge Mountains, is the highest point in Virginia at 5,729 feet. The lowest point is at sea level along the Atlantic coast.
Q: How does the elevation map help understand Virginia’s climate?
A: Elevation significantly influences climate. Higher elevations are generally cooler and receive more rainfall, while lower elevations are warmer and drier. The elevation map helps understand the distribution of climate zones across the state.
Q: How does the elevation map impact agriculture in Virginia?
A: The elevation map helps identify areas with suitable soil types and water resources for different agricultural practices. Higher elevations are often suitable for livestock grazing, while lower elevations are ideal for crops like corn and soybeans.
Q: What are some of the challenges associated with Virginia’s topography?
A: Virginia’s diverse topography presents challenges like steep slopes, narrow valleys, and areas prone to flooding. These challenges need to be considered during infrastructure development, land-use planning, and disaster preparedness.
Tips for Using the Virginia Elevation Map:
- Utilize online resources: Several websites and applications provide access to detailed elevation maps of Virginia.
- Identify key features: Focus on understanding the major geological features, such as the Blue Ridge Mountains, the Piedmont Plateau, and the Coastal Plain.
- Consider the impact on infrastructure: Analyze how elevation influences the design and construction of roads, bridges, and other infrastructure projects.
- Explore recreational opportunities: Utilize the elevation map to plan hiking trails, camping trips, and other outdoor activities.
- Understand environmental implications: Analyze how elevation impacts the distribution of natural resources, wildlife habitats, and potential environmental risks.
Conclusion:
The Virginia elevation map is a powerful tool for understanding the state’s complex topography, revealing the interplay of geological forces and their impact on the environment, infrastructure, and human activity. By carefully studying and interpreting this map, we can gain valuable insights into the state’s natural resources, potential challenges, and opportunities for sustainable development, conservation, and recreation. The elevation map serves as a valuable resource for researchers, planners, developers, and anyone seeking a deeper understanding of Virginia’s diverse and dynamic landscape.
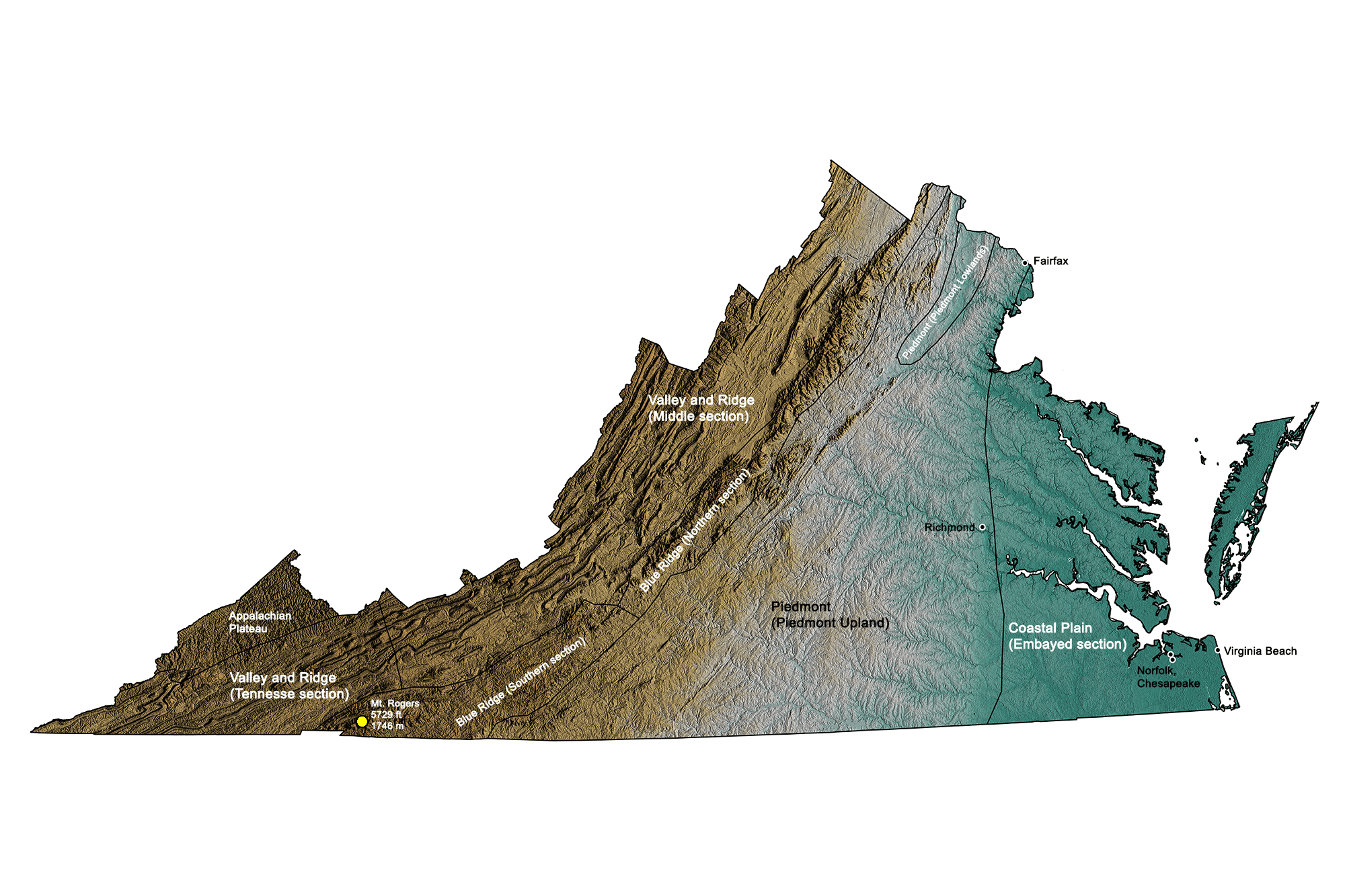
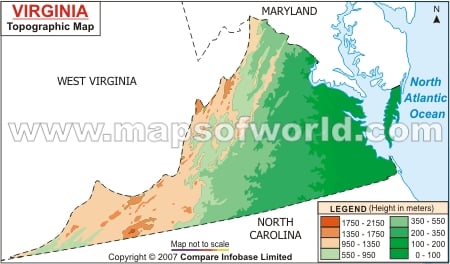
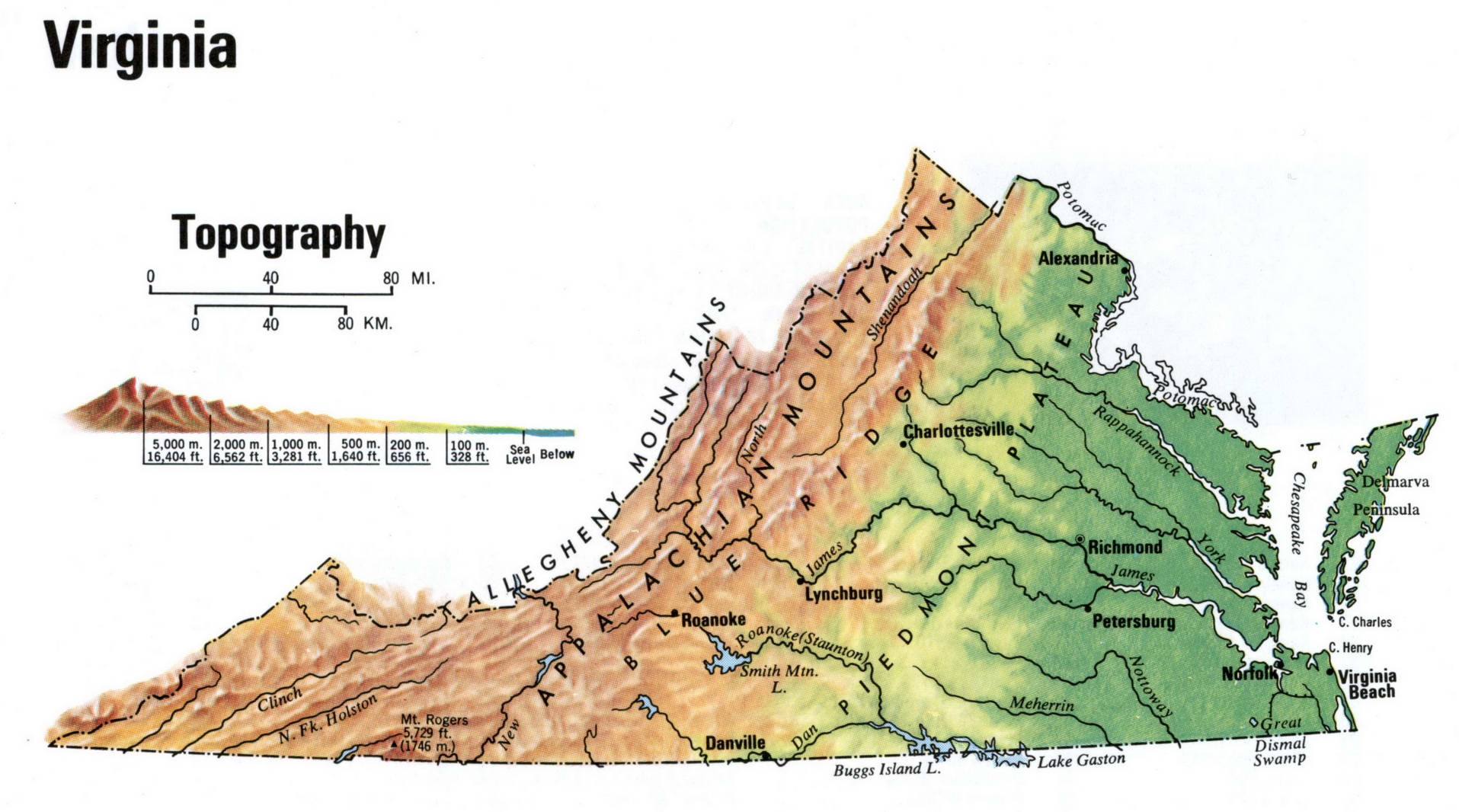

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling Virginia’s Topography: A Comprehensive Look at the State’s Elevation Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!