Unlocking Potential: A Comprehensive Guide to the Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) Map
Related Articles: Unlocking Potential: A Comprehensive Guide to the Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unlocking Potential: A Comprehensive Guide to the Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unlocking Potential: A Comprehensive Guide to the Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) Map
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unlocking Potential: A Comprehensive Guide to the Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) Map
- 3.1 Understanding the Fundamentals of fMRI Mapping
- 3.2 The Significance of fMRI Mapping: Unveiling the Brain’s Secrets
- 3.3 Benefits of fMRI Mapping: A Powerful Tool for Exploration
- 3.4 FAQs on fMRI Mapping: Addressing Common Questions
- 3.5 Tips for Understanding fMRI Mapping
- 3.6 Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for Exploring the Brain
- 4 Closure
Unlocking Potential: A Comprehensive Guide to the Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) Map

The human brain, a complex and intricate organ, is responsible for orchestrating our thoughts, emotions, and actions. Understanding its intricate workings has been a long-standing pursuit in neuroscience, and the advent of functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) has revolutionized this quest. fMRI, a non-invasive neuroimaging technique, allows researchers and clinicians to visualize brain activity in real-time, providing invaluable insights into the neural processes underlying various cognitive functions and neurological disorders.
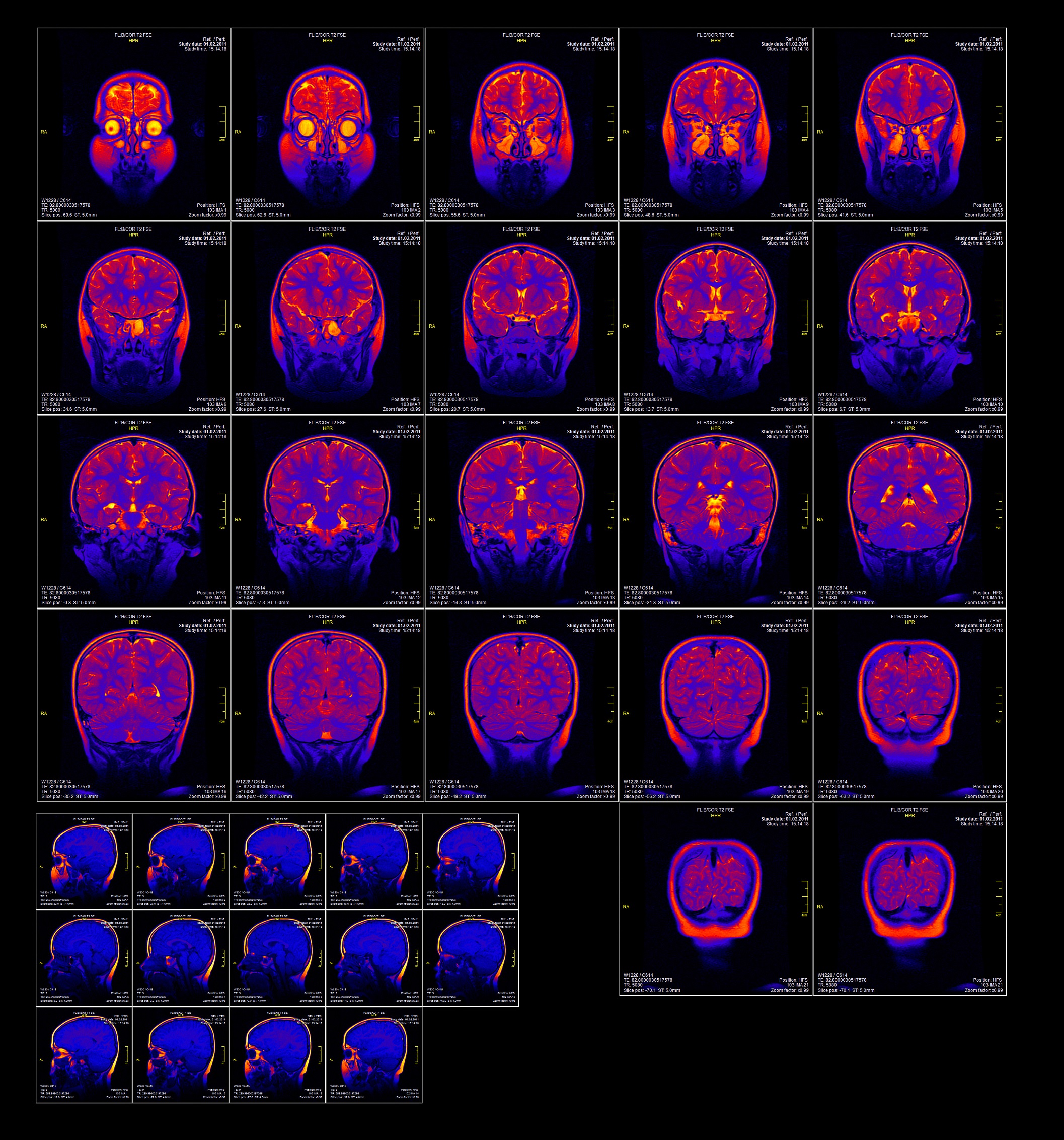
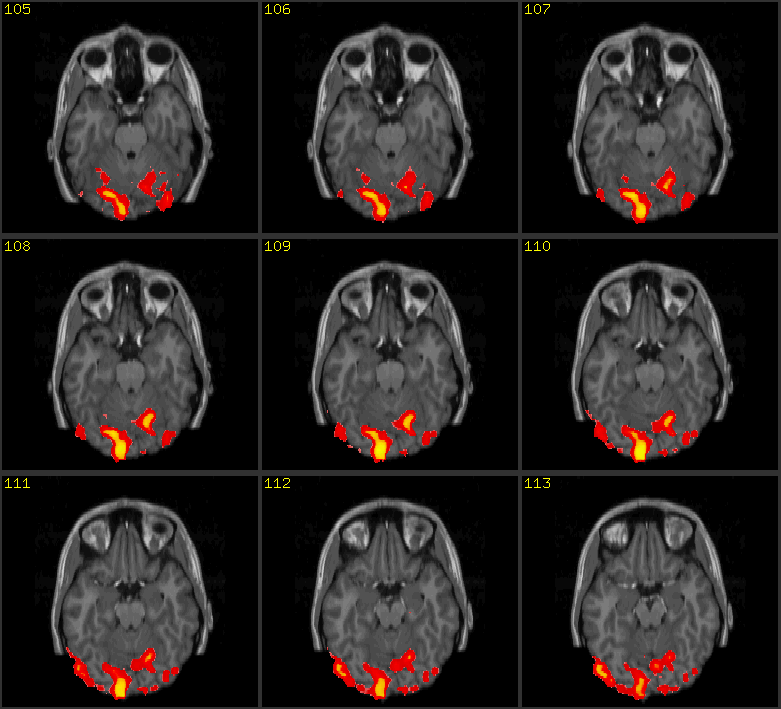
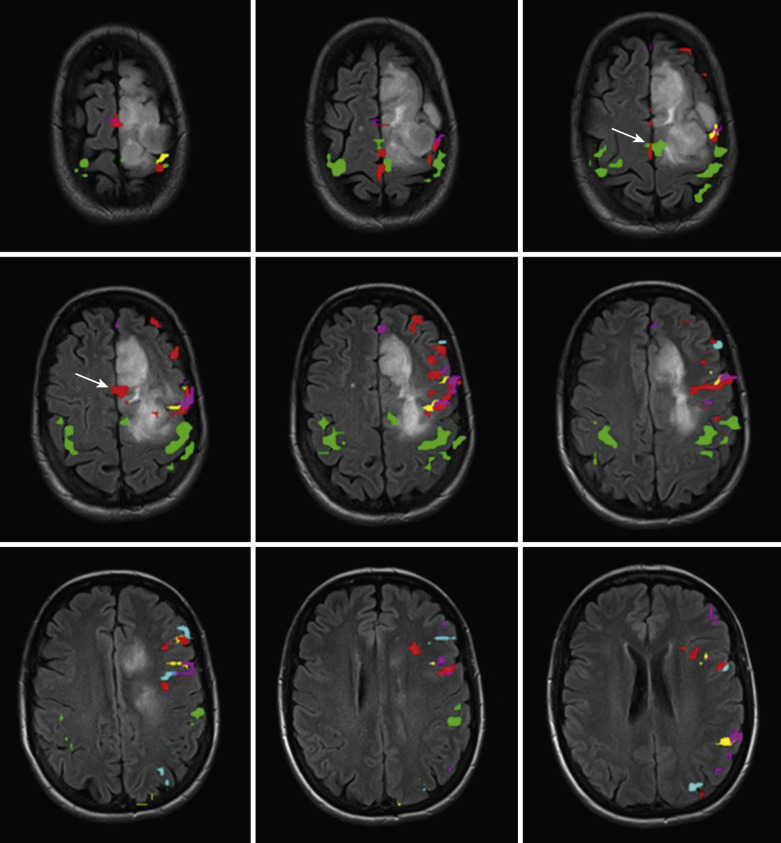
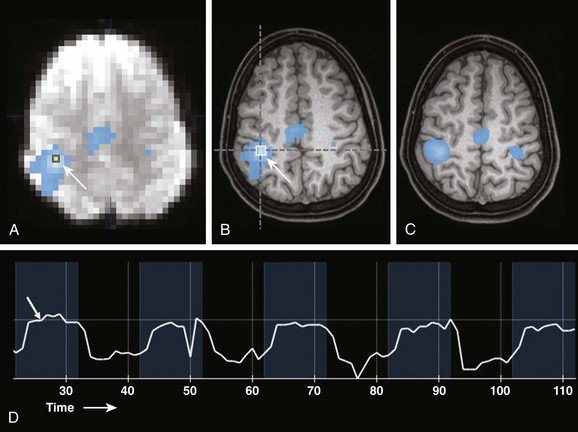
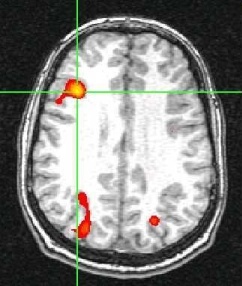
At the heart of fMRI lies the fMRI map, a visual representation of brain activity. This map, generated by analyzing fMRI data, depicts different regions of the brain and their corresponding levels of activity, offering a window into the intricate network of neural connections that govern our thoughts and actions.
Understanding the Fundamentals of fMRI Mapping
fMRI operates on the principle of blood-oxygen-level-dependent (BOLD) contrast. When a specific brain region becomes active, it requires more oxygenated blood. This increased blood flow, rich in oxygen, alters the magnetic properties of the surrounding tissues, creating a detectable signal that fMRI scanners can capture. By analyzing these signal changes, researchers can infer which brain areas are involved in a particular cognitive task or experience.
The resulting fMRI data, often represented as a series of images, is then processed and analyzed to create an fMRI map. This map typically depicts the brain’s anatomy, highlighting areas of increased or decreased activity using a color scale. Red or yellow colors usually indicate higher activity, while blue or green colors represent lower activity.
The Significance of fMRI Mapping: Unveiling the Brain’s Secrets
fMRI mapping has emerged as an indispensable tool for researchers and clinicians across various fields. Its applications extend from fundamental neuroscience research to clinical diagnosis and treatment:
1. Neuroscience Research:
- Cognitive Function: fMRI maps are instrumental in understanding the neural basis of cognitive processes like language, memory, attention, and decision-making. Researchers can pinpoint the brain regions involved in these functions by analyzing fMRI data acquired during specific tasks.
- Brain Connectivity: By studying the patterns of activity and communication between different brain regions, fMRI mapping provides insights into the intricate network of connections that govern brain function.
- Neural Plasticity: fMRI maps can track changes in brain activity over time, revealing how the brain adapts and reorganizes itself in response to learning, experience, or injury.
2. Clinical Applications:
- Neurological Disorders: fMRI mapping plays a crucial role in diagnosing and monitoring neurological disorders like stroke, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and epilepsy. It helps identify areas of brain damage, track disease progression, and evaluate the effectiveness of treatments.
- Psychiatric Disorders: fMRI mapping is increasingly used in understanding and diagnosing psychiatric disorders like depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia. It can help identify brain regions associated with specific symptoms and assess the effectiveness of various therapies.
- Pain Management: fMRI maps can provide insights into the neural mechanisms underlying pain perception, enabling clinicians to develop more effective pain management strategies.
Benefits of fMRI Mapping: A Powerful Tool for Exploration
The significance of fMRI mapping stems from its numerous benefits, making it a powerful tool for exploring the intricacies of the human brain:
- Non-invasive: Unlike invasive techniques like surgery or electroencephalography (EEG), fMRI is non-invasive, posing no risk of physical harm or discomfort to the participant.
- High Spatial Resolution: fMRI offers excellent spatial resolution, allowing researchers to pinpoint the precise brain regions involved in specific activities with remarkable accuracy.
- Real-time Imaging: fMRI provides real-time imaging of brain activity, enabling researchers to study dynamic changes in neural activity during cognitive tasks or emotional experiences.
- Versatility: fMRI mapping is a versatile technique applicable to a wide range of research questions and clinical applications.
FAQs on fMRI Mapping: Addressing Common Questions
1. What are the limitations of fMRI mapping?
While fMRI mapping is a powerful tool, it has limitations:
- Temporal Resolution: fMRI has relatively low temporal resolution compared to other neuroimaging techniques like EEG. It cannot capture rapid neural activity changes occurring within milliseconds.
- Indirect Measure: fMRI measures blood flow changes, which are an indirect indicator of neural activity. It cannot directly measure the electrical activity of neurons.
- Cost and Accessibility: fMRI scanners are expensive to purchase and operate, limiting their availability and accessibility.
2. Can fMRI mapping be used to "read minds"?
fMRI mapping can reveal brain activity associated with specific thoughts, emotions, or actions. However, it cannot accurately translate these brain signals into specific thoughts or intentions. The interpretation of fMRI data remains complex and requires careful consideration of the context and experimental design.
3. How is fMRI data analyzed?
fMRI data analysis involves several steps, including:
- Preprocessing: Raw fMRI data is preprocessed to correct for motion artifacts, remove noise, and align images across different time points.
- Statistical Analysis: Statistical methods are used to identify brain regions exhibiting significant activity changes in response to specific tasks or stimuli.
- Visualization: The results of statistical analysis are visualized as fMRI maps, depicting brain activity patterns across different regions.
4. What are the ethical considerations associated with fMRI mapping?
Ethical considerations in fMRI research include:
- Informed Consent: Participants should be fully informed about the nature and risks of fMRI procedures before providing their consent.
- Data Privacy: fMRI data contains sensitive information about individuals’ brain activity and must be handled with utmost care and confidentiality.
- Interpretation and Misuse: fMRI data interpretation requires expertise and should be done responsibly, avoiding oversimplification or misrepresentation of findings.
Tips for Understanding fMRI Mapping
- Focus on the context: fMRI maps should always be interpreted within the context of the research question or clinical application.
- Consider the limitations: Be aware of the limitations of fMRI, such as its temporal resolution and indirect measure of neural activity.
- Consult with experts: When interpreting fMRI data, it is essential to consult with experts in neuroimaging and related fields.
- Stay informed: Keep abreast of advancements in fMRI technology and research, as the field is constantly evolving.
Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for Exploring the Brain
fMRI mapping has emerged as a transformative tool in neuroscience, offering unprecedented insights into the workings of the human brain. Its non-invasive nature, high spatial resolution, and versatility have revolutionized research on cognitive functions, neurological disorders, and psychiatric conditions. While fMRI mapping has limitations, its benefits continue to drive advancements in our understanding of the brain and its intricate workings. As research progresses and technology evolves, fMRI mapping will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in unlocking the secrets of the human mind and improving our understanding of the brain’s complex processes.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking Potential: A Comprehensive Guide to the Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!