A World of Proportions: Understanding the Importance of Accurate Geographic Representation
Related Articles: A World of Proportions: Understanding the Importance of Accurate Geographic Representation
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A World of Proportions: Understanding the Importance of Accurate Geographic Representation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A World of Proportions: Understanding the Importance of Accurate Geographic Representation

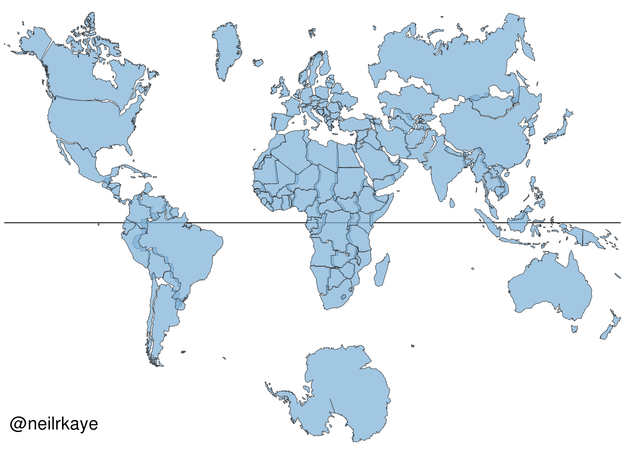
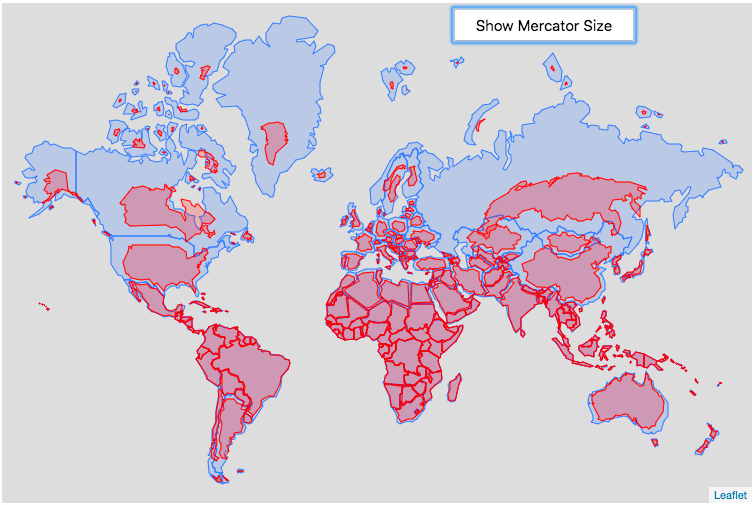
The world map, a ubiquitous tool for understanding our planet, often presents a distorted view of reality. This distortion, a consequence of projecting a spherical Earth onto a flat surface, can lead to misperceptions about the relative size and shape of continents and countries. A world map in proportion addresses this challenge by accurately representing the area of each landmass, providing a more truthful and insightful view of the world.
The Problem with Conventional World Maps
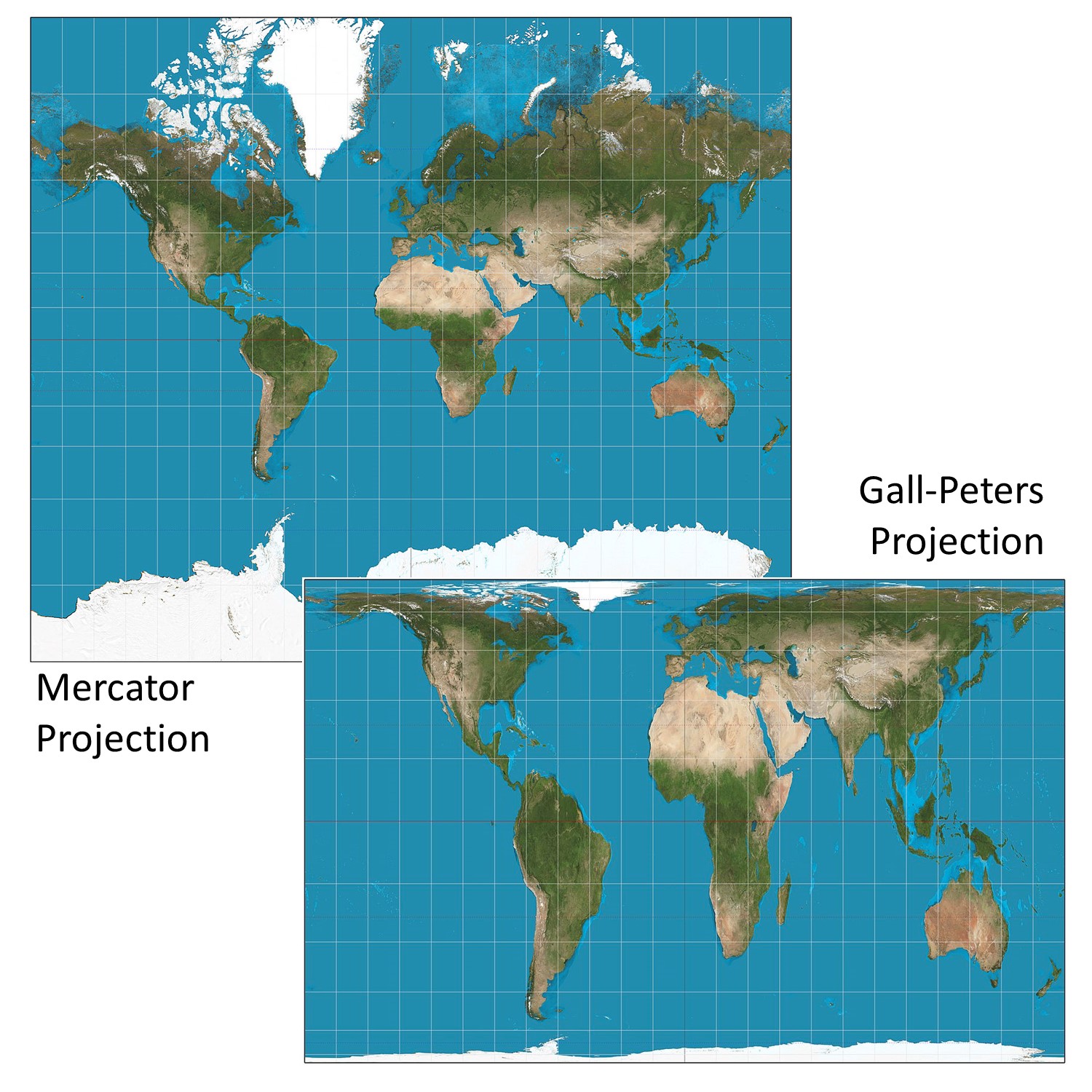
Traditional world maps, like the Mercator projection, prioritize preserving angles and shapes. This means that areas closer to the poles appear significantly larger than they actually are, while equatorial regions are compressed. For instance, Greenland, on a Mercator projection, appears larger than the entire continent of Africa, despite being only about 14% of its size. This misrepresentation can lead to skewed perceptions about the importance and influence of different regions.
The Solution: World Maps in Proportion
World maps in proportion, also known as equal-area projections, prioritize preserving the relative size of landmasses. These maps use mathematical formulas to ensure that the area of each region is represented accurately in proportion to its actual size on the globe. This allows for a more balanced and realistic understanding of the world’s geography.
Benefits of Using World Maps in Proportion
The use of world maps in proportion offers several advantages:
- Accurate Representation: They eliminate the distortions inherent in conventional maps, presenting a more truthful depiction of the relative size and shape of continents and countries.
- Enhanced Understanding: They promote a more balanced and objective understanding of the world, particularly regarding the geographical distribution of population, resources, and political power.
- Improved Education: They serve as valuable tools for education, providing a more accurate representation of the world for students and educators.
- Global Perspective: They foster a more holistic view of the planet, encouraging a sense of global interconnectedness and responsibility.
Types of World Maps in Proportion
Several different projections are used to create world maps in proportion, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some popular examples include:
- Gall-Peters Projection: This projection is known for its accurate representation of landmasses, but it can distort the shape of continents, especially near the poles.
- Winkel Tripel Projection: This projection balances area accuracy with shape preservation, making it a popular choice for general-purpose maps.
- Robinson Projection: This projection offers a compromise between area accuracy and shape distortion, making it suitable for educational purposes.
Beyond the Map: Understanding the Importance of Context
While world maps in proportion offer a more accurate representation of the world, it’s crucial to remember that maps are only tools. They provide a visual representation of geographic information, but they cannot capture the full complexity of the world.
To truly understand the world, we must consider other factors beyond size and shape. These include:
- Population Density: While a map might show the relative size of countries, it doesn’t reveal how densely populated they are.
- Economic Development: A map doesn’t illustrate the economic strength or influence of different countries.
- Cultural Diversity: Maps cannot convey the rich tapestry of cultures and traditions that exist across the globe.
FAQs about World Maps in Proportion:
Q: Why are traditional world maps distorted?
A: Traditional world maps use projections that prioritize preserving angles or shapes, leading to distortions in area representation.
Q: What is the difference between a Mercator projection and a Gall-Peters projection?
A: The Mercator projection preserves angles and shapes, but distorts area. The Gall-Peters projection preserves area but can distort shapes.
Q: Are world maps in proportion the perfect solution?
A: No, all projections have limitations. World maps in proportion prioritize area accuracy, but they can still distort shapes.
Q: How can I find a world map in proportion?
A: Many online resources and educational materials use world maps in proportion. You can also find them in atlases and textbooks.
Tips for Using World Maps in Proportion:
- Compare different projections: Examine how different projections represent the same region to understand their strengths and weaknesses.
- Consider the purpose of the map: Choose a projection that best suits the specific information you want to convey.
- Supplement with additional data: Use maps in conjunction with other data sources to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the world.
- Engage in critical thinking: Recognize that maps are representations, not absolute truths, and consider the potential biases they might contain.
Conclusion:
World maps in proportion are essential tools for understanding our planet. They provide a more accurate and balanced representation of the relative size and shape of landmasses, fostering a more informed and holistic view of the world. By using these maps and considering their limitations, we can gain a more nuanced understanding of the global landscape and its complexities. This understanding is crucial for fostering global cooperation, promoting environmental sustainability, and building a more equitable and just world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A World of Proportions: Understanding the Importance of Accurate Geographic Representation. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!