Navigating the Terrain of Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Number Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Terrain of Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Number Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Terrain of Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Number Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Terrain of Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Number Maps

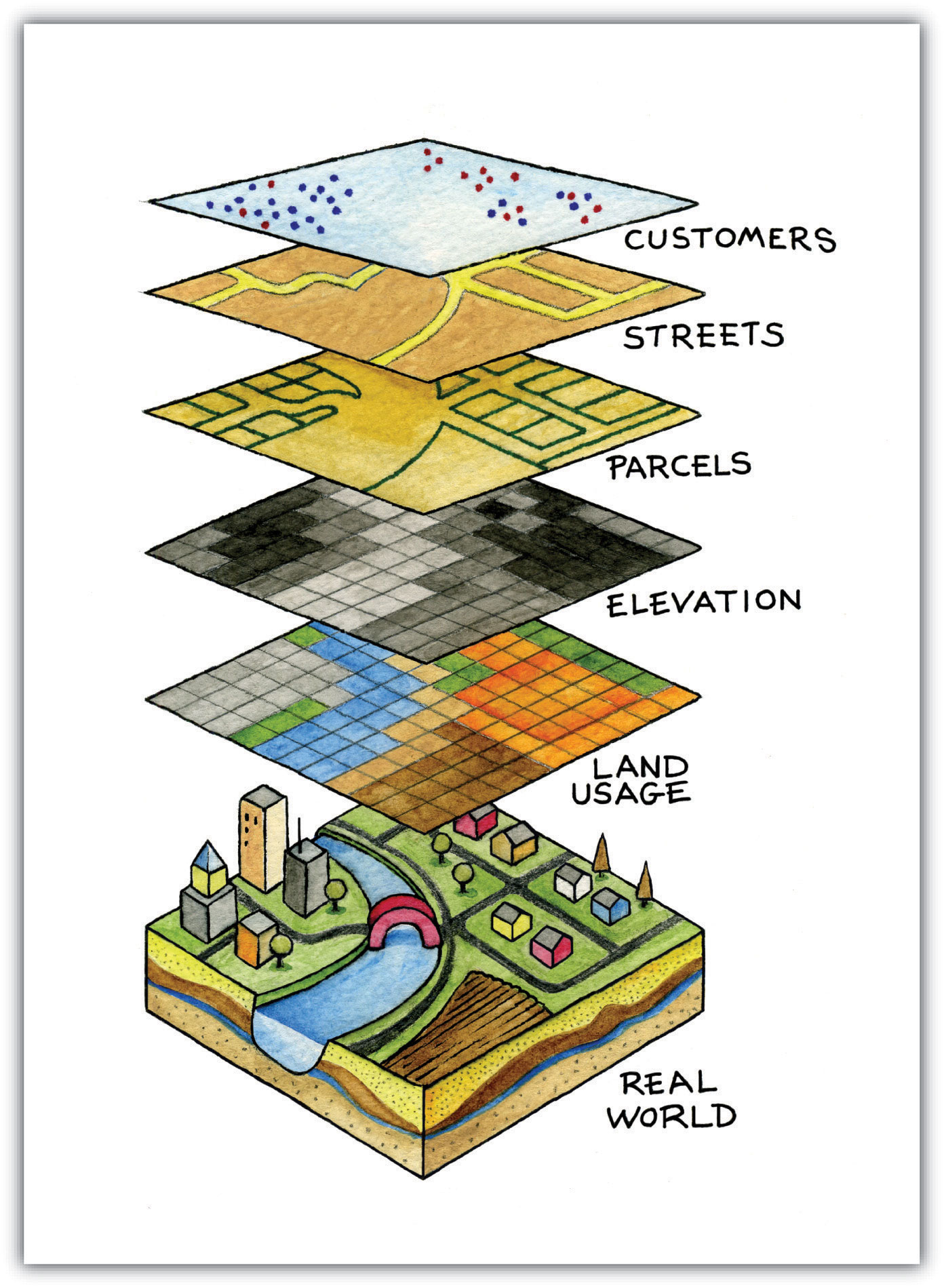
The world of data is vast and complex, often resembling a labyrinth of interconnected pathways. To make sense of this intricate landscape, we need tools that can illuminate the relationships and patterns hidden within. Number maps, also known as numerical maps, are precisely such tools. They serve as visual representations of numerical data, transforming abstract figures into intuitive and insightful visualizations.
Understanding the Essence of Number Maps
At their core, number maps are graphical representations that display numerical data in a spatial context. They leverage the power of spatial visualization, enabling viewers to grasp complex relationships and trends that might otherwise be obscured in tables or lists. This visual approach enhances data comprehension and facilitates deeper analysis.
Types of Number Maps and their Applications
Number maps come in various forms, each tailored to specific data types and analytical goals. Some common types include:
-
Choropleth maps: These maps use color gradients or patterns to represent numerical data across geographical regions. They are frequently used to visualize population density, income levels, or disease prevalence across countries, states, or even smaller administrative units.
-
Dot density maps: Utilizing dots to represent individual data points, dot density maps provide a clear visual representation of the distribution and concentration of data. This type of map is particularly effective for visualizing population distribution, crime rates, or the spread of disease.
-
Proportional symbol maps: These maps use symbols of varying sizes to represent the magnitude of numerical data at different locations. The size of the symbol is directly proportional to the value being represented. This technique is commonly employed to visualize the distribution of economic activity, population size, or natural resource reserves.
-
Flow maps: Flow maps depict the movement of data or objects across space. They use lines or arrows to illustrate the direction and intensity of flows, such as migration patterns, trade routes, or transportation networks.
The Benefits of Using Number Maps
The use of number maps offers a multitude of benefits for data analysis and communication:
-
Improved Data Comprehension: By presenting data visually, number maps make it easier for individuals to understand and interpret complex information. They facilitate the identification of patterns, outliers, and trends that might be overlooked in tabular data.
-
Enhanced Data Exploration: Number maps encourage exploration and discovery. By interacting with the map, users can zoom in on specific areas, filter data, and uncover hidden insights. This interactive nature fosters a deeper understanding of the data and its underlying relationships.
-
Effective Data Communication: Number maps serve as powerful communication tools. They provide a clear and concise way to convey complex data to a wide audience, including those with limited analytical expertise. This visual approach makes data more accessible and engaging.
-
Identification of Spatial Relationships: Number maps highlight the spatial relationships between data points, enabling the identification of geographical patterns and clusters. This spatial context is crucial for understanding the distribution and influence of data across space.
-
Support for Decision-Making: By providing a clear and comprehensive view of data, number maps inform better decision-making. They help identify areas requiring attention, prioritize resources, and develop effective strategies.
FAQs about Number Maps
Q: What software can be used to create number maps?
A: There are numerous software applications available for creating number maps. Some popular options include:
- ArcGIS: A powerful geographic information system (GIS) software widely used for creating professional-grade maps.
- QGIS: A free and open-source GIS software that offers a wide range of mapping capabilities.
- Google Maps: A user-friendly platform for creating basic maps with customizable markers and data layers.
- Tableau: A data visualization tool that allows users to create interactive and visually appealing maps.
- Power BI: A business intelligence platform that provides comprehensive mapping capabilities, including the ability to create dynamic and interactive maps.
Q: How can I choose the right type of number map for my data?
A: The choice of number map depends on the type of data you are visualizing and the analytical goals you are trying to achieve. Consider the following factors:
- Data Type: The type of data (e.g., continuous, categorical, ordinal) will determine the most appropriate map type.
- Analytical Goals: What insights are you trying to gain from the data? This will help determine the best way to visualize the data.
- Audience: Consider the level of understanding and technical expertise of your audience when choosing a map type.
Q: What are some common challenges in creating number maps?
A: Creating effective number maps can be challenging, especially for beginners. Common challenges include:
- Data Preparation: Cleaning, transforming, and preparing data for mapping can be time-consuming and require specific skills.
- Map Design: Choosing appropriate map projections, color schemes, and symbols is crucial for conveying data accurately and effectively.
- Data Interpretation: Interpreting the results of number maps requires a strong understanding of the data and its context.
- Accessibility: Ensuring that maps are accessible to users with disabilities requires careful consideration of design elements.
Tips for Creating Effective Number Maps
- Start with a clear purpose: Define your analytical goals and the specific insights you aim to communicate.
- Choose the right map type: Select a map type that best suits the data and your analytical goals.
- Use appropriate data sources: Ensure that your data is accurate, reliable, and relevant to your purpose.
- Pay attention to map design: Choose a clear and consistent color scheme, symbols, and labels that enhance readability and visual appeal.
- Include a legend: Provide a clear legend that explains the meaning of the map’s symbols, colors, and other elements.
- Consider accessibility: Ensure that your map is accessible to users with disabilities by using appropriate color contrast, font sizes, and alternative text.
Conclusion
Number maps are powerful tools that unlock the potential of data visualization. They transform abstract numbers into compelling visual narratives, fostering deeper understanding, facilitating data exploration, and informing better decision-making. By leveraging the benefits of number maps, individuals and organizations can navigate the complex terrain of data with greater clarity and insight, ultimately leading to more informed and effective outcomes.


![]()
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Terrain of Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Number Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!