Unraveling the Topography of Massachusetts: A Comprehensive Look at Its Elevation Map
Related Articles: Unraveling the Topography of Massachusetts: A Comprehensive Look at Its Elevation Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Topography of Massachusetts: A Comprehensive Look at Its Elevation Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Topography of Massachusetts: A Comprehensive Look at Its Elevation Map
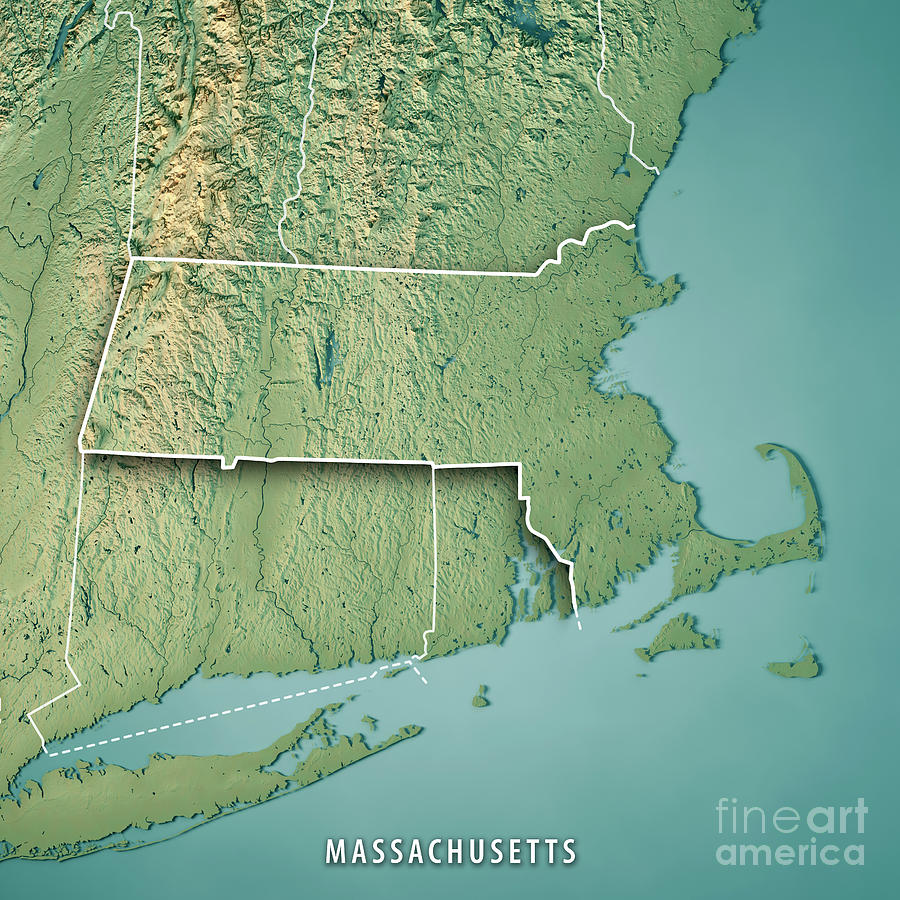
Massachusetts, a state rich in history and culture, boasts a diverse landscape sculpted by geological forces over millennia. This diversity is beautifully captured in its elevation map, a visual representation of the state’s terrain, revealing a tapestry of mountains, valleys, plains, and coastlines. Understanding this map is key to appreciating the state’s natural beauty, appreciating its influence on its history, and understanding the various challenges and opportunities presented by its varied topography.
A Visual Journey Through Massachusetts’ Topography
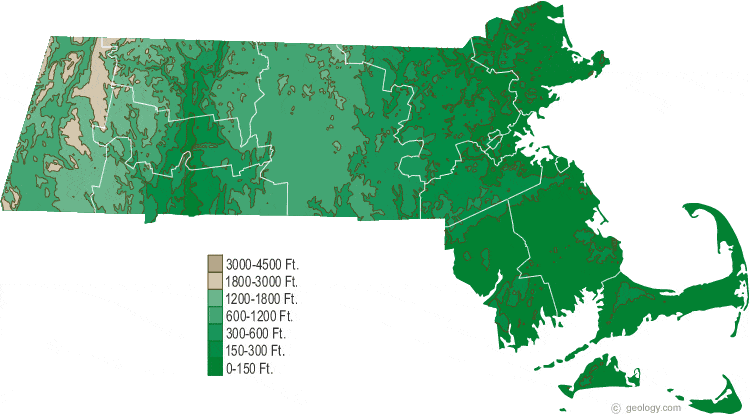
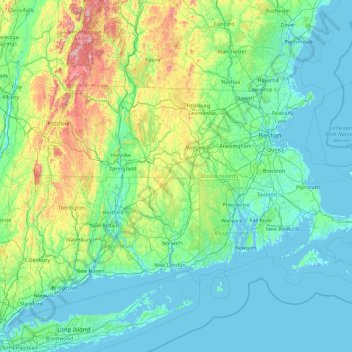
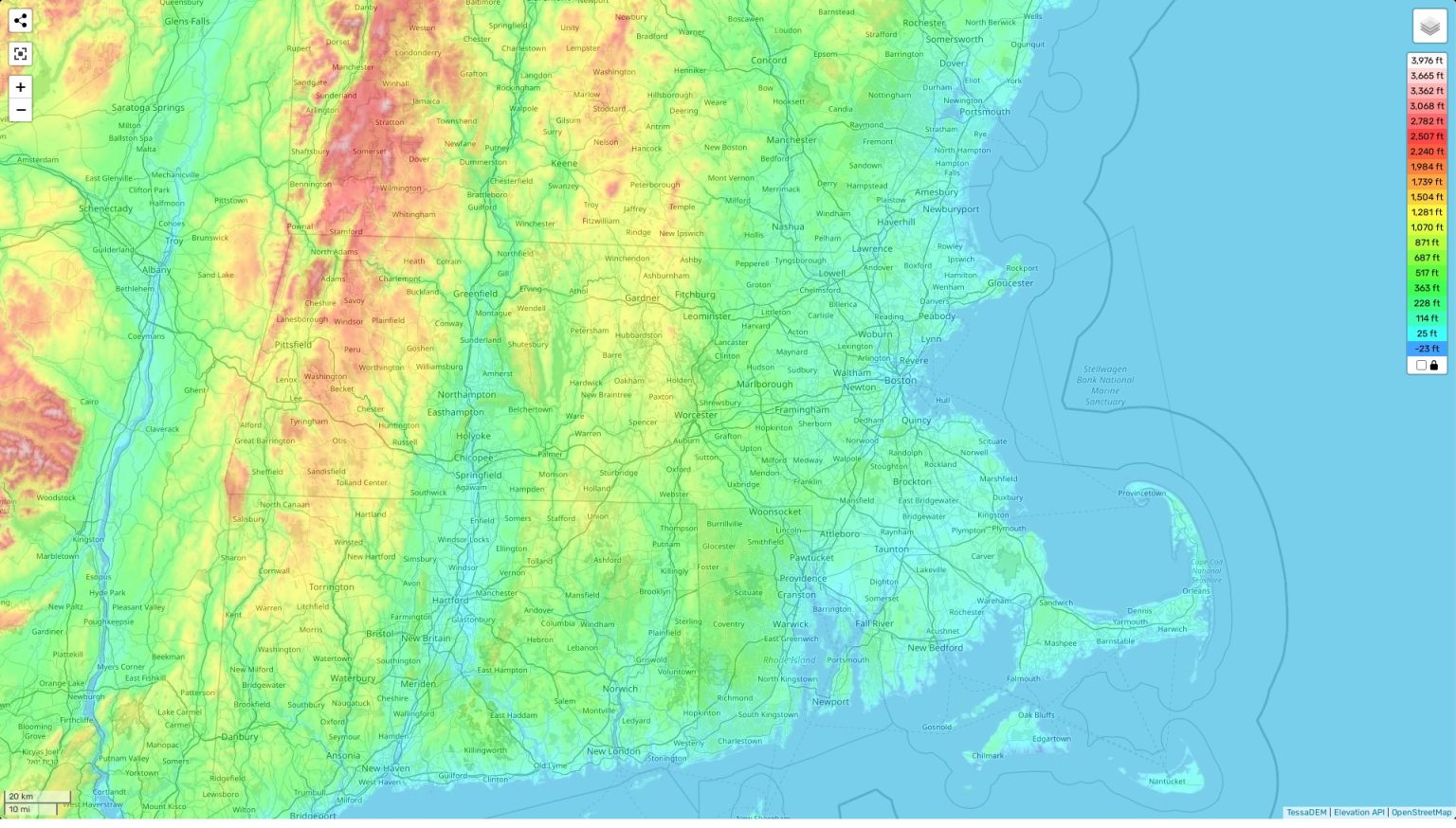
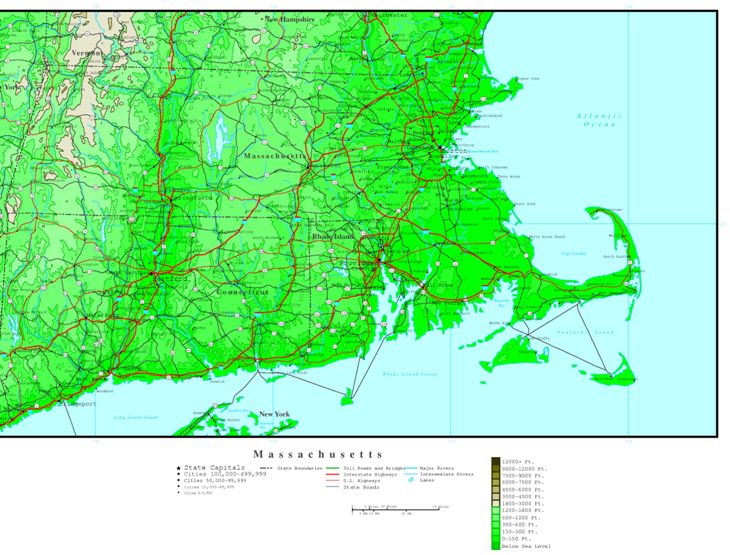
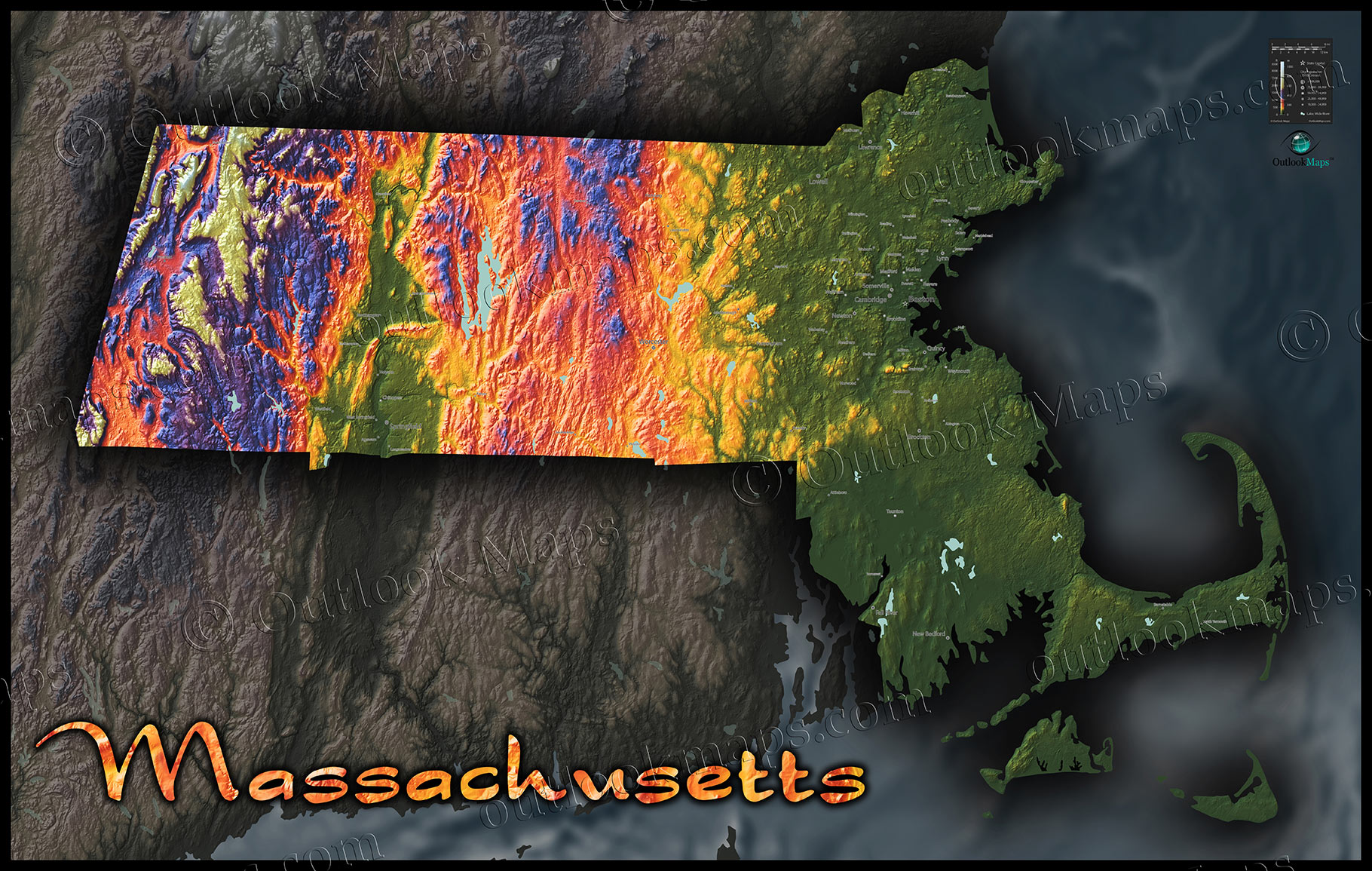
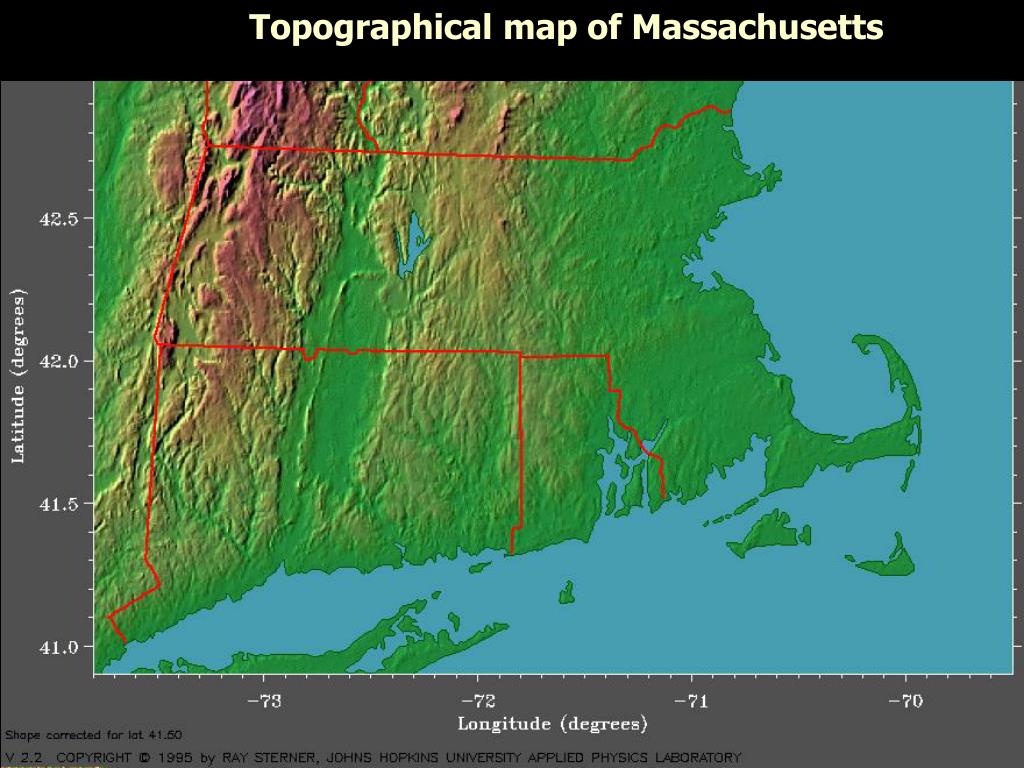
The Massachusetts elevation map showcases a predominantly low-lying landscape with a gentle slope from west to east. The western portion, characterized by the Berkshire Hills, presents the highest elevations, reaching over 3,000 feet. Mount Greylock, the state’s highest peak, stands tall at 3,491 feet, offering panoramic views of the surrounding countryside. The Berkshires themselves are a series of rolling hills and valleys, contributing to the region’s picturesque beauty and its popularity as a tourist destination.
Moving eastward, the elevation gradually decreases, transitioning into the rolling hills and valleys of the central region. This area, known as the Central Plateau, is dotted with numerous lakes and ponds, adding to the region’s natural charm. The eastern portion of the state, including the Boston metropolitan area, lies at a significantly lower elevation, with much of the land being less than 500 feet above sea level. The coastline, a defining feature of Massachusetts, is characterized by a series of bays, inlets, and islands, offering stunning views and opportunities for maritime activities.
The Importance of Elevation in Shaping Massachusetts
The elevation map is not merely a visual representation of the state’s terrain; it provides crucial insights into the forces that have shaped Massachusetts’ history, its environment, and its economy.
-
Historical Significance: The varied topography has played a vital role in shaping Massachusetts’ history. The rugged terrain of the Berkshires offered refuge to early settlers, while the coastal plains provided access to trade routes and fishing grounds. The presence of rivers and lakes facilitated transportation and agriculture, contributing to the growth of settlements and towns.
-
Environmental Influence: The elevation map reveals the distribution of natural resources, impacting the state’s biodiversity and ecological systems. The higher elevations of the Berkshires support distinct ecosystems, including boreal forests and alpine meadows, while the lower elevations are home to diverse wetland habitats and coastal ecosystems. The variation in elevation also influences the distribution of precipitation, leading to varying levels of humidity and rainfall across the state.
-
Economic Impact: The elevation map directly impacts the state’s economic activities. The rolling hills and valleys of the central region support agriculture, while the coastal areas are vital for fishing and tourism. The presence of mountains and hills has fostered the development of ski resorts and other outdoor recreation activities, contributing to the state’s tourism industry.
Navigating the Elevation Map: A Deeper Dive
The elevation map is a powerful tool for understanding the complexities of Massachusetts’ landscape. By analyzing its contours, we can gain valuable insights into:
-
Drainage Patterns: The elevation map reveals the flow of water across the state, highlighting the presence of rivers, streams, and lakes. This information is crucial for understanding the state’s water resources, flood risks, and water management strategies.
-
Soil Types: The elevation map can be used to infer the distribution of different soil types. Higher elevations tend to have thinner, less fertile soils, while lower elevations often boast more fertile soils suitable for agriculture.
-
Climate Variations: The elevation map helps understand the variation in climate across the state. Higher elevations generally experience colder temperatures and higher precipitation than lower elevations.
-
Land Use Patterns: The elevation map can be used to analyze land use patterns, identifying areas suitable for different activities, such as agriculture, forestry, and urban development.
Frequently Asked Questions about Massachusetts’ Elevation Map
Q: What is the highest point in Massachusetts?
A: The highest point in Massachusetts is Mount Greylock, located in the Berkshires, at an elevation of 3,491 feet.
Q: How does the elevation map impact the state’s climate?
A: The elevation map reveals that higher elevations generally experience colder temperatures and higher precipitation than lower elevations. This variation in climate is evident in the state’s diverse ecosystems, with different plant and animal species adapted to varying conditions.
Q: What are the key features of Massachusetts’ elevation map?
A: The key features include the Berkshire Hills, the Central Plateau, and the coastal plains. The Berkshires present the highest elevations, while the Central Plateau is characterized by rolling hills and valleys. The coastal plains are relatively flat and extend along the Atlantic coast.
Q: How does the elevation map influence the state’s economy?
A: The elevation map influences the state’s economy by shaping its natural resources, agriculture, tourism, and recreation opportunities. The mountains and hills support skiing and other outdoor activities, while the coastal areas are vital for fishing and tourism.
Tips for Understanding and Utilizing the Elevation Map
-
Explore Online Resources: Numerous online resources, including the USGS National Map, provide interactive elevation maps of Massachusetts. These resources allow you to zoom in on specific areas, view elevation profiles, and download data.
-
Utilize Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software provides powerful tools for analyzing and visualizing elevation data. This allows you to create maps, conduct spatial analysis, and develop models to understand the impact of elevation on various aspects of the state.
-
Consult with Experts: Geographers, environmental scientists, and other experts can provide valuable insights into the elevation map and its implications for specific areas of interest.
Conclusion
The Massachusetts elevation map is a powerful tool for understanding the state’s diverse landscape and the forces that have shaped its history, environment, and economy. By analyzing its contours, we gain a deeper appreciation for the state’s natural beauty, the challenges and opportunities presented by its varied topography, and the interconnectedness of its natural and human systems. This understanding is crucial for informed decision-making, sustainable development, and preserving the unique character of Massachusetts for future generations.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Topography of Massachusetts: A Comprehensive Look at Its Elevation Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!