The Complex Tapestry of Ethnicity in the Middle East: A Geographic and Historical Overview
Related Articles: The Complex Tapestry of Ethnicity in the Middle East: A Geographic and Historical Overview
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Complex Tapestry of Ethnicity in the Middle East: A Geographic and Historical Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Complex Tapestry of Ethnicity in the Middle East: A Geographic and Historical Overview

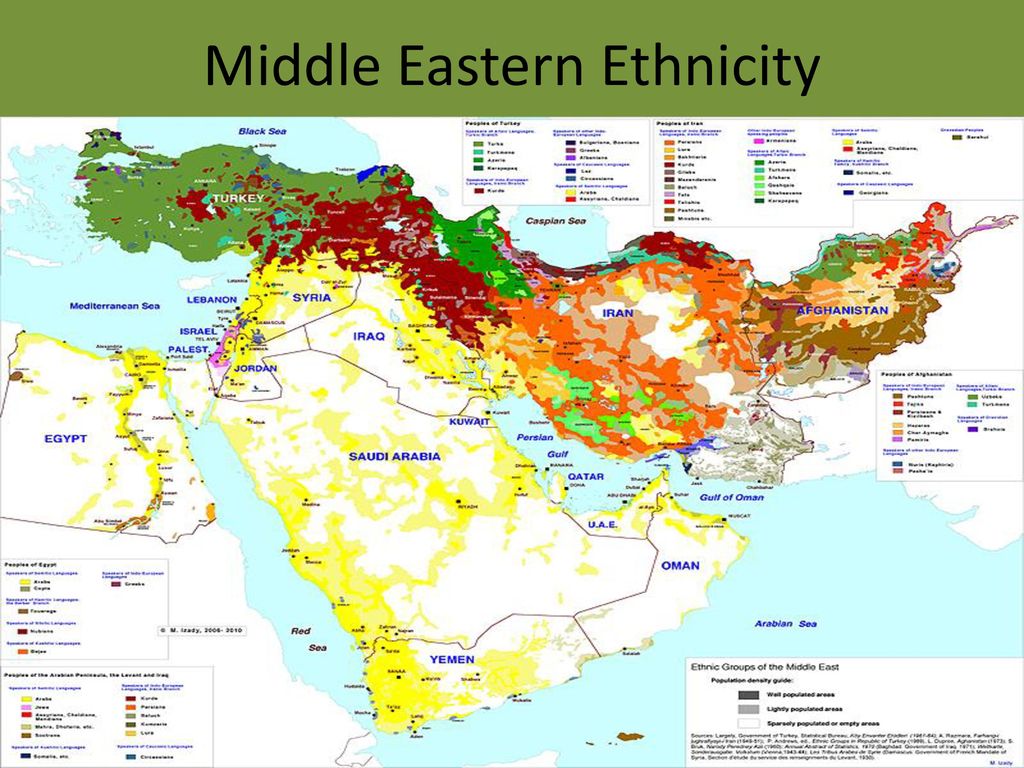
The Middle East, a region spanning diverse landscapes and cultures, is a melting pot of ethnicities, each with its unique history, language, and traditions. Understanding the ethnic map of the Middle East is crucial for navigating the complexities of its political landscape, appreciating its rich cultural heritage, and fostering a deeper understanding of the region’s history.
Defining the Middle East: A Geographic and Cultural Framework
The term "Middle East" itself is a relatively modern construct, primarily used in the West to refer to a region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, and parts of North Africa. However, within the region, the term "Middle East" is less common, with many preferring alternative terms like "Mashreq" (the East), "Arab World," or "Greater Syria."
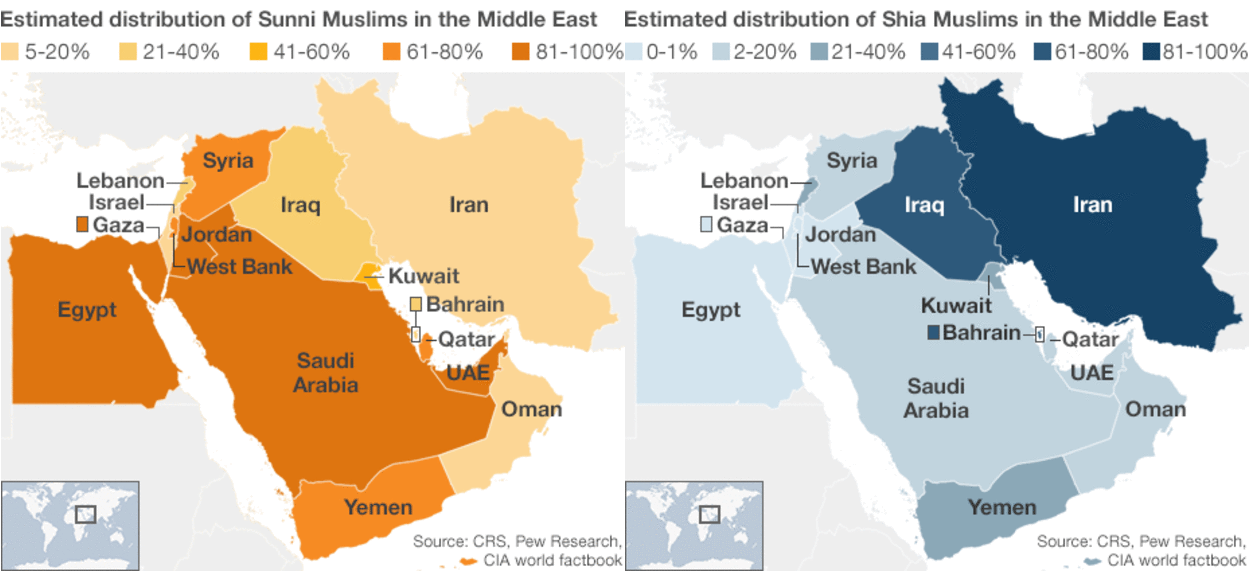
This geographical ambiguity is further compounded by the region’s diverse cultural landscape. While Islam is the dominant religion, a multitude of other faiths and belief systems coexist, including Christianity, Judaism, Zoroastrianism, and various forms of paganism. Furthermore, the region’s ethnic tapestry is woven with threads of Arab, Turkic, Persian, Kurdish, and other groups, each contributing to the region’s vibrant cultural mosaic.
Mapping the Ethnic Landscape: A Journey through Diverse Communities
Arabs: The largest ethnic group in the Middle East, Arabs are spread across the region, with significant populations in countries like Saudi Arabia, Egypt, Iraq, Syria, and Lebanon. Their cultural influence is profound, shaping the region’s language, literature, art, and cuisine. Arab identity is further strengthened by a shared history, rooted in the Arabian Peninsula, and a common language, Arabic, spoken in various dialects across the region.
Persians: Predominantly residing in Iran, Persians have a distinct cultural identity shaped by their language, Persian, and their rich literary and artistic heritage. Their influence extends beyond Iran, with significant Persian communities found in Afghanistan, Tajikistan, and other parts of Central Asia.
Turks: Primarily located in Turkey, Turks have a rich history and cultural identity, marked by their language, Turkish, and their unique artistic traditions. Turkish influence extends beyond Turkey, with significant Turkish communities found in Cyprus, Azerbaijan, and other parts of the Middle East.
Kurds: A large ethnic group with a distinct cultural identity, Kurds are primarily found in a region spanning parts of Turkey, Iraq, Iran, and Syria. Their language, Kurdish, and their rich cultural heritage have been a source of pride and resilience, despite facing historical marginalization and political challenges.
Berbers: Predominantly residing in North Africa, Berbers have a long and rich history, with their own distinct language and cultural traditions. While often considered a separate ethnic group, Berbers have historically interacted and intermingled with Arabs, contributing to the diverse cultural landscape of North Africa.
Other Ethnic Groups: The Middle East is home to numerous other ethnic groups, including Assyrians, Armenians, Circassians, and various minority groups, each contributing to the region’s cultural diversity. These groups often have distinct languages, traditions, and histories, further enriching the complex ethnic mosaic of the Middle East.
The Importance of Understanding the Ethnic Map: Navigating a Complex and Dynamic Region
Understanding the ethnic map of the Middle East is crucial for navigating its complex political landscape. Ethnic identities often play a significant role in shaping political allegiances, leading to conflicts and tensions over issues like land, resources, and political representation. Furthermore, understanding the historical and cultural context of different ethnic groups is crucial for fostering intergroup dialogue and promoting peace and stability in the region.
FAQs on the Ethnic Map of the Middle East
1. What is the most dominant ethnic group in the Middle East?
The largest ethnic group in the Middle East is Arabs, with significant populations in countries like Saudi Arabia, Egypt, Iraq, Syria, and Lebanon.
2. Are all Arabs Muslims?
While Islam is the dominant religion among Arabs, not all Arabs are Muslims. There are significant Christian communities in the Arab world, particularly in countries like Lebanon, Egypt, and Palestine.
3. What are the main languages spoken in the Middle East?
The most widely spoken languages in the Middle East are Arabic, Persian, Turkish, and Kurdish. However, numerous other languages are spoken by various ethnic minorities, reflecting the region’s linguistic diversity.
4. How has the ethnic map of the Middle East evolved over time?
The ethnic map of the Middle East has been shaped by centuries of migrations, conquests, and cultural exchanges. Historical events like the Arab conquests, the Ottoman Empire, and the rise of nationalism have all contributed to the region’s dynamic ethnic landscape.
5. What are the challenges faced by ethnic minorities in the Middle East?
Ethnic minorities in the Middle East often face challenges related to political representation, cultural preservation, and economic opportunities. These challenges can stem from historical marginalization, political instability, and discrimination.
Tips for Navigating the Ethnic Map of the Middle East
-
Approach the region with an open mind and a willingness to learn. The Middle East is a complex and diverse region, and understanding its ethnic landscape requires an appreciation for its rich history, cultural traditions, and the challenges faced by its various communities.
-
Engage with different perspectives. Seek out information from a variety of sources, including books, articles, documentaries, and conversations with people from the region. This will help you develop a nuanced understanding of the region’s ethnic complexities.
-
Respect the diversity of cultures and identities. Recognize that the Middle East is home to a multitude of cultures and identities, each with its own unique history, traditions, and values. Avoid making generalizations or stereotypes about any particular ethnic group.
-
Promote dialogue and understanding. Engage in respectful conversations with people from different ethnic backgrounds, fostering an environment of mutual understanding and respect. This is crucial for building bridges and promoting peace and stability in the region.
Conclusion
The ethnic map of the Middle East is a complex and dynamic landscape, reflecting the region’s rich history, diverse cultures, and ongoing political challenges. Understanding this map is crucial for navigating the complexities of the region, fostering intergroup dialogue, and promoting peace and stability. By embracing the region’s diversity and respecting its various ethnic groups, we can contribute to a more peaceful and harmonious future for the Middle East.

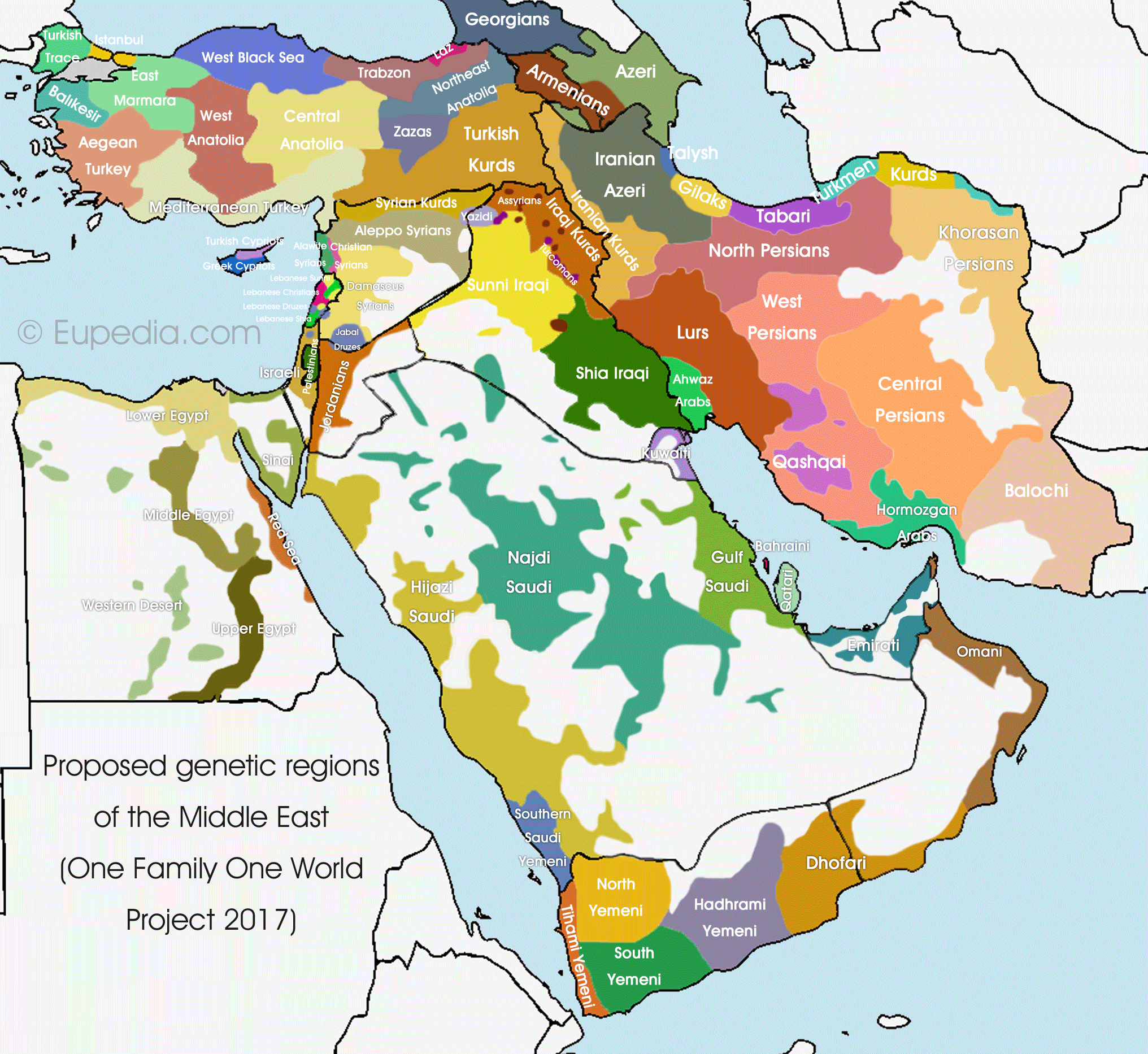


![Map of Ethnic Groups in the Middle East [7290 × 5726] : MapPorn](https://external-preview.redd.it/bSD-6RkmSEt4D2hplhHjk-1G2viYH465nUu4KUwuGDk.jpg?width=1200u0026height=628.272251309u0026auto=webpu0026s=3c30a72b38ec0909143713041a09ff2831581d89)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Complex Tapestry of Ethnicity in the Middle East: A Geographic and Historical Overview. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!