A Tapestry of Landforms: Exploring the Physical Features of North America
Related Articles: A Tapestry of Landforms: Exploring the Physical Features of North America
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Tapestry of Landforms: Exploring the Physical Features of North America. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tapestry of Landforms: Exploring the Physical Features of North America

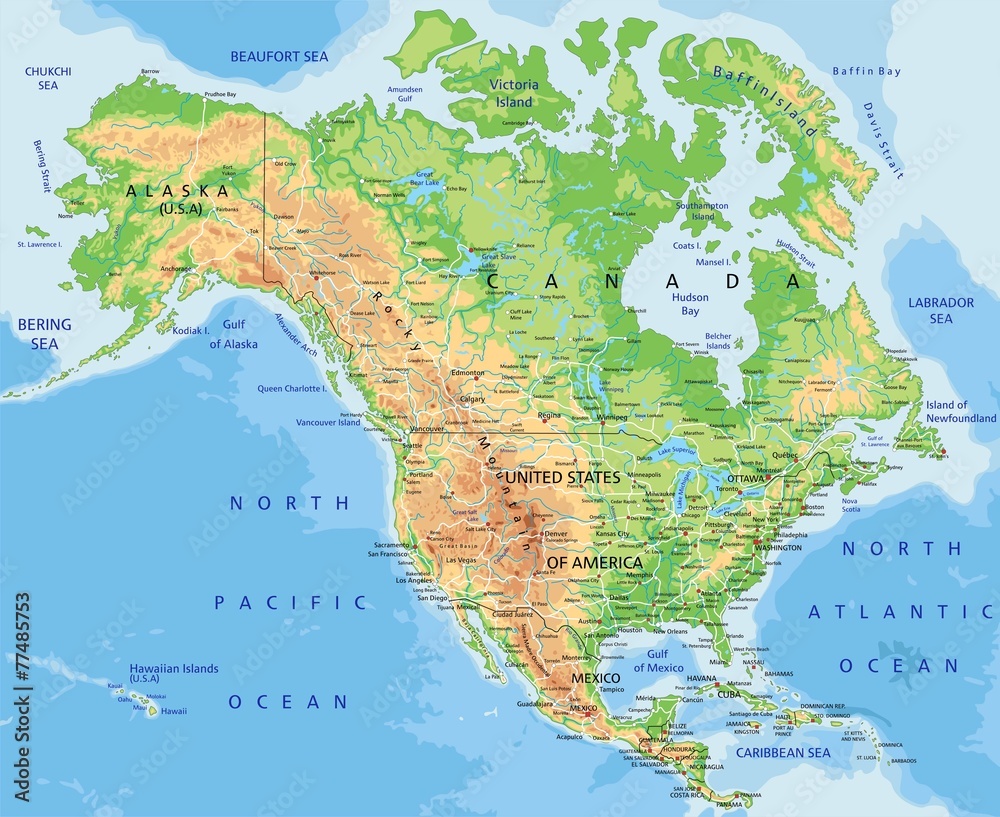
North America, the third largest continent, boasts a remarkable diversity of physical features that have shaped its history, culture, and ecology. From towering mountain ranges to vast plains, from shimmering deserts to verdant forests, the continent offers a captivating landscape for exploration and understanding. This article delves into the key physical features of North America, examining their formation, characteristics, and significance.
Mountain Ranges: Pillars of the Continent
The defining feature of North America’s western landscape are its imposing mountain ranges, remnants of ancient tectonic activity. The Rocky Mountains, stretching from Canada to New Mexico, are the backbone of the continent, a formidable barrier that influences weather patterns and creates diverse ecosystems. The Appalachian Mountains, older and less dramatic than the Rockies, run along the eastern seaboard, shaping the topography of the eastern United States.
The Pacific Coast: A Land of Subduction and Volcanoes
The western edge of North America is marked by the Pacific Coast, a region shaped by the collision of tectonic plates. This interaction creates a chain of volcanic mountains, including Mount St. Helens and Mount Rainier, and deep trenches along the ocean floor. The Cascadia Subduction Zone, located off the coast of the Pacific Northwest, poses a significant seismic risk, highlighting the dynamic nature of this region.
The Great Plains: A Vast Expanse of Grasslands
Stretching east of the Rocky Mountains lies the Great Plains, a vast expanse of flat, fertile land. Once dominated by grasslands, the plains have been transformed by agriculture, becoming a key food-producing region of North America. The Mississippi River, the continent’s largest, flows through the heart of the plains, providing transportation and irrigation.
The Canadian Shield: A Cradle of Ancient Rocks
The Canadian Shield, a vast expanse of ancient, igneous and metamorphic rocks, covers much of Canada. This region, characterized by rocky terrain and numerous lakes, is home to vast mineral deposits and boreal forests. Its geology provides valuable insights into Earth’s early history.
The Interior Lowlands: A Land of Transition
Located between the Appalachian Mountains and the Great Plains, the Interior Lowlands comprise a transition zone with diverse landscapes, including rolling hills, fertile valleys, and extensive forests. This region is heavily influenced by the Mississippi River, which serves as a major waterway and a source of fertile soil.
The Gulf Coastal Plain: A Low-Lying Coastal Region
The Gulf Coastal Plain, stretching along the Gulf of Mexico, is characterized by flat, low-lying terrain, fertile soils, and extensive wetlands. This region is vulnerable to hurricanes and sea-level rise, highlighting the challenges of climate change.
The Great Basin: A Desert Realm
The Great Basin, located in the western United States, is a vast, arid region dominated by mountains, valleys, and salt flats. This region experiences extreme temperatures and low rainfall, making it a challenging environment for life.
The Arctic: A Frozen Frontier
The Arctic, encompassing northern Canada, Greenland, and parts of Alaska, is a region of extreme cold, vast ice sheets, and unique ecosystems. This region is facing the effects of climate change, with melting glaciers and rising sea levels posing significant threats.
Understanding the Importance of North America’s Physical Features
The physical features of North America are not merely scenic landscapes but play a vital role in shaping the continent’s environment, economy, and culture.
- Resource Distribution: Mountains and plains influence the distribution of natural resources, from mineral deposits and timber to fertile farmland and abundant water sources.
- Climate and Weather Patterns: Mountain ranges act as barriers, influencing precipitation patterns and creating diverse climate zones.
- Biodiversity and Ecosystems: The variety of landscapes supports a rich tapestry of ecosystems, from boreal forests and grasslands to deserts and coastal wetlands.
- Human Settlement and Development: Physical features have shaped human settlement patterns, influencing the development of agriculture, transportation, and infrastructure.
FAQs by Physical Features of North America
1. What is the highest mountain in North America?
The highest mountain in North America is Denali, located in the Alaskan Range. It reaches an elevation of 20,310 feet (6,190 meters).
2. What are the major rivers of North America?
Some of the major rivers in North America include the Mississippi River, the Missouri River, the Rio Grande, the Yukon River, and the Mackenzie River.
3. What are the major deserts of North America?
The major deserts of North America include the Mojave Desert, the Sonoran Desert, the Great Basin Desert, and the Chihuahuan Desert.
4. What is the significance of the Canadian Shield?
The Canadian Shield is a vast source of mineral resources, including nickel, copper, gold, and diamonds. It also plays a crucial role in regulating water flow and supporting a diverse ecosystem.
5. What are the challenges faced by the Arctic region due to climate change?
Climate change is causing the Arctic ice sheets to melt at an alarming rate, leading to rising sea levels and threatening the unique ecosystems and indigenous communities that depend on the region.
Tips by Physical Features of North America
- Use maps and atlases: Visualizing the continent’s physical features through maps and atlases enhances understanding and helps in identifying key locations.
- Explore the outdoors: Visiting national parks and other natural areas provides firsthand experience of the diverse landscapes of North America.
- Learn about geological processes: Understanding the formation of mountains, deserts, and other features through geological studies provides a deeper appreciation for the dynamic nature of the continent.
- Engage with local communities: Interacting with people who live in different regions of North America provides insights into how physical features shape their lives and cultures.
Conclusion by Physical Features of North America
The physical features of North America are a testament to the continent’s rich geological history and dynamic processes. From towering mountain ranges to vast plains, from shimmering deserts to verdant forests, these features have shaped the continent’s environment, resources, and culture. Understanding these features is essential for appreciating the complexity and beauty of North America and for addressing the challenges of managing its resources and protecting its diverse ecosystems.


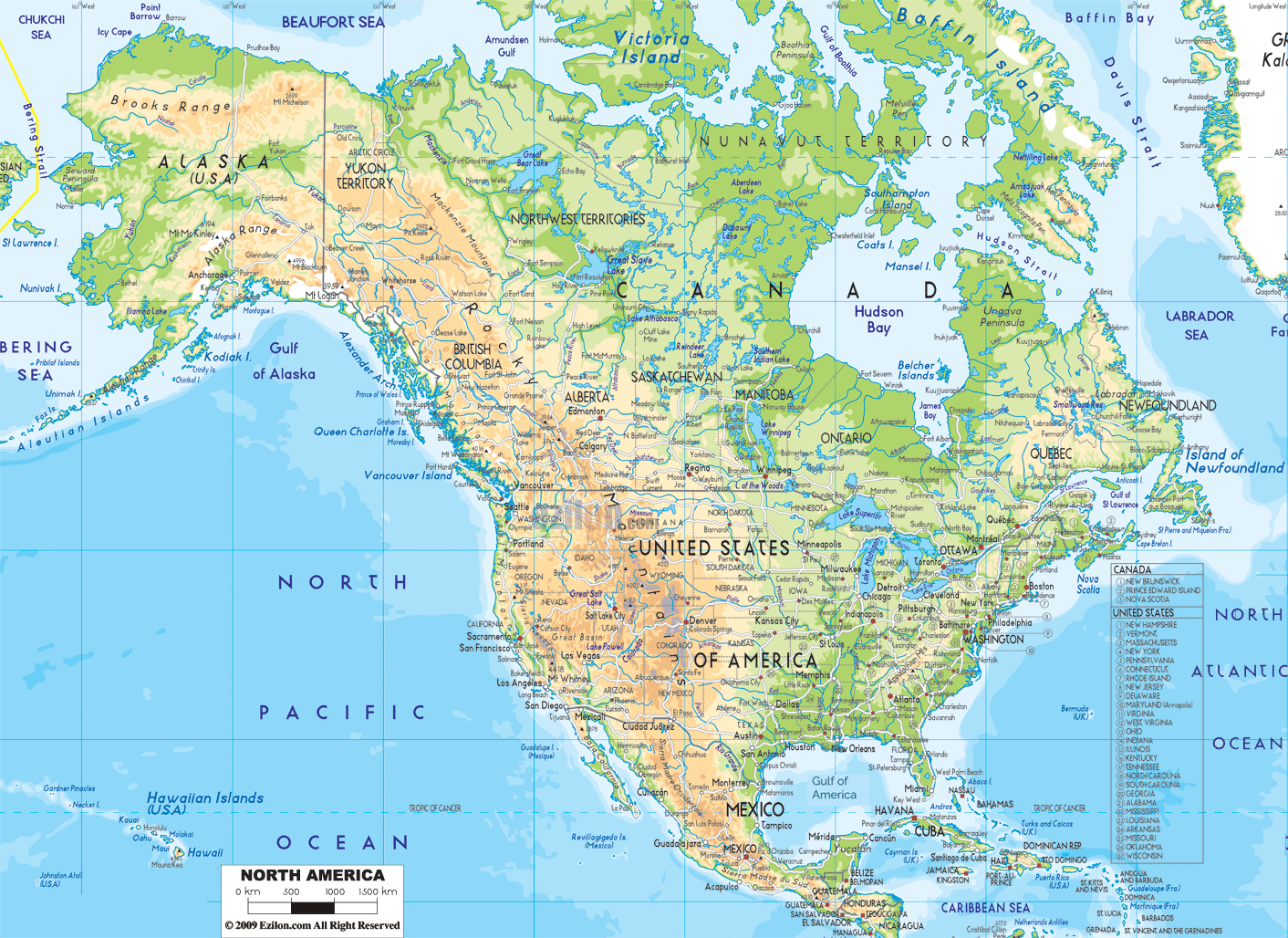
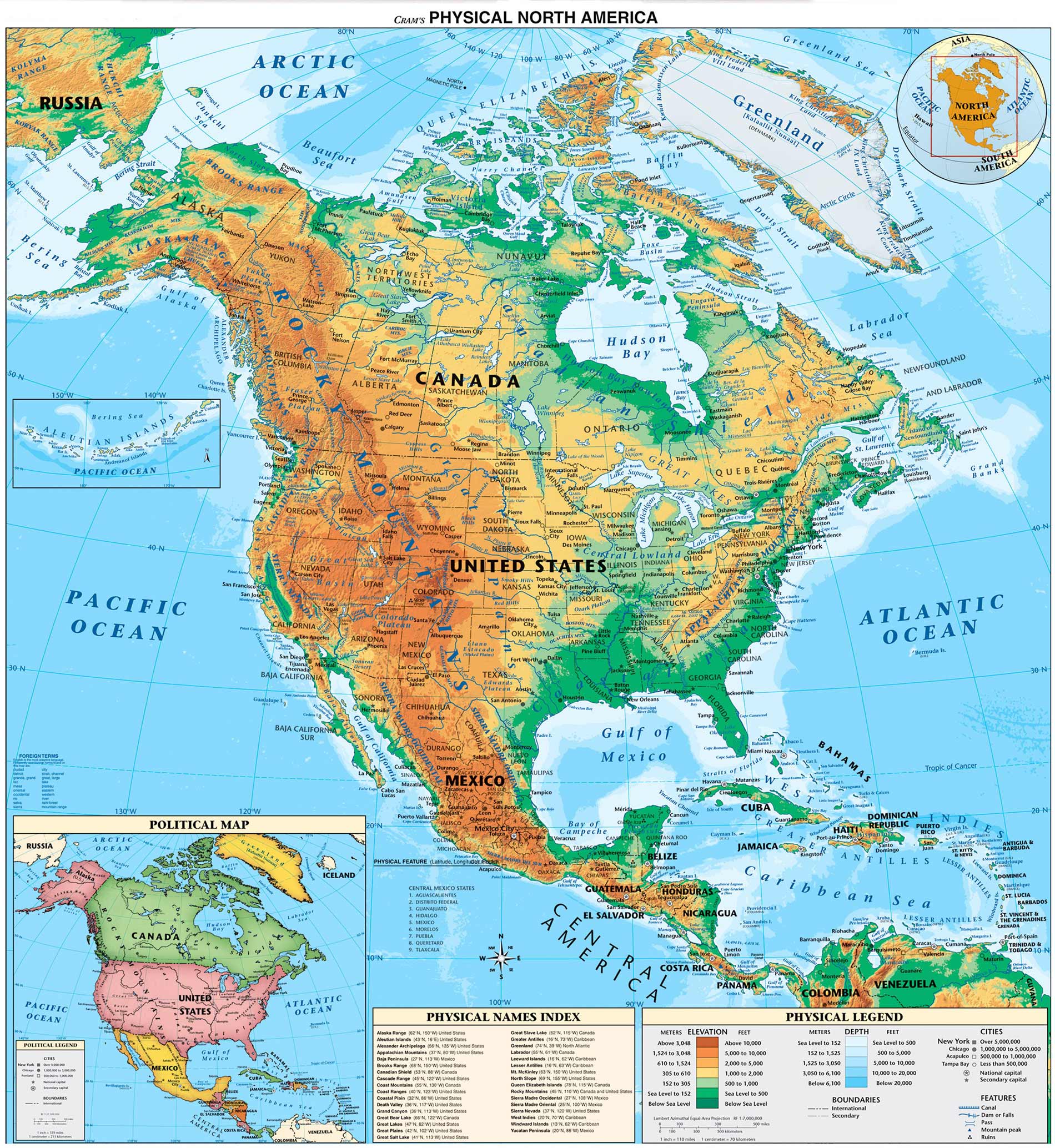

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tapestry of Landforms: Exploring the Physical Features of North America. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!