A Shared Landscape: Exploring the Geography of California and Mexico
Related Articles: A Shared Landscape: Exploring the Geography of California and Mexico
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Shared Landscape: Exploring the Geography of California and Mexico. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Shared Landscape: Exploring the Geography of California and Mexico

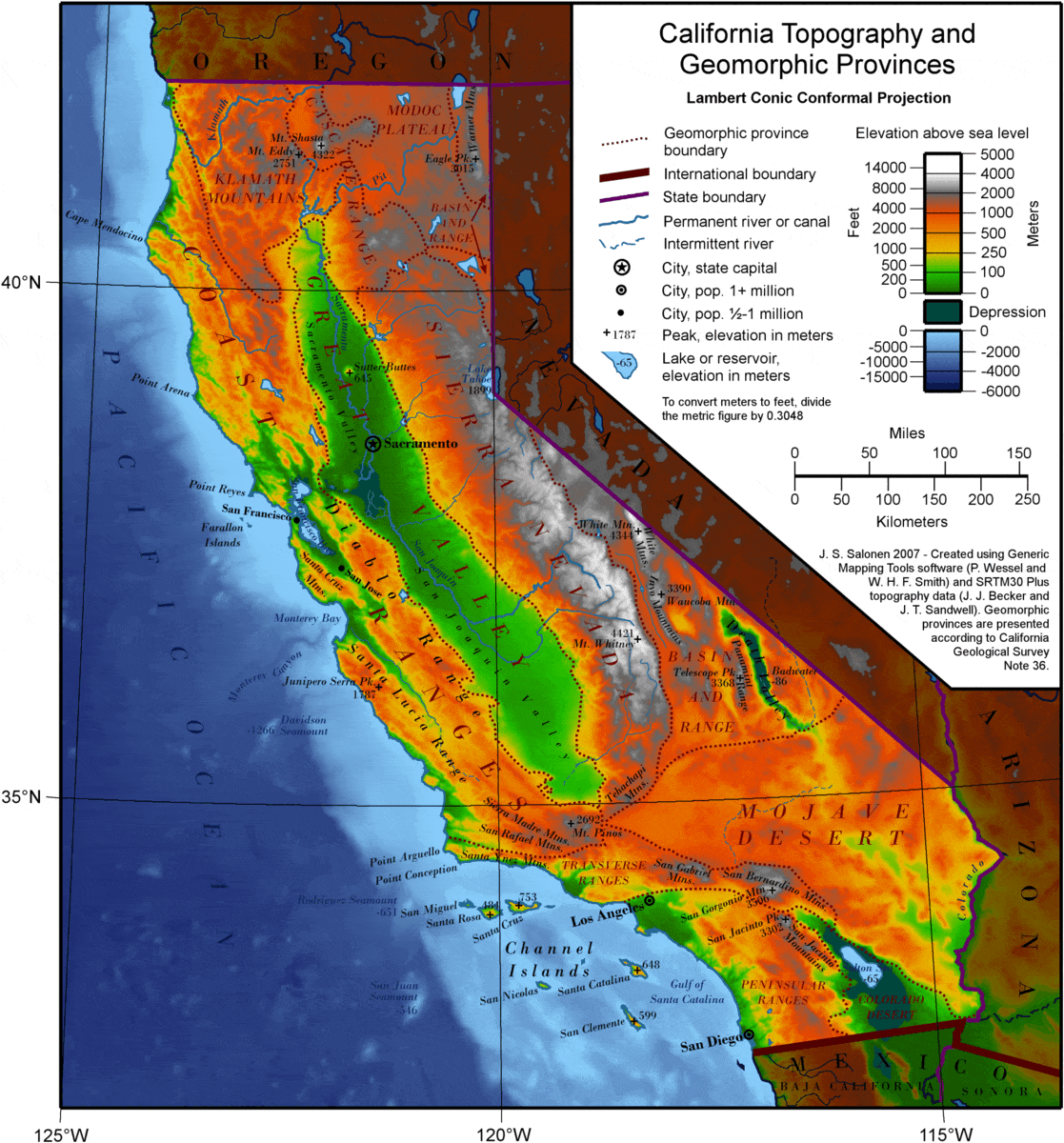
The intricate relationship between California and Mexico is not just a matter of shared history and culture; it is deeply rooted in the very geography that binds these two regions. A closer look at the map reveals a complex interplay of landforms, climate zones, and ecological systems that have shaped both the natural and human landscapes of California and Mexico.
The Border: A Line Drawn on a Shared Landscape
The most obvious feature on any map of California and Mexico is the international border, a seemingly arbitrary line drawn across a vast and diverse landscape. This border, established in 1848 with the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, divides not only nations but also ecosystems, cultural traditions, and even family ties.
The border, marked by the Colorado River in the east and the Pacific Ocean in the west, traverses diverse terrains. It cuts through the arid deserts of the Sonoran and Mojave, crosses the fertile valleys of the Imperial Valley and the San Joaquin Valley, and winds its way through the rugged Sierra Nevada mountains. This geographical diversity creates a mosaic of environments, each with its own unique challenges and opportunities.
The Influence of the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean, a dominant force in both California and Mexico, exerts a significant influence on the climate and ecosystems of both regions. The California Current, a cold current flowing south along the Pacific coast, brings cool, moist air to California, contributing to the state’s temperate climate and supporting a diverse marine ecosystem.
Mexico’s Pacific coast, on the other hand, experiences a more tropical climate, with warm temperatures and abundant rainfall. This difference in climate has led to the development of distinct ecosystems on either side of the border. California boasts redwood forests, coastal chaparral, and diverse marine life, while Mexico’s Pacific coast features tropical rainforests, mangroves, and a rich array of coral reefs.
The Mountains and Valleys: Shaping the Landscape
The Sierra Nevada mountains, a prominent feature on the map of California, form a natural barrier between the state’s interior and the Pacific coast. These mountains, which rise to over 14,000 feet, are a source of water for California’s cities and agriculture, and they also provide habitat for a wide variety of wildlife.
Mexico’s Baja California peninsula, separated from the mainland by the Gulf of California, is characterized by a rugged mountain range known as the Sierra de Baja California. These mountains, which run the length of the peninsula, are home to unique desert ecosystems and endemic species.
The valleys that lie between the mountains are equally important. The Central Valley of California, a vast expanse of fertile land, is the heart of the state’s agriculture industry. In Mexico, the fertile valleys of Sonora and Sinaloa are renowned for their agricultural production, particularly for fruits and vegetables.
A Shared Ecosystem: The Importance of Conservation
The map of California and Mexico reveals a shared landscape with interconnected ecosystems. The Colorado River, which flows through the southwestern United States and northern Mexico, is a vital source of water for both regions. The river’s watershed encompasses diverse habitats, including deserts, forests, and wetlands, supporting a wealth of biodiversity.
However, the Colorado River’s flow has been significantly reduced by dams and water diversions, leading to ecological challenges in both California and Mexico. The need for coordinated conservation efforts across the border is paramount to ensure the health of this shared resource.
The Human Connection: A Legacy of Exchange and Interaction
The map also reveals the human connection between California and Mexico. Centuries of migration, trade, and cultural exchange have left an indelible mark on the landscape. From the indigenous tribes who lived in both regions before European colonization to the modern-day flow of people and goods, the border has been a dynamic and ever-changing space.
The historical connection between California and Mexico is evident in the shared cultural heritage, language, and cuisine of the two regions. The influence of Mexican culture is particularly strong in California, where the state’s vibrant Hispanic community is a testament to the enduring ties between the two nations.
FAQs on the Map of California and Mexico
1. What is the significance of the border between California and Mexico?
The border represents a complex relationship between two nations, shaping the flow of people, goods, and ideas. It also serves as a boundary between distinct ecosystems and cultural landscapes.
2. How does the Pacific Ocean influence the climate and ecosystems of California and Mexico?
The Pacific Ocean brings cool, moist air to California, creating a temperate climate. In contrast, Mexico’s Pacific coast experiences a more tropical climate due to warmer ocean currents. These differences in climate have led to the development of distinct ecosystems on either side of the border.
3. What are the major geographical features of California and Mexico?
California is characterized by the Sierra Nevada mountains, the Central Valley, and the Pacific coast. Mexico’s Baja California peninsula, the Sonoran Desert, and the Sierra Madre Occidental mountain range are prominent geographical features.
4. How do the mountains and valleys shape the landscape of California and Mexico?
Mountains provide natural barriers, influence rainfall patterns, and serve as habitat for diverse species. Valleys, on the other hand, offer fertile land for agriculture and support dense populations.
5. What are the environmental challenges facing California and Mexico?
Both regions face challenges related to water scarcity, pollution, and climate change. The Colorado River, a shared resource, is facing depletion due to dams and water diversions.
Tips for Understanding the Map of California and Mexico
- Explore interactive maps: Online mapping tools provide detailed information about geographical features, climate zones, and population density.
- Read about the history and culture: Understanding the historical relationship between California and Mexico provides context for the present-day landscape.
- Visit both regions: Experiencing the diverse landscapes and cultures of California and Mexico firsthand will deepen your understanding of the shared geography.
Conclusion: A Shared Landscape, A Shared Future
The map of California and Mexico reveals a complex and interconnected landscape, shaped by both natural forces and human intervention. The border, while a physical divide, does not erase the shared history, culture, and ecology that bind these two regions. Understanding this shared landscape is crucial for addressing the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead, ensuring a sustainable future for both California and Mexico.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Shared Landscape: Exploring the Geography of California and Mexico. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!