Navigating the German Landscape: A Guide to the Political Map
Related Articles: Navigating the German Landscape: A Guide to the Political Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the German Landscape: A Guide to the Political Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the German Landscape: A Guide to the Political Map
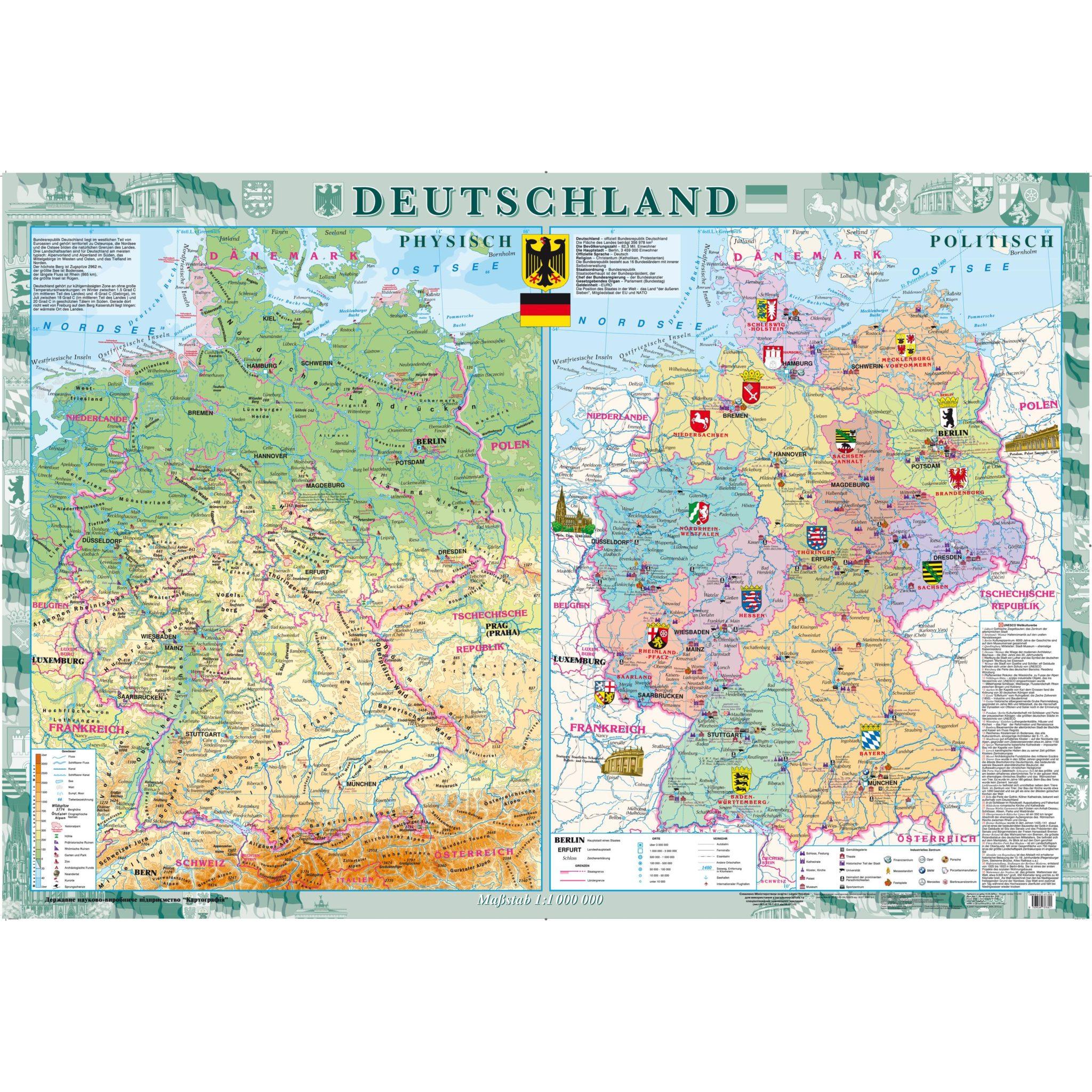
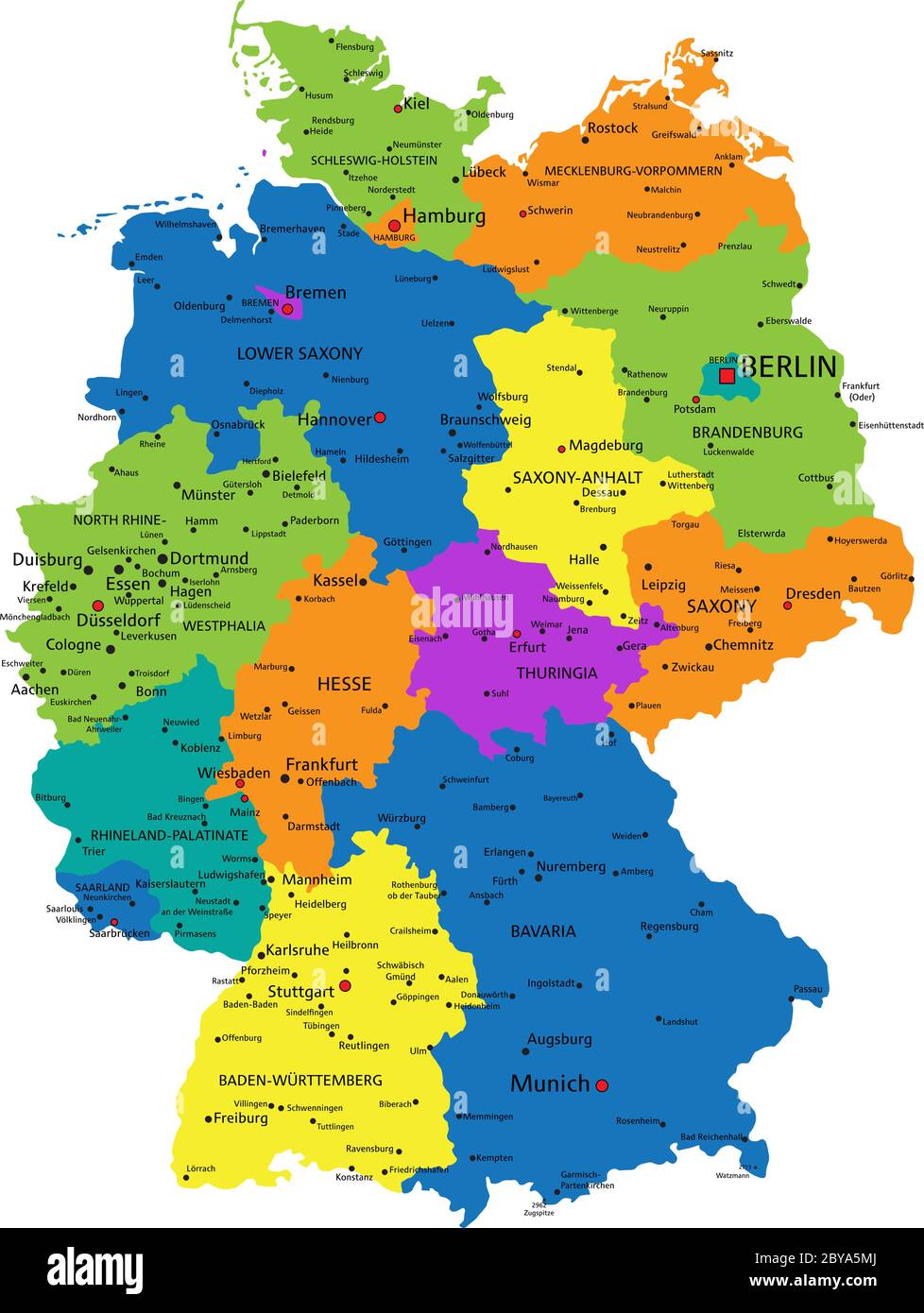
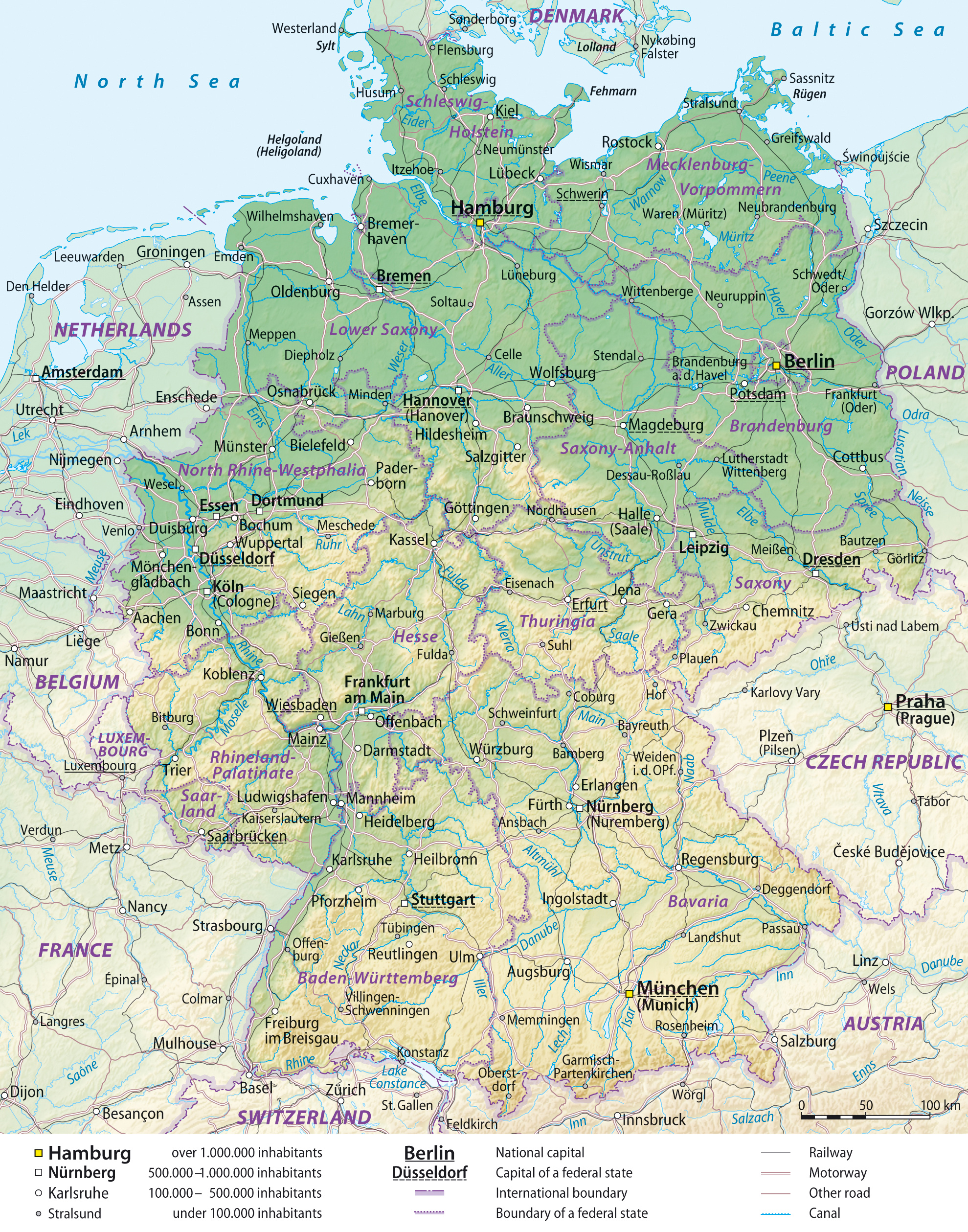
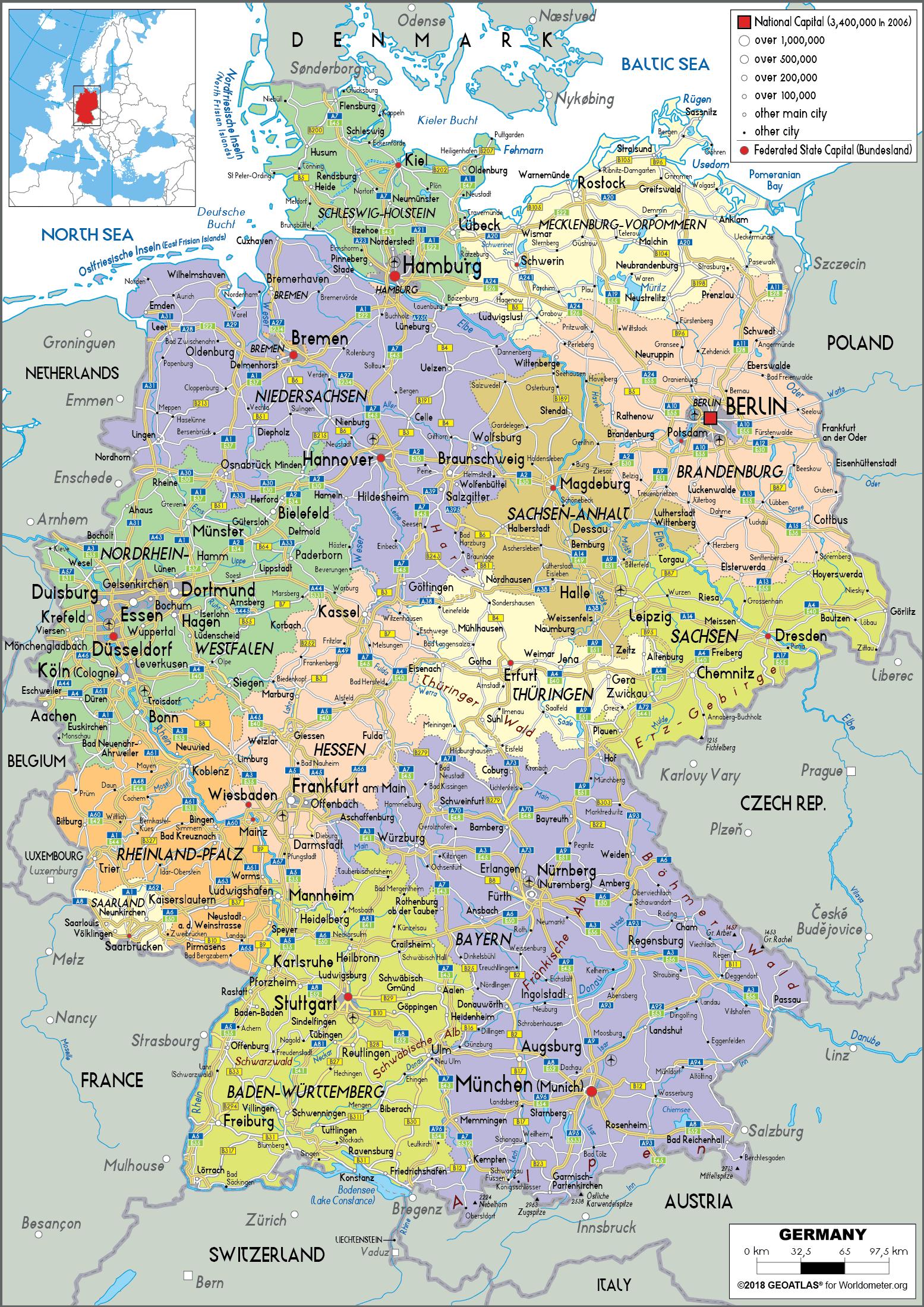
Germany, a nation renowned for its rich history, cultural diversity, and economic prowess, is also a fascinating study in political geography. Understanding the intricate tapestry of German politics requires a close examination of its political map, a visual representation that reveals the country’s administrative divisions and their respective power structures.
A Nation Divided and United: The Federal Republic of Germany
Germany’s political map is defined by its federal structure, a system where power is shared between the central government and individual states, known as Länder. This decentralized system reflects the nation’s historical experience, particularly the period of division following World War II. The Federal Republic of Germany, established in 1949, encompassed the western part of the country, while the German Democratic Republic (GDR) occupied the east.
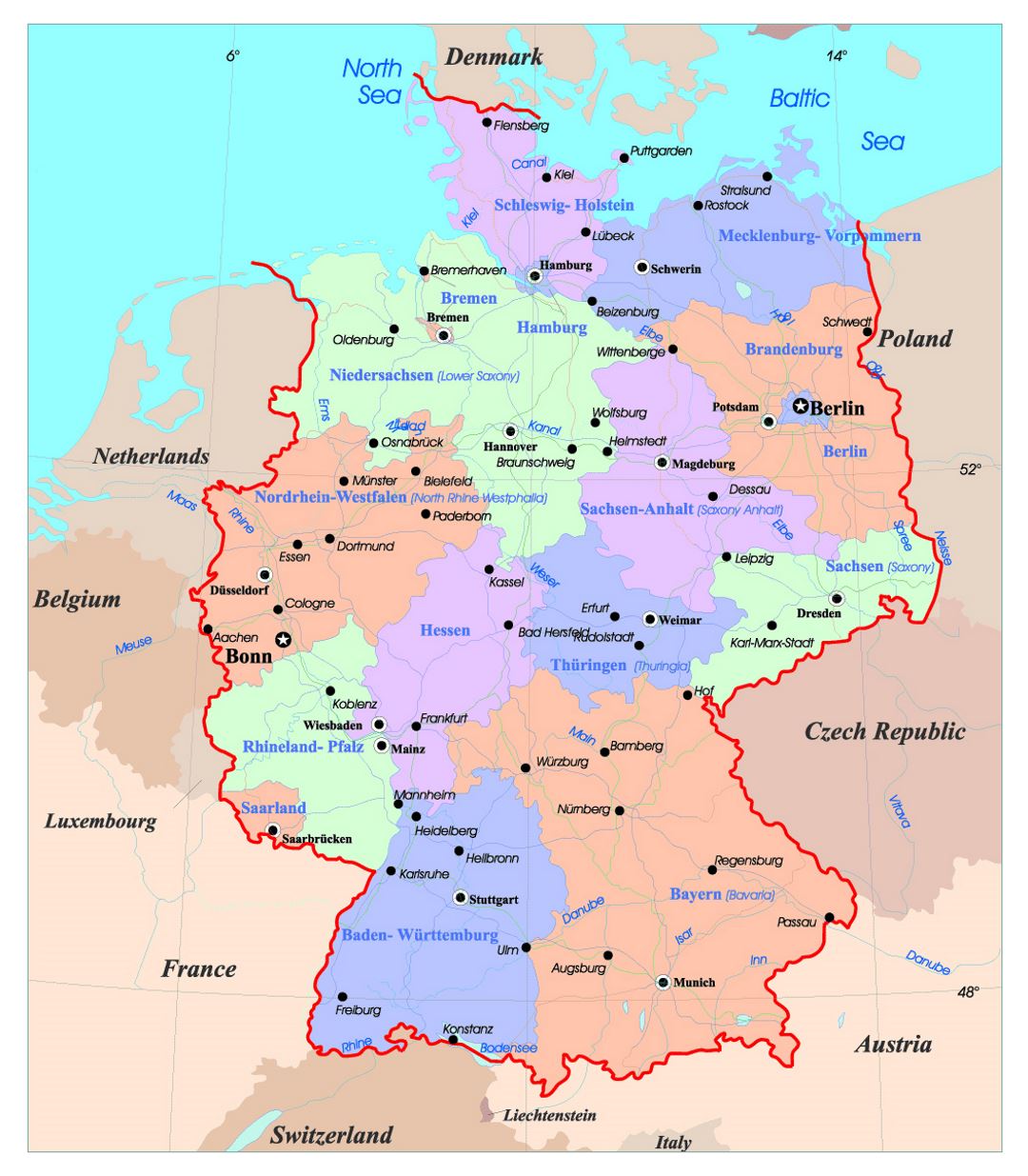
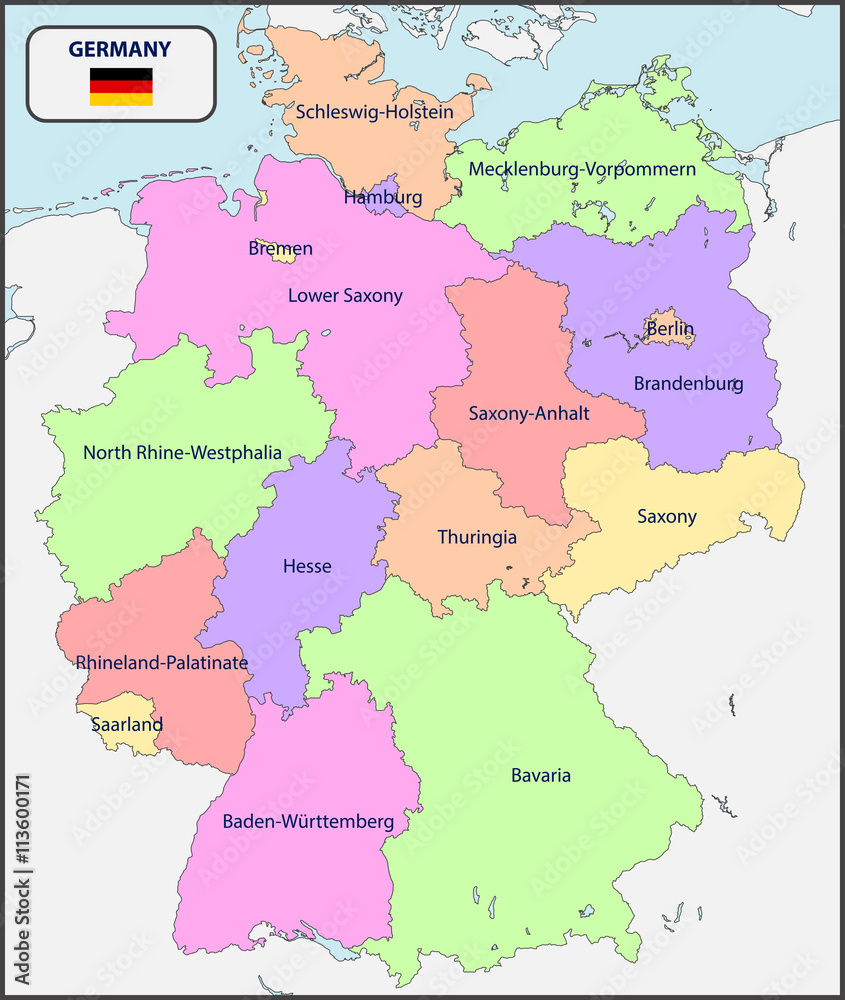
The reunification of Germany in 1990 marked a pivotal moment, merging the two distinct political entities into a unified nation. The existing federal structure was retained, with the GDR’s five Länder being integrated into the existing system, bringing the total number of Länder to 16.
Understanding the Länder: A Mosaic of Diversity
Each of the 16 Länder possesses its own unique identity, shaped by history, culture, and regional characteristics. They are not merely administrative units but possess a degree of autonomy, with their own parliaments, governments, and legislative powers.
Key Features of the Political Map:
- The Länder: The 16 Länder are the fundamental building blocks of the German political map. Their distinct identities and diverse landscapes create a rich tapestry across the nation.
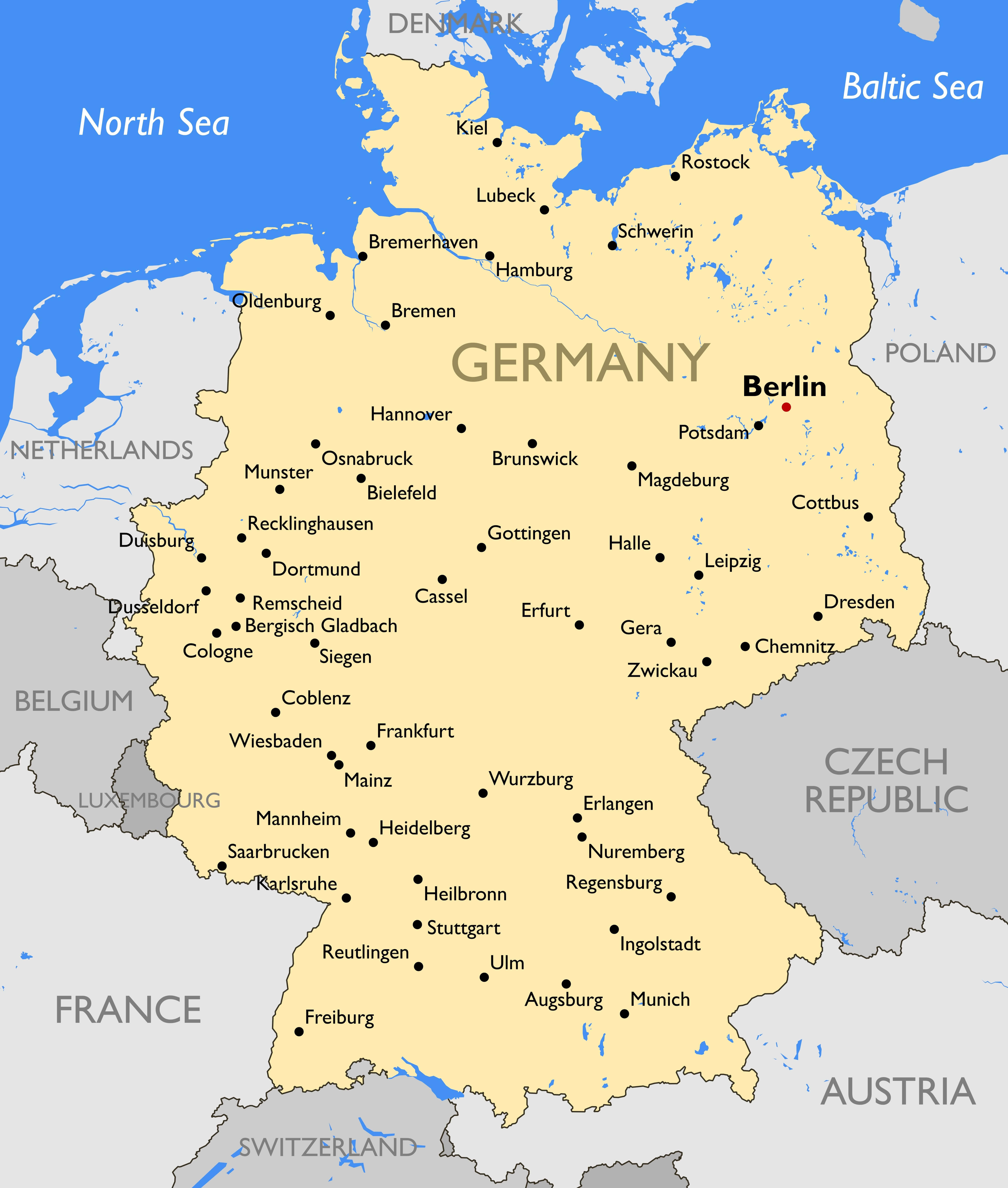
- Capital Cities: Each Land has its own capital city, serving as the seat of its government and parliament. These cities, such as Berlin, Munich, and Hamburg, play a significant role in regional politics and governance.
- Administrative Divisions: Within each Land, there are further administrative divisions, such as districts (Kreise) and municipalities (Gemeinden). These divisions facilitate local governance and provide a framework for community engagement.
- The Bundestag: The German parliament, known as the Bundestag, is located in Berlin. It comprises 736 members elected through a proportional representation system, reflecting the diverse political landscape across the nation.
- The Bundesrat: The Bundesrat, the upper house of the German parliament, represents the interests of the Länder. Each Land has a number of votes based on its population, ensuring regional representation in the national legislative process.
The Importance of the Political Map:
The political map of Germany is not merely a static representation of administrative divisions. It is a dynamic tool that reveals the complex interplay of federalism, regional identities, and national politics. It serves as a visual guide to understanding:
- Power Distribution: The map highlights the balance of power between the federal government and the Länder, showcasing the decentralized nature of German governance.
- Political Landscape: The map provides insights into the political affiliations of different regions, illustrating the regional variations in party support and political ideologies.
- Regional Development: The map can help analyze regional economic disparities, infrastructural development, and social issues, providing valuable data for policy formulation and planning.
FAQs about the German Political Map:
1. How does the federal structure of Germany work?
Germany’s federal structure ensures a balance of power between the central government and the 16 Länder. The federal government has primary responsibility for areas like foreign policy, defense, and currency, while the Länder have significant autonomy over areas like education, healthcare, and policing.
2. What is the role of the Bundesrat?
The Bundesrat, the upper house of the German parliament, represents the interests of the Länder. It has the power to veto legislation passed by the Bundestag, ensuring that regional concerns are considered in the national legislative process.
3. Are there any significant regional differences in Germany?
Yes, Germany exhibits significant regional differences in terms of culture, language, economic development, and political affiliations. These differences are reflected in the political map, highlighting the diverse nature of the nation.
4. What is the importance of local government in Germany?
Local government plays a crucial role in German society, providing essential services, managing local infrastructure, and promoting community engagement. The political map demonstrates the hierarchical structure of governance, from the federal level down to the local municipalities.
5. How does the political map influence policy decisions?
The political map provides valuable insights into the regional variations in demographics, economic activity, and social issues. This information is crucial for policymakers in tailoring policies to address specific regional needs and challenges.
Tips for Understanding the German Political Map:
- Focus on the Länder: Pay close attention to the names, locations, and characteristics of each Land. Understanding their distinct identities is key to comprehending the regional variations in German politics.
- Study the Capital Cities: Explore the capital cities of each Land, recognizing their role as centers of regional power and governance.
- Analyze the Political Landscape: Examine the political affiliations of different regions, identifying the dominant parties and their respective strengths.
- Consider Historical Context: Understanding the historical development of the German political map, including the period of division and reunification, provides crucial context for interpreting the current political landscape.
- Engage with Local Perspectives: Seek out information and perspectives from individuals and communities within different regions to gain a deeper understanding of their local concerns and priorities.
Conclusion:
The political map of Germany is a powerful tool for understanding the nation’s complex political structure and the diverse regional identities that shape its character. By delving into its intricacies, we gain a deeper appreciation for the balance of power between the federal government and the Länder, the role of regional politics, and the diverse voices that contribute to the vibrant tapestry of German society.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the German Landscape: A Guide to the Political Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!