A Nuclear Landscape: Understanding the Distribution and Significance of Nuclear Power Plants in the United States
Related Articles: A Nuclear Landscape: Understanding the Distribution and Significance of Nuclear Power Plants in the United States
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Nuclear Landscape: Understanding the Distribution and Significance of Nuclear Power Plants in the United States. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Nuclear Landscape: Understanding the Distribution and Significance of Nuclear Power Plants in the United States
![U.S. Nuclear Power Plants and Production by State [1650x1275] : MapPorn](https://external-preview.redd.it/IabWt3J8zmHtcCP04mPXZQaKuufPN2t7tvlvUtSatUU.png?width=960u0026crop=smartu0026auto=webpu0026s=35c6857a877c048ddb83a9b7b0f8b2ef93024b3b)
The United States boasts a significant network of nuclear power plants, strategically positioned across its vast landscape. These facilities play a crucial role in the nation’s energy portfolio, contributing a substantial portion of its electricity generation. Understanding the distribution and significance of these plants requires a comprehensive examination of their geographical spread, operational characteristics, and the multifaceted role they play in the American energy landscape.
A Geographic Overview:
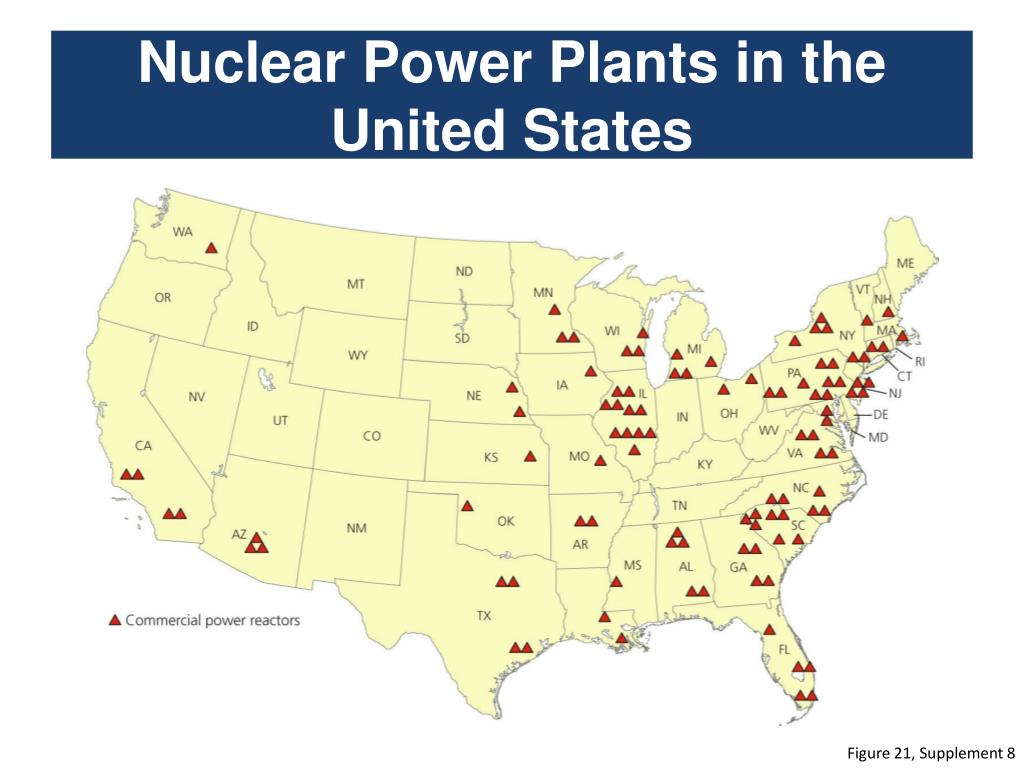
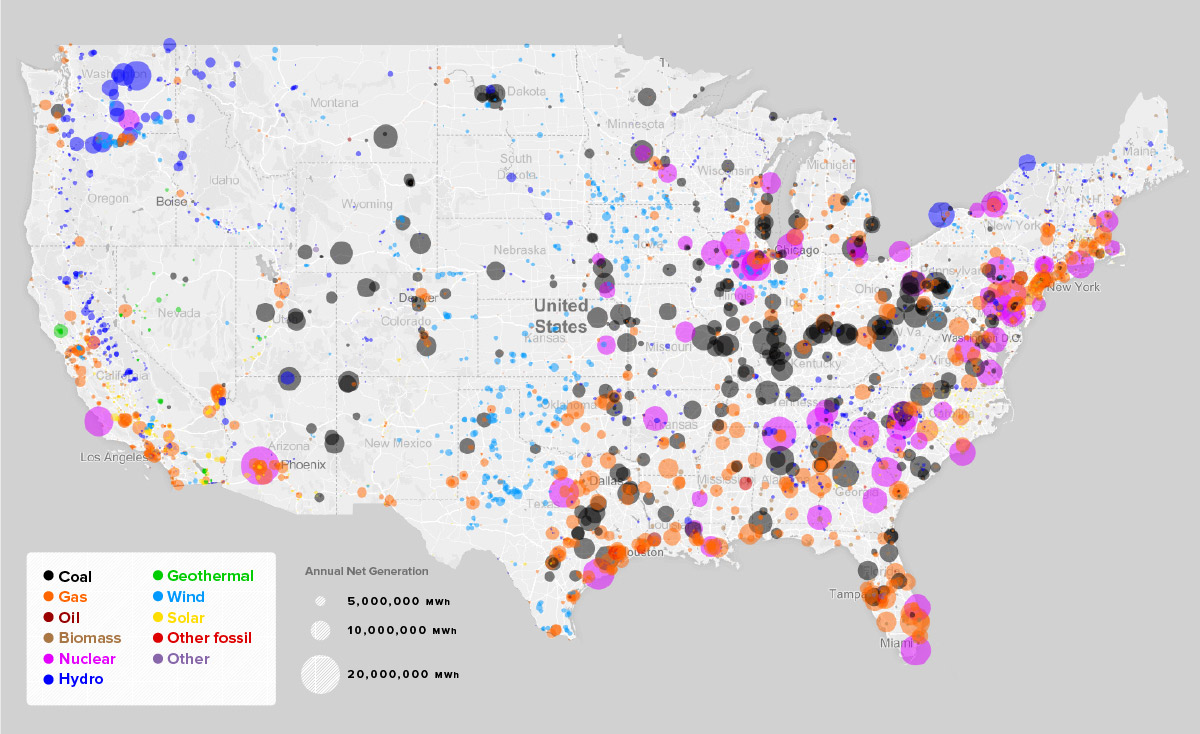
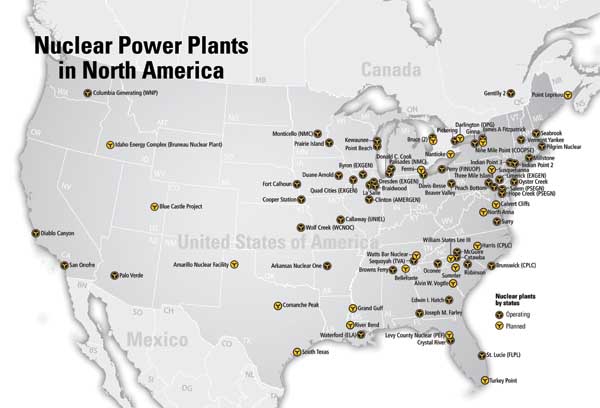
The map of nuclear power plants in the United States reveals a distinct pattern, with a concentration in specific regions and a relative absence in others. The Eastern Seaboard, particularly the Mid-Atlantic and New England regions, houses a notable cluster of nuclear facilities. This distribution can be attributed to several factors:
- Proximity to population centers: The Eastern Seaboard is densely populated, necessitating a reliable source of electricity. Nuclear power plants, with their high output capacity, are well-suited to meet the energy demands of large urban areas.
- Access to cooling water: Nuclear reactors require ample cooling water for their operation. The Eastern Seaboard’s proximity to the Atlantic Ocean and numerous rivers provides a readily available source.
- Historical development: Early nuclear power technologies were developed in the eastern part of the United States, leading to the establishment of the first commercial nuclear plants in this region.
Moving westward, nuclear plants become less frequent, with pockets of concentration in the Midwest and the Southeast. The Midwest, particularly along the Great Lakes, benefits from access to cooling water and proximity to industrial centers. The Southeast, with its growing population and burgeoning energy needs, has also seen an increase in nuclear power generation.
The Western states, however, have a much sparser distribution of nuclear plants. This can be attributed to:
- Limited water resources: The arid climate of the West poses challenges for accessing sufficient cooling water, a critical requirement for nuclear reactors.
- Seismic activity: Many Western states are prone to earthquakes, raising concerns about the safety of nuclear facilities in these regions.
- Alternative energy sources: The abundance of wind and solar resources in the West has led to a greater focus on renewable energy sources.
Beyond Geography: Operational Characteristics and Importance
While geographical distribution provides a snapshot of nuclear power plant locations, understanding their operational characteristics and their role in the American energy landscape is crucial.
- High power output: Nuclear power plants are renowned for their high power output, generating significantly more electricity than fossil fuel plants of comparable size. This makes them an efficient source for meeting the energy needs of large populations.
- Low carbon emissions: Unlike fossil fuel power plants, nuclear plants do not emit greenhouse gases during operation. This makes them a critical component of efforts to mitigate climate change.
- Baseload power: Nuclear plants are designed to operate continuously, providing a reliable and consistent source of electricity, known as baseload power. This stability is essential for maintaining a robust and resilient energy grid.
- Fuel efficiency: Nuclear power plants use uranium, a highly energy-dense fuel, allowing them to operate for extended periods without requiring frequent refueling. This contributes to their overall efficiency.
However, the operation of nuclear power plants is not without challenges:
- Waste management: Nuclear power plants generate radioactive waste, which requires careful and long-term management. This poses challenges for ensuring the safe and responsible disposal of this waste.
- Safety concerns: Accidents at nuclear power plants, such as the Chernobyl and Fukushima disasters, have raised public concerns about their safety. Strict regulations and advanced safety features are in place to mitigate these risks.
- High capital costs: The construction of nuclear power plants is a capital-intensive endeavor, requiring significant upfront investment. This can be a barrier to the development of new nuclear facilities.
- Nuclear proliferation: The use of uranium in nuclear reactors raises concerns about the potential for nuclear weapons proliferation. International agreements and safeguards are in place to address this issue.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
1. What is the current status of nuclear power in the United States?
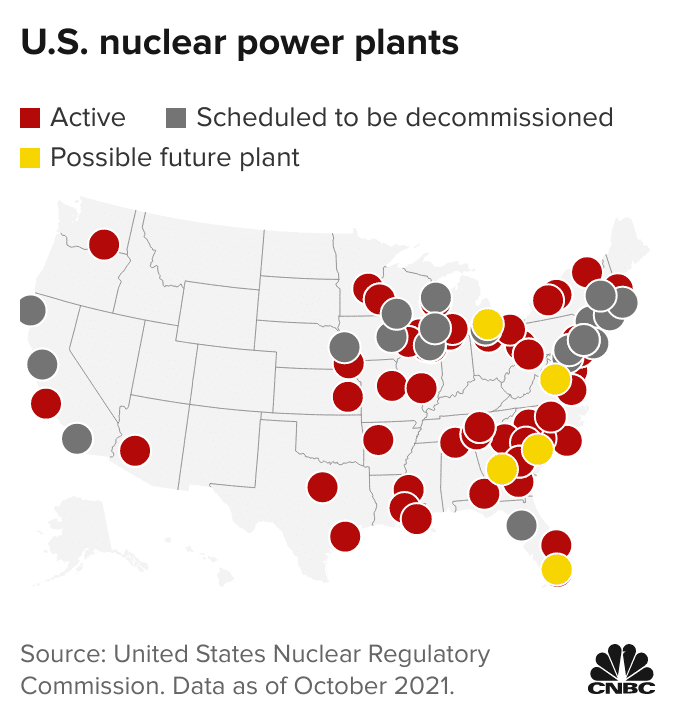
The United States currently operates 92 nuclear reactors at 54 power plants, providing approximately 20% of the country’s electricity. While the number of operating plants has remained relatively stable in recent years, there has been a decline in new construction.
2. Are nuclear power plants safe?
The safety of nuclear power plants is a complex issue. While accidents can occur, modern reactors are designed with multiple safety features to mitigate risks. Regulatory bodies, such as the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC), enforce strict safety standards and conduct regular inspections to ensure the safe operation of these facilities.
3. What are the environmental impacts of nuclear power?
Nuclear power plants have a relatively low carbon footprint compared to fossil fuel plants. However, they do generate radioactive waste, which requires careful management. Additionally, the mining and processing of uranium fuel can have environmental impacts, including habitat disruption and water contamination.
4. What is the future of nuclear power in the United States?
The future of nuclear power in the United States is uncertain. While the technology offers potential benefits in terms of carbon-free energy generation, challenges related to waste management, safety concerns, and high capital costs pose significant hurdles. The role of nuclear power in the nation’s energy mix will likely depend on factors such as government policy, public perception, and the development of advanced reactor technologies.
Tips for Understanding the US Nuclear Landscape
- Consult authoritative sources: The Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) website provides comprehensive information about nuclear power in the United States.
- Explore interactive maps: Several online resources offer interactive maps that visualize the location and characteristics of nuclear power plants.
- Engage in informed discussions: Participate in discussions about nuclear power, seeking out diverse perspectives and evidence-based information.
Conclusion:
The distribution of nuclear power plants in the United States reflects a complex interplay of factors, including geography, energy needs, and technological advancements. These facilities play a significant role in the nation’s energy portfolio, contributing to electricity generation and mitigating climate change. However, challenges related to waste management, safety concerns, and high capital costs continue to shape the future of nuclear power in the United States. As the nation seeks to transition to a cleaner energy future, understanding the complexities and potential of nuclear power will be crucial for informed decision-making.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Nuclear Landscape: Understanding the Distribution and Significance of Nuclear Power Plants in the United States. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!