Navigating the Middle East: A Geographical and Cultural Journey
Related Articles: Navigating the Middle East: A Geographical and Cultural Journey
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Middle East: A Geographical and Cultural Journey. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Middle East: A Geographical and Cultural Journey
The Middle East, a region often characterized by its complexities and dynamism, holds a unique position in the world. Understanding its geography and cultural landscape is crucial for navigating its complexities, appreciating its rich history, and fostering meaningful engagement. This article will explore the Middle East through the lens of its diverse geography, highlighting its cultural tapestry and the challenges and opportunities that shape its future.
Mapping the Middle East: A Geographical Overview
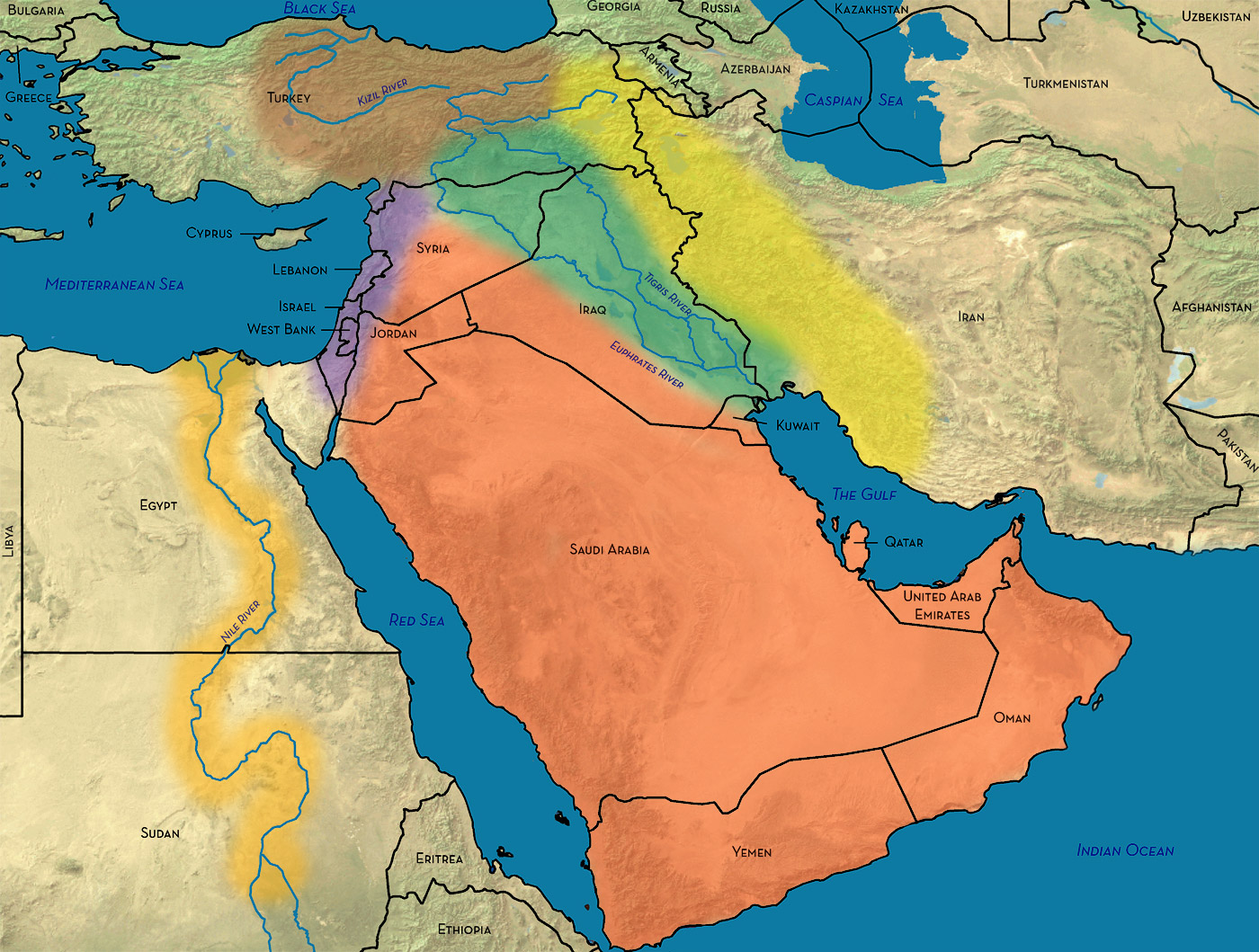
The Middle East, also known as Western Asia, is a geographically diverse region spanning a vast area from the Mediterranean Sea in the west to the Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean in the east. Its northern border stretches along the Caucasus Mountains, while the southern border extends to the Horn of Africa.
Key Geographical Features:
- Deserts: The region is dominated by vast deserts, including the Arabian Desert, the largest continuous desert in the world, and the Sahara Desert, which extends into North Africa. These deserts play a significant role in shaping the region’s climate, vegetation, and human settlements.
- Mountain Ranges: Mountain ranges, such as the Zagros Mountains in Iran and the Taurus Mountains in Turkey, provide natural barriers and influence regional weather patterns.
- Water Bodies: The region is home to several important bodies of water, including the Mediterranean Sea, the Red Sea, the Persian Gulf, and the Arabian Sea. These waterways have historically served as vital trade routes and sources of sustenance.
- Rivers: The region’s major rivers, such as the Nile, the Euphrates, and the Tigris, have played a crucial role in the development of agriculture and civilizations.
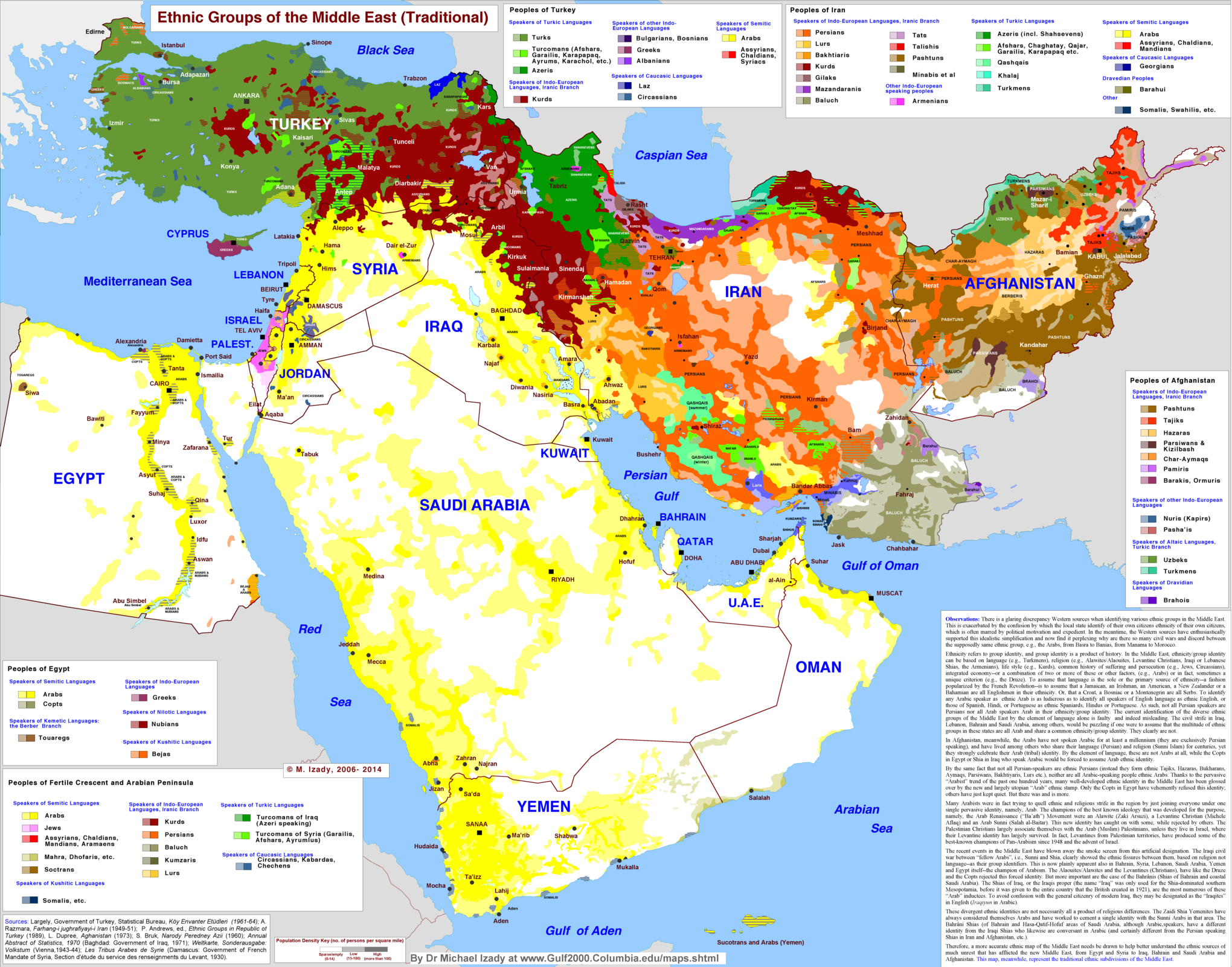
Cultural Tapestry: A Mosaic of Diverse Identities
The Middle East is a melting pot of cultures, religions, and ethnicities. This diversity is a testament to the region’s long and rich history, marked by the rise and fall of empires, the spread of religions, and the constant movement of people across its borders.
Key Cultural Elements:
- Religion: The Middle East is the birthplace of major world religions, including Islam, Christianity, and Judaism. These religions have shaped the region’s social values, traditions, and political systems.
- Language: Arabic is the most widely spoken language in the Middle East, but the region is also home to other languages, including Persian, Turkish, Kurdish, and Hebrew. This linguistic diversity reflects the region’s cultural complexity.
- Arts and Literature: The Middle East has a rich artistic and literary heritage, spanning centuries of poetry, music, architecture, and visual arts. These traditions continue to evolve and inspire contemporary artists and writers.
Challenges and Opportunities: A Region in Transition
The Middle East faces numerous challenges, including political instability, economic disparities, and social tensions. However, the region also possesses significant potential for progress and development.
Key Challenges:
- Political Instability: The region has been plagued by conflict and instability for decades, fueled by political tensions, sectarian divisions, and external interventions.
- Economic Disparities: The Middle East is home to both wealthy oil-producing countries and developing nations struggling with poverty and unemployment.
- Social Tensions: The region is experiencing growing social tensions related to gender equality, religious freedom, and cultural identity.
Key Opportunities:
- Economic Diversification: Many Middle Eastern countries are seeking to diversify their economies away from oil dependence, investing in sectors such as tourism, technology, and renewable energy.
- Regional Cooperation: Increased cooperation between Middle Eastern nations can help address shared challenges and promote economic growth.
- Youth Empowerment: The region’s young population presents a significant opportunity for innovation, entrepreneurship, and social change.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the major countries in the Middle East?
A: The Middle East encompasses a diverse range of countries, including:
- Arab States: Bahrain, Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Libya, Morocco, Oman, Palestine, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Sudan, Syria, Tunisia, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen.
- Non-Arab States: Cyprus, Iran, Israel, and Turkey.
Q: What is the significance of the Middle East in global affairs?
A: The Middle East holds significant geopolitical importance due to its strategic location, vast oil reserves, and its influence on global religious and cultural dynamics.
Q: What are the major challenges facing the Middle East?
A: The Middle East faces a number of challenges, including:
- Political Instability: The region is home to ongoing conflicts, political transitions, and sectarian tensions.
- Economic Disparities: The region’s wealth is unevenly distributed, leading to social and economic challenges.
- Environmental Degradation: Climate change, water scarcity, and desertification pose significant threats to the region’s environment and livelihoods.
Tips for Understanding the Middle East:
- Engage with diverse perspectives: Seek out information from a variety of sources, including academic research, news reports, and cultural perspectives.
- Learn about the history and culture: Understanding the region’s rich history and diverse cultures can provide valuable context for current events.
- Be respectful of cultural differences: Recognize and appreciate the diverse values and traditions that shape the Middle East.
Conclusion:
The Middle East is a region of profound complexity and dynamism. Its diverse geography, cultural tapestry, and ongoing challenges and opportunities present a unique and fascinating landscape for exploration and understanding. By engaging with its history, culture, and current affairs, we can gain valuable insights into this critical region and its role in shaping the world.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Middle East: A Geographical and Cultural Journey. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
