Unlocking the Tapestry of Western Europe: A Geographic Exploration
Related Articles: Unlocking the Tapestry of Western Europe: A Geographic Exploration
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Tapestry of Western Europe: A Geographic Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking the Tapestry of Western Europe: A Geographic Exploration
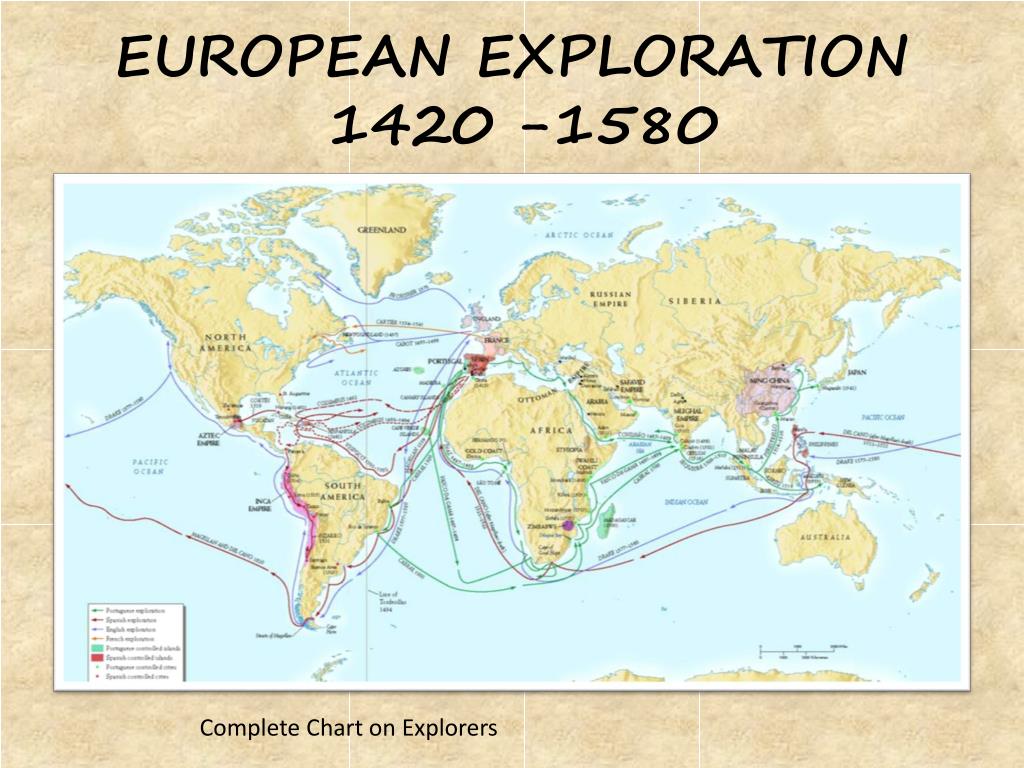
Western Europe, a region teeming with history, culture, and diverse landscapes, holds a pivotal position on the global stage. Understanding its intricate geography, marked by distinctive physical features and political boundaries, is crucial for comprehending its past, present, and future. This article delves into the Western European map, offering a comprehensive analysis of its key features, significance, and implications.
A Mosaic of Landscapes:
Western Europe’s diverse landscape is a testament to its complex geological history. The region is characterized by:
- The European Plain: This vast, low-lying expanse stretches from the North Sea to the Ural Mountains, encompassing fertile agricultural lands and important waterways like the Rhine and Danube rivers.
- The Alps: A majestic mountain range, the Alps form a natural barrier between northern and southern Europe, influencing climate patterns and shaping cultural identities.
- The Pyrenees: A formidable mountain range marking the border between France and Spain, the Pyrenees contribute to the region’s biodiversity and offer stunning vistas.
- The Massif Central: A plateau in central France, the Massif Central boasts volcanic landscapes, deep gorges, and rich mineral deposits.
- The Scandinavian Peninsula: Characterized by fjords, glaciers, and vast forests, Scandinavia offers breathtaking natural beauty and a unique ecosystem.
- The British Isles: A collection of islands separated from mainland Europe, the British Isles boast a diverse range of landscapes, from rolling hills to rugged coastlines.
A Tapestry of Nations:
Western Europe is a mosaic of nations, each with its own history, culture, and political system. Key countries in the region include:
- France: With its vibrant culture, rich history, and diverse landscapes, France is a leading European power.
- Germany: A powerhouse of the European economy, Germany is renowned for its engineering prowess and industrial strength.
- Italy: A cultural and artistic treasure trove, Italy boasts ancient ruins, Renaissance masterpieces, and breathtaking natural beauty.
- Spain: A vibrant mix of ancient traditions and modern influences, Spain is known for its sunny climate, vibrant culture, and diverse landscapes.
- United Kingdom: A global power with a rich history, the United Kingdom comprises England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland, each with its own distinct identity.
- Portugal: A country steeped in history and culture, Portugal boasts stunning coastlines, picturesque villages, and a rich maritime heritage.
- Belgium: A crossroads of cultures, Belgium is known for its diverse linguistic landscape, its world-renowned chocolate, and its vibrant capital city, Brussels.
- Netherlands: Famous for its canals, windmills, and tulips, the Netherlands is a leading agricultural producer and a key player in international trade.
- Luxembourg: A small but wealthy nation, Luxembourg is a major financial center and a hub for international businesses.
- Ireland: Known for its stunning landscapes, its rich literary heritage, and its friendly people, Ireland is a popular tourist destination.
- Switzerland: A landlocked country in the heart of Europe, Switzerland is renowned for its picturesque scenery, its neutrality, and its banking system.
- Austria: A country steeped in history and culture, Austria is known for its music, its stunning mountains, and its vibrant capital city, Vienna.
The Importance of Geography:
The geography of Western Europe has profoundly shaped its history, culture, and economy. Its diverse landscapes have provided resources, influenced trade routes, and fostered cultural exchange. The region’s proximity to the Atlantic Ocean has facilitated maritime trade and exploration, while its central location in Europe has made it a crossroads for ideas and influences.
Key Features and Significance:
- Strategic Location: Western Europe’s central position in Europe has made it a pivotal region for trade, diplomacy, and cultural exchange.
- Natural Resources: The region boasts diverse natural resources, including fertile agricultural land, mineral deposits, and forests, contributing to its economic prosperity.
- Infrastructure: Western Europe has a highly developed infrastructure, including extensive road networks, railways, and ports, facilitating trade and connectivity.
- Cultural Heritage: The region is home to a wealth of cultural heritage, including ancient ruins, medieval castles, Renaissance masterpieces, and modern architecture.
- Political Stability: Western Europe is generally considered a politically stable region, fostering economic growth and international cooperation.
FAQs about Western Europe:
1. What is the largest country in Western Europe?
France is the largest country in Western Europe, encompassing an area of 551,695 square kilometers.
2. What is the most densely populated country in Western Europe?
The Netherlands has the highest population density in Western Europe, with over 500 people per square kilometer.
3. What is the highest mountain in Western Europe?
Mont Blanc, located in the Alps, is the highest mountain in Western Europe, reaching a height of 4,808.73 meters.
4. What are the main languages spoken in Western Europe?
Western Europe is home to a diverse range of languages, with the most widely spoken being English, French, German, Spanish, Italian, and Portuguese.
5. What are the main religions practiced in Western Europe?
Christianity is the dominant religion in Western Europe, with Catholicism, Protestantism, and Eastern Orthodoxy being the major denominations.
Tips for Understanding Western Europe:
- Study the history: Understanding the region’s rich history is crucial for appreciating its current landscape and cultural nuances.
- Explore the map: Familiarize yourself with the key geographical features and political boundaries of Western Europe.
- Learn about the diverse cultures: Western Europe is a melting pot of cultures, each with its own unique traditions and customs.
- Travel and experience the region: There is no better way to understand Western Europe than to experience it firsthand.
Conclusion:
The Western European map is a window into a region of immense historical, cultural, and economic significance. Understanding its intricate geography, diverse landscapes, and political boundaries is essential for appreciating the complexities and interconnectedness of this dynamic region. As Western Europe continues to evolve, its geographical features will remain crucial in shaping its future and influencing its role in the world.

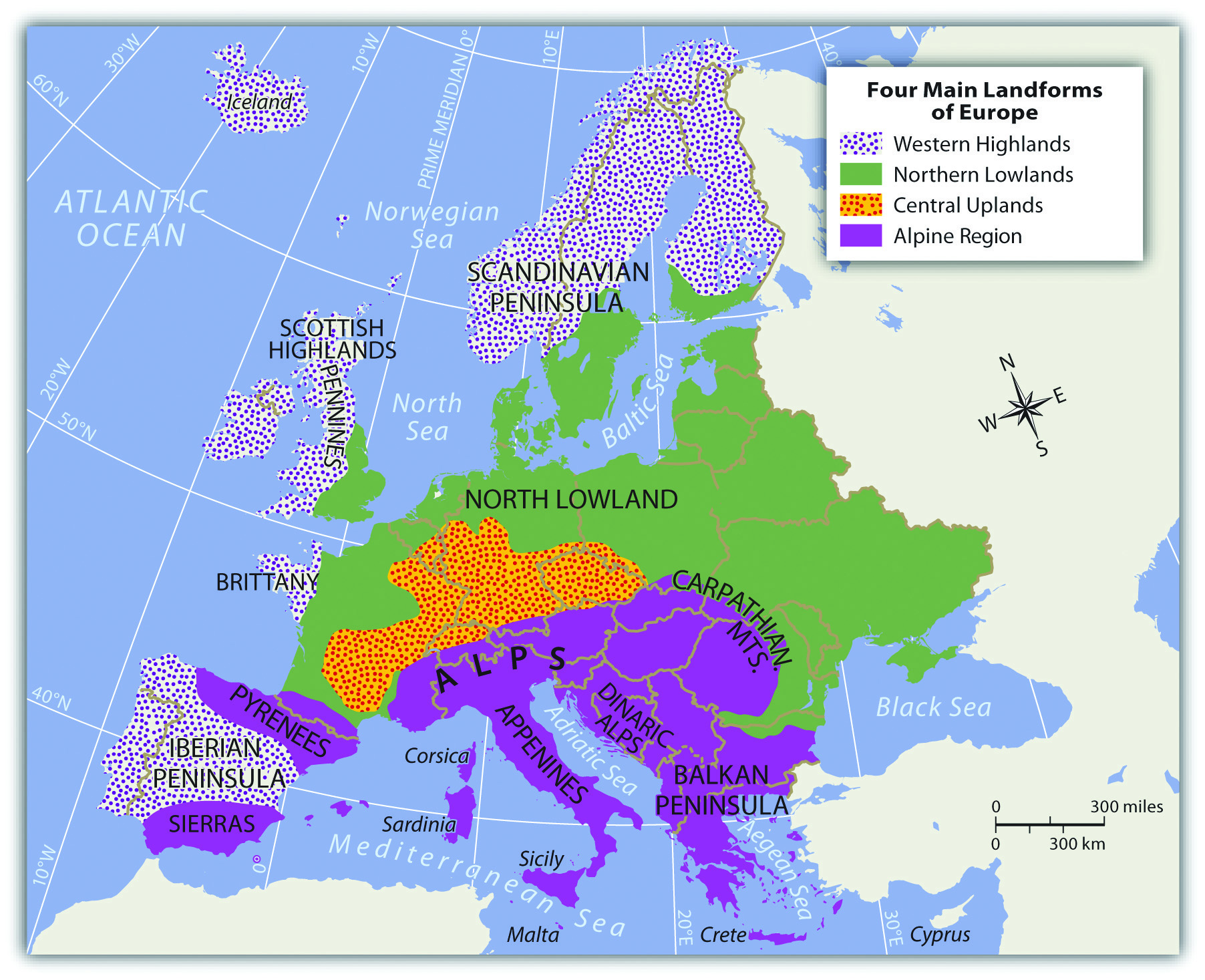




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Tapestry of Western Europe: A Geographic Exploration. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!