Understanding Mountain Lion Distribution: A Comprehensive Guide to Maps and Their Importance
Related Articles: Understanding Mountain Lion Distribution: A Comprehensive Guide to Maps and Their Importance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding Mountain Lion Distribution: A Comprehensive Guide to Maps and Their Importance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding Mountain Lion Distribution: A Comprehensive Guide to Maps and Their Importance
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding Mountain Lion Distribution: A Comprehensive Guide to Maps and Their Importance
- 3.1 The Importance of Mountain Lion Maps
- 3.2 Types of Mountain Lion Maps
- 3.3 Data Sources for Mountain Lion Maps
- 3.4 Challenges and Limitations
- 3.5 FAQs About Mountain Lion Maps
- 3.6 Tips for Understanding Mountain Lion Maps
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding Mountain Lion Distribution: A Comprehensive Guide to Maps and Their Importance
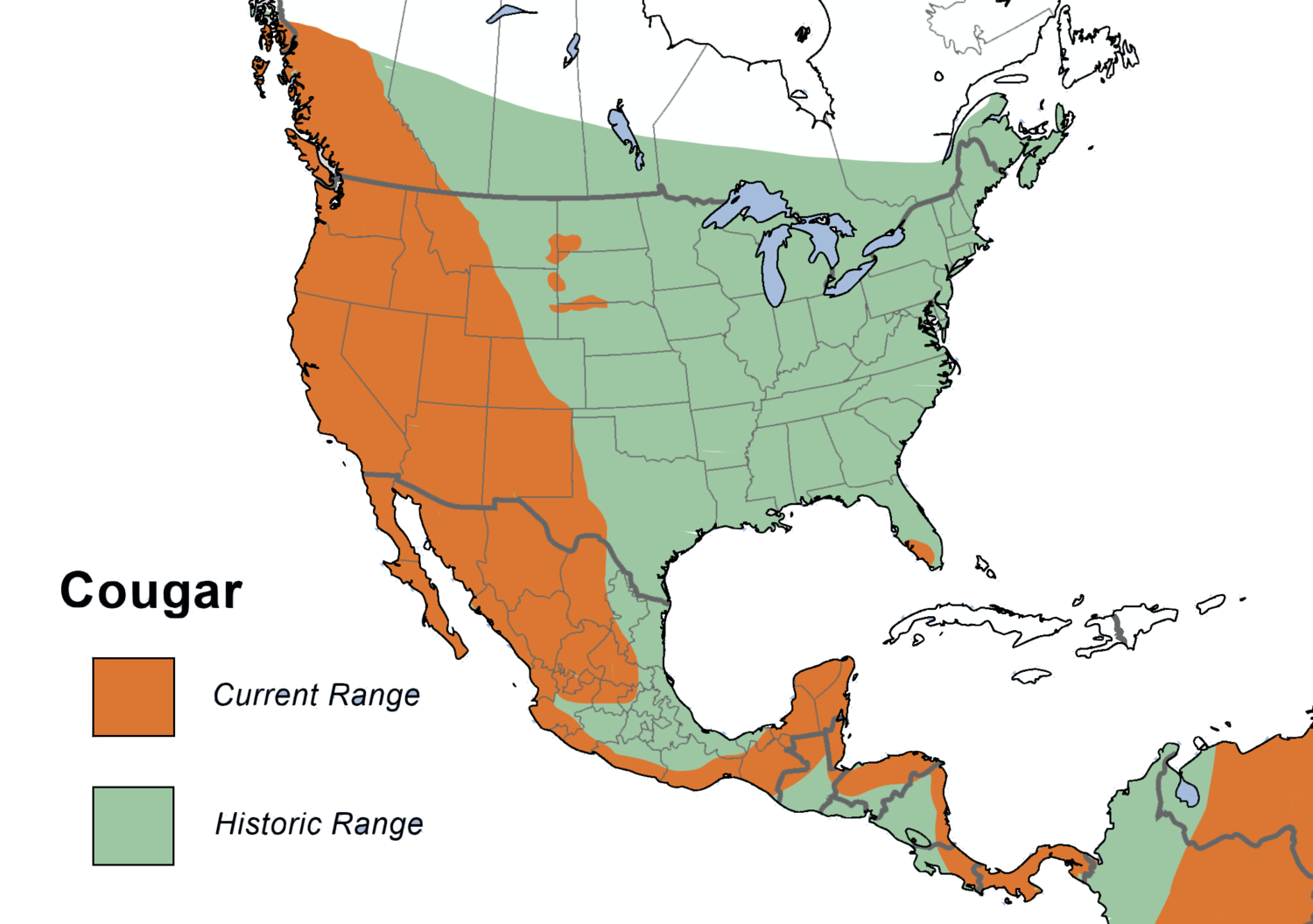
Mountain lions, also known as cougars, puma, or panthers, are apex predators found throughout the Americas. Their elusive nature and vast range make tracking their distribution a complex task. However, the development of mountain lion maps has revolutionized our understanding of these magnificent creatures, offering invaluable insights into their ecology, behavior, and conservation needs.
The Importance of Mountain Lion Maps
Mountain lion maps are crucial for several reasons:
1. Understanding Population Dynamics: By mapping the distribution of mountain lions, scientists can assess population density, identify areas with high or low concentrations, and monitor changes over time. This information is crucial for conservation efforts, allowing researchers to prioritize areas for protection and management.
2. Identifying Habitat Use Patterns: Mountain lions require specific habitats, such as forests, grasslands, and rocky terrain. Mapping their distribution helps identify these preferred habitats and understand how they utilize the landscape. This knowledge aids in habitat restoration and management strategies to ensure the long-term survival of these animals.
3. Predicting Potential Conflicts: Mountain lion maps are instrumental in identifying areas where human-wildlife conflicts are more likely to occur. By understanding where mountain lions are present and their movement patterns, communities can take proactive steps to mitigate potential conflicts, such as educating residents about coexistence and implementing preventative measures.
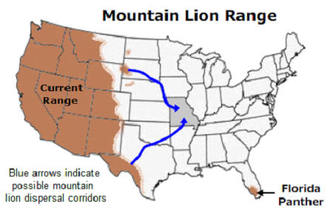
4. Guiding Conservation Efforts: Mapping mountain lion distribution provides a clear picture of their range and allows for the development of targeted conservation strategies. This includes identifying key corridors for movement, protecting critical habitats, and mitigating threats such as habitat loss and fragmentation.
5. Assessing the Impact of Climate Change: As climate change alters landscapes and wildlife habitats, mountain lion maps can be used to assess the potential impact on their distribution and survival. By monitoring changes in their range and habitat use over time, scientists can predict future challenges and develop adaptive management strategies.
Types of Mountain Lion Maps
Mountain lion maps can be categorized based on their purpose and the data they incorporate:
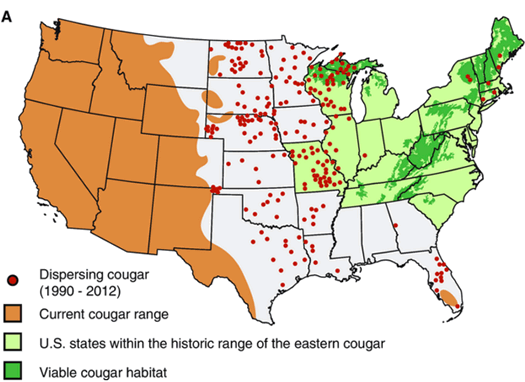
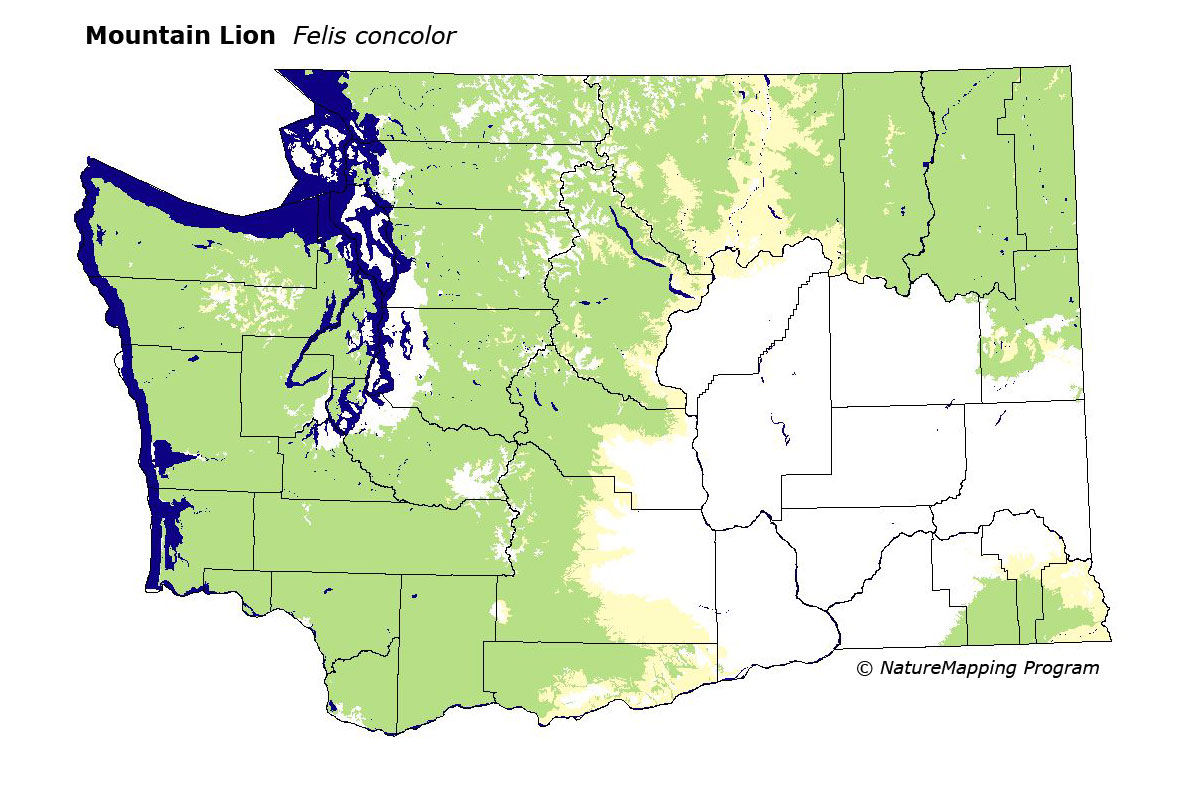
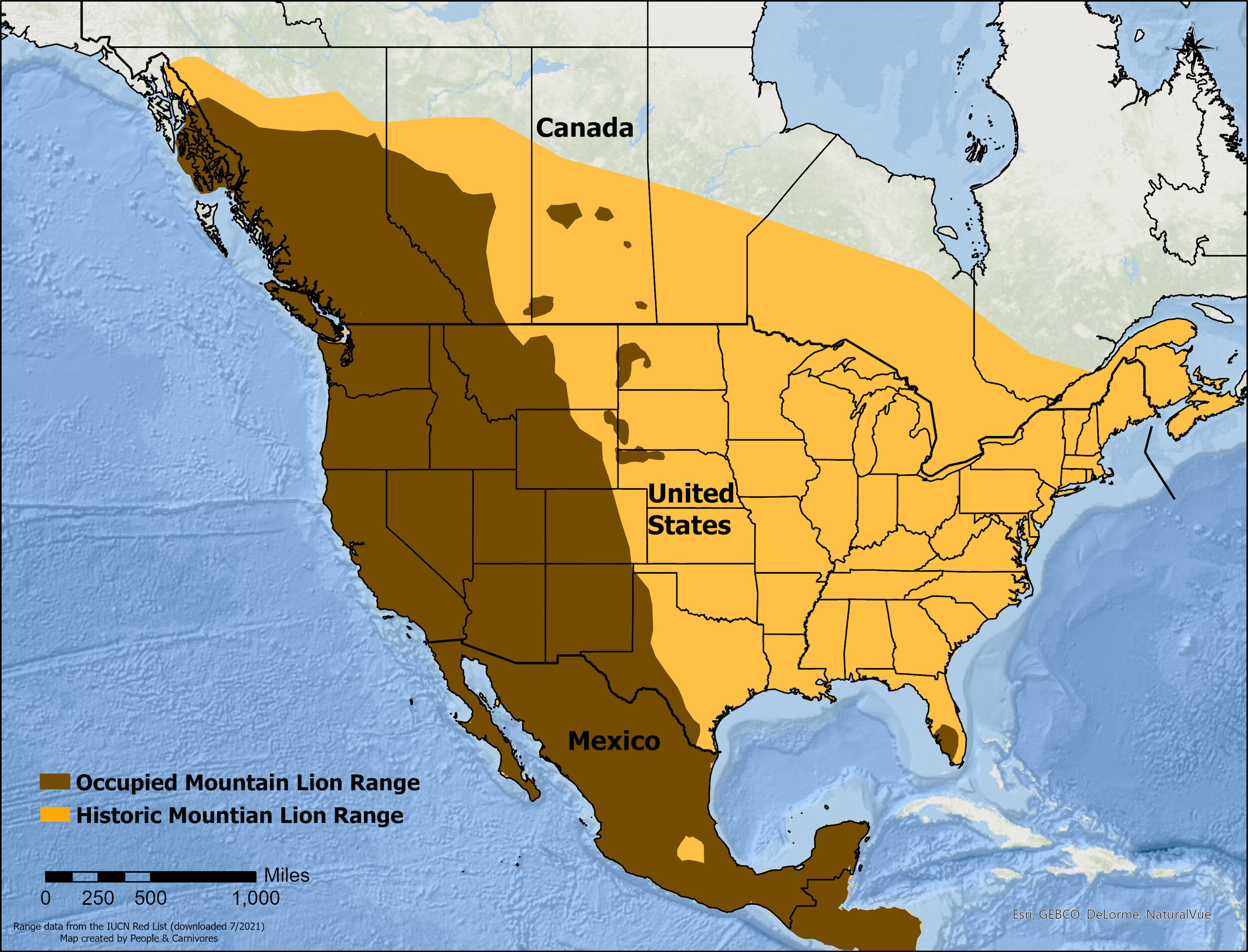
1. Geographic Range Maps: These maps depict the overall distribution of mountain lions across their entire range, outlining the areas where they are known to occur. They provide a general overview of their presence but lack detailed information about population density or habitat use.
2. Density Maps: These maps utilize data from various sources, such as camera traps, scat surveys, and sightings, to estimate the density of mountain lions in specific areas. This information is crucial for understanding population trends and identifying areas with high or low concentrations.
3. Habitat Suitability Maps: These maps combine environmental data, such as vegetation type, elevation, and water availability, with known mountain lion locations to predict areas with suitable habitat. This helps identify potential areas for colonization and understand the factors influencing their habitat selection.
4. Movement Maps: Using GPS tracking data from collared mountain lions, these maps depict individual movement patterns, migration routes, and home ranges. This information is vital for understanding their spatial ecology and identifying potential corridors for movement.
5. Conflict Maps: These maps overlay mountain lion distribution with human population density and land use data to identify areas with a higher risk of human-wildlife conflicts. This helps communities prepare for potential interactions and implement preventative measures.
Data Sources for Mountain Lion Maps
Mountain lion maps rely on various data sources, each with its own strengths and limitations:
1. Sightings: Citizen science initiatives and reports from wildlife agencies provide valuable information on mountain lion presence. However, sightings can be biased towards areas with higher human activity and may not accurately reflect the true distribution.
2. Camera Traps: Remote cameras deployed in the field capture images of animals passing by, providing valuable data on species presence, abundance, and activity patterns. Camera trap data is particularly useful for areas with low human activity and can provide more accurate estimates of population density.
3. Scat Surveys: Analyzing mountain lion scat (feces) can reveal information about diet, genetic makeup, and population size. This method is particularly useful for areas with low visibility and can provide insights into the health and condition of the population.
4. GPS Tracking: Collaring mountain lions with GPS transmitters allows scientists to track their movements in real-time, providing detailed information on home range size, migration routes, and habitat use. This method is expensive and labor-intensive, but provides the most accurate data on individual behavior and movement patterns.
5. Genetic Analysis: Analyzing genetic samples from scat, hair, or tissue can reveal genetic diversity, population connectivity, and the presence of specific lineages. This information is crucial for understanding population structure and identifying areas with genetically distinct populations.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their value, mountain lion maps face several challenges and limitations:
1. Data Availability: Data availability can vary greatly across geographic regions, making it difficult to create accurate maps for all areas. Some regions may have limited data due to inaccessibility, low human population density, or lack of funding for research.
2. Data Quality: The quality of data collected can vary depending on the methods used and the expertise of the individuals involved. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to misleading maps and inaccurate conclusions.
3. Elusive Nature of Mountain Lions: Mountain lions are elusive and solitary animals, making it challenging to obtain accurate data on their distribution and abundance. Their secretive nature requires specialized methods and extensive field work to gather reliable data.
4. Dynamic Nature of Populations: Mountain lion populations are dynamic and can fluctuate over time due to factors such as habitat change, prey availability, and human activity. Maps based on static data may not accurately reflect current population distribution and require regular updates.
5. Interpretation of Data: Interpreting data and drawing conclusions from mountain lion maps requires careful consideration of the methods used, data limitations, and potential biases. Misinterpretation can lead to inaccurate conclusions and misguided conservation efforts.
FAQs About Mountain Lion Maps
1. How are mountain lion maps created?
Mountain lion maps are created by combining data from various sources, such as sightings, camera traps, scat surveys, GPS tracking, and genetic analysis. The data is then processed and analyzed using geographic information systems (GIS) software to create maps that visualize the distribution, density, habitat use, and movement patterns of mountain lions.
2. What are the benefits of using mountain lion maps?
Mountain lion maps offer several benefits, including:
- Understanding population dynamics and trends.
- Identifying areas with high or low concentrations of mountain lions.
- Identifying preferred habitats and understanding habitat use patterns.
- Predicting potential conflicts between humans and mountain lions.
- Guiding conservation efforts and identifying areas for protection.
- Assessing the impact of climate change on mountain lion distribution.
3. How accurate are mountain lion maps?
The accuracy of mountain lion maps depends on the quality and availability of data, the methods used, and the expertise of the individuals involved. Maps based on comprehensive data from multiple sources are generally more accurate than those relying on limited data.
4. Can I use mountain lion maps to predict where mountain lions are located?
Mountain lion maps can provide a general idea of their distribution, but they cannot predict the exact location of individual animals. Mountain lions are elusive and their movements can be unpredictable.
5. What can I do to help with mountain lion conservation?
You can support mountain lion conservation by:
- Reducing your impact on their habitat by supporting responsible land use practices.
- Educating yourself and others about mountain lions and their role in the ecosystem.
- Supporting organizations dedicated to mountain lion research and conservation.
Tips for Understanding Mountain Lion Maps
1. Consider the Data Sources: Pay attention to the data sources used to create the map and their limitations. Maps based on limited data or biased sources may not accurately reflect the true distribution.
2. Interpret with Caution: Avoid drawing definitive conclusions based solely on a map. Consider other factors, such as habitat availability, prey abundance, and human activity, that can influence mountain lion distribution.
3. Look for Patterns and Trends: Analyze the map for patterns and trends in mountain lion distribution, such as areas with high density, preferred habitats, or corridors for movement.
4. Consult with Experts: If you have questions about a specific map or need help interpreting the data, consult with experts in wildlife ecology or conservation.
5. Stay Informed: Keep up to date on the latest research and conservation efforts related to mountain lions by following reputable organizations and publications.
Conclusion
Mountain lion maps are essential tools for understanding the distribution, ecology, and conservation needs of these magnificent predators. By combining data from various sources and utilizing advanced mapping techniques, scientists and conservationists can gain valuable insights into their populations, habitats, and movement patterns. This information is crucial for developing effective conservation strategies, mitigating human-wildlife conflicts, and ensuring the long-term survival of these apex predators. As our understanding of mountain lions continues to evolve, so too will the sophistication and accuracy of the maps that guide our efforts to protect them.

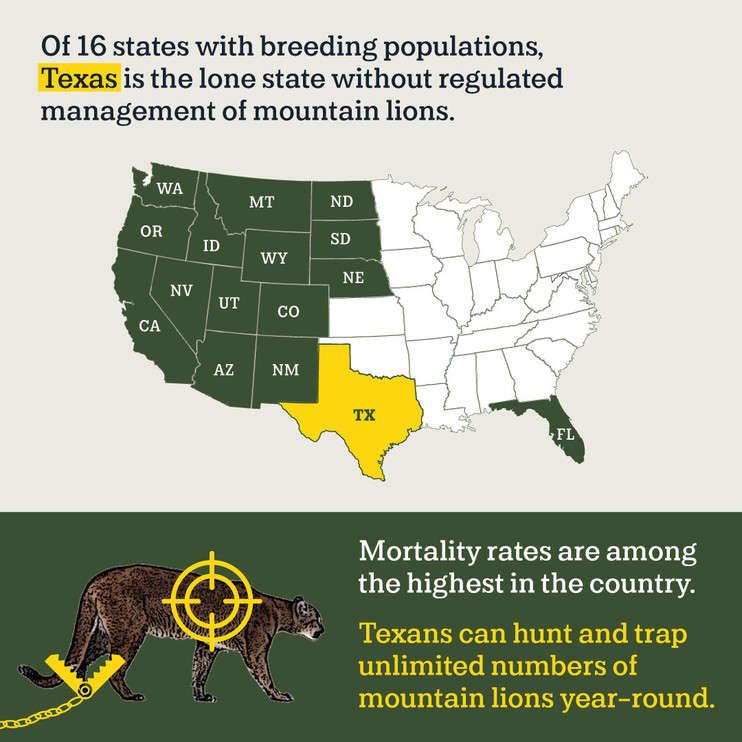
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Mountain Lion Distribution: A Comprehensive Guide to Maps and Their Importance. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!