Dividing the Electorate: An Exploration of Voting Districts Maps
Related Articles: Dividing the Electorate: An Exploration of Voting Districts Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Dividing the Electorate: An Exploration of Voting Districts Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Dividing the Electorate: An Exploration of Voting Districts Maps

The intricate web of democracy relies on a fundamental principle: representation. To ensure that the voices of all citizens are heard and considered, geographical areas are divided into smaller units, known as voting districts. These districts, depicted on voting districts maps, form the foundation of electoral systems, dictating how citizens elect representatives and ultimately, shaping the political landscape.
Understanding the Foundation: What are Voting Districts Maps?
Voting districts maps are visual representations of how a geographical area is divided into distinct electoral units. Each district encompasses a specific population, and voters within that district elect a representative to a legislative body. These maps are the tangible manifestation of the process of apportionment, the allocation of seats in a legislature based on population.
The Importance of Fair and Equitable Maps:
The integrity of electoral processes hinges on the fairness and equity of voting districts maps. Ideal maps strive to achieve the following:
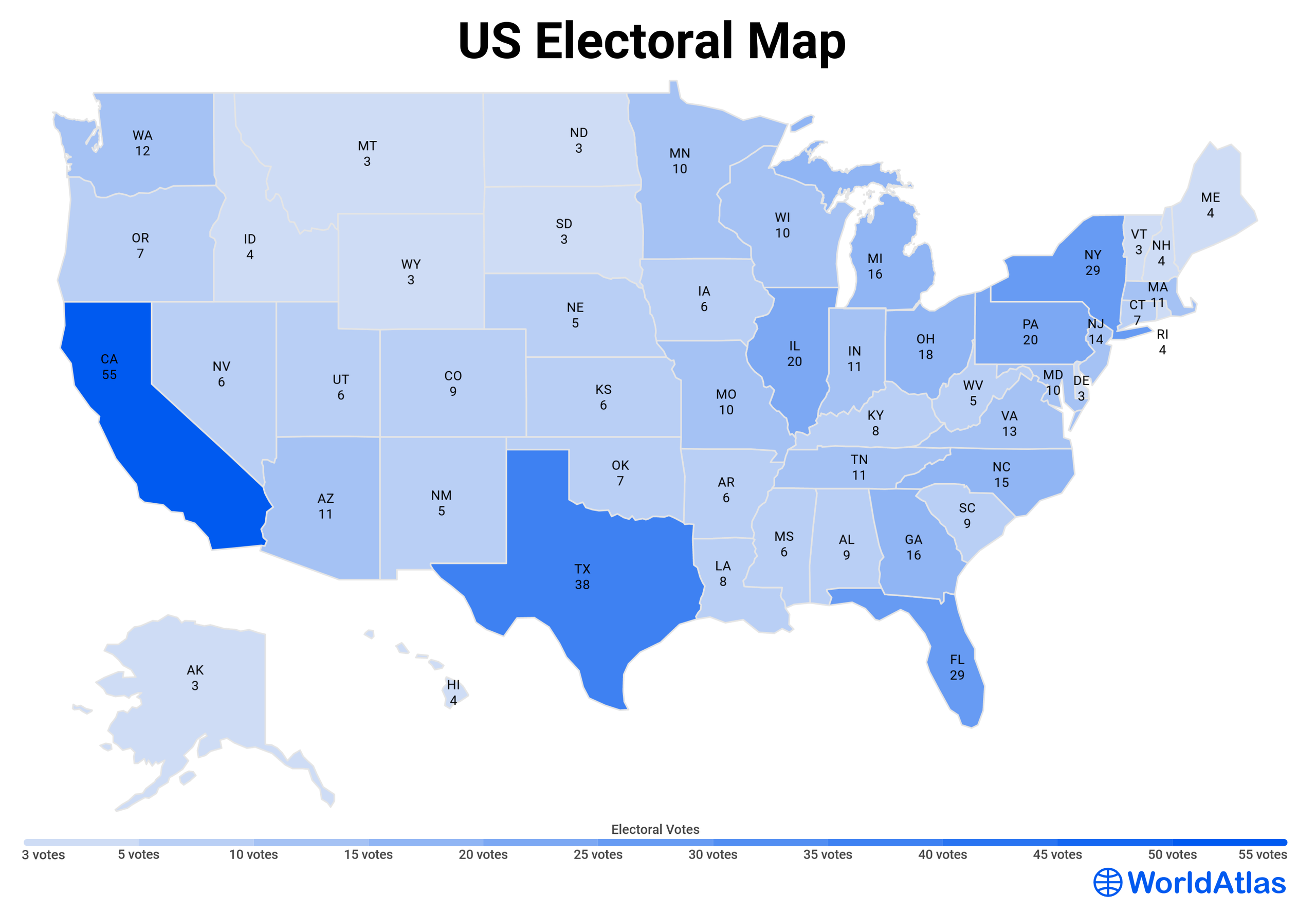
- Equal Representation: Each district should contain roughly the same number of people, ensuring that each voter’s voice carries equal weight. This principle, known as "one person, one vote," is a cornerstone of democratic representation.
- Compactness and Contiguity: Districts should be geographically cohesive, minimizing sprawling and fragmented boundaries. This promotes community cohesion and ensures that representatives are accountable to a clearly defined constituency.
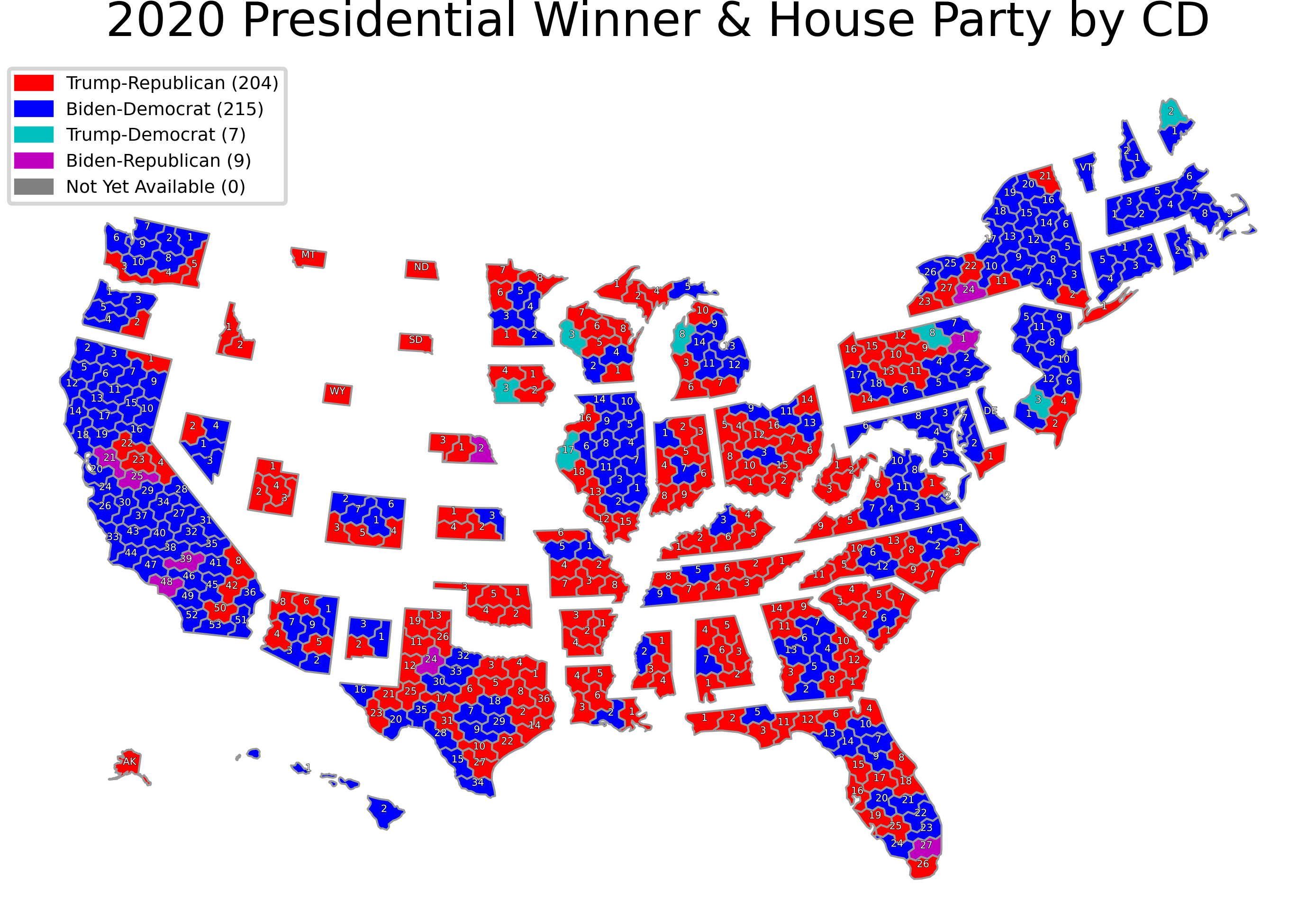
- Minimizing Gerrymandering: The practice of manipulating district boundaries to favor a particular political party or group is known as gerrymandering. Fair maps aim to prevent this practice by ensuring that districts are drawn based on neutral criteria, not political advantage.
Types of Voting Districts Maps:
Different electoral systems utilize varying types of voting districts maps, each with its own characteristics and implications:
- Single-Member Districts: Each district elects a single representative, commonly used in countries with a first-past-the-post system. This system simplifies the electoral process but can lead to wasted votes if a candidate wins with a narrow majority.
- Multi-Member Districts: Multiple representatives are elected from each district, often employed in proportional representation systems. This allows for a more diverse representation of political views within a district but can make it challenging to attribute specific policies to individual representatives.
- At-Large Districts: Representatives are elected from the entire geographical area, rather than specific districts. This system can be more efficient but may limit the representation of local interests.
The Process of Creating Voting Districts Maps:
The creation of voting districts maps is a complex process, often involving multiple stakeholders and a series of steps:
- Data Collection: Population data, demographic information, and geographical boundaries are gathered to inform the map-making process.
- Districting Criteria: Specific criteria are established, outlining the principles that will guide the creation of districts, such as population equality, compactness, and contiguity.
- Map Development: Using specialized software and algorithms, maps are drawn and refined to meet the established criteria.
- Public Review and Feedback: Drafts of proposed maps are made available for public review and feedback, allowing citizens to voice concerns and suggest improvements.
- Finalization and Implementation: After incorporating public input and addressing any concerns, maps are finalized and implemented for use in future elections.
Challenges and Controversies:
Despite their crucial role in democratic processes, voting districts maps are not without their challenges and controversies:
- Gerrymandering: The manipulation of district boundaries to favor a particular party or group remains a persistent issue, leading to concerns about fair and equal representation.
- Partisan Bias: The process of map-making can be influenced by political agendas, with parties often seeking to create districts that maximize their electoral advantage.
- Lack of Transparency: The lack of transparency in the map-making process can erode public trust and fuel accusations of bias or corruption.
FAQs on Voting Districts Maps:
Q: Why are voting districts maps important?
A: Voting districts maps are essential for ensuring fair and equal representation in democratic systems. They determine how voters are grouped for elections, influencing the outcome of elections and the composition of legislative bodies.
Q: How are voting districts maps created?
A: The process of creating voting districts maps involves data collection, defining districting criteria, map development, public review, and finalization. This process aims to ensure that maps are fair, equitable, and representative.
Q: What are the challenges associated with voting districts maps?
A: Challenges include the potential for gerrymandering, partisan bias in the map-making process, and a lack of transparency. These issues can undermine the fairness and integrity of elections.
Tips for Understanding and Engaging with Voting Districts Maps:
- Research your local district: Understand the boundaries of your voting district and the demographic characteristics of its residents.
- Stay informed about map-making processes: Follow the news and participate in public forums to learn about how maps are created and to voice your opinions.
- Support organizations advocating for fair and equitable maps: Many organizations work to ensure that maps are drawn fairly and transparently.
Conclusion:
Voting districts maps are fundamental components of democratic systems, shaping how citizens elect representatives and influencing the political landscape. While challenges and controversies exist, ongoing efforts to ensure fairness, transparency, and inclusivity in the map-making process are crucial for maintaining the integrity of elections and fostering a robust democracy. By understanding the complexities of voting districts maps and engaging in the process of map-making, citizens can contribute to ensuring that their voices are heard and represented effectively.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Dividing the Electorate: An Exploration of Voting Districts Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
