A Journey Through the Body’s Muscular Network: Understanding the Map of Muscles
Related Articles: A Journey Through the Body’s Muscular Network: Understanding the Map of Muscles
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through the Body’s Muscular Network: Understanding the Map of Muscles. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through the Body’s Muscular Network: Understanding the Map of Muscles

The human body is a marvel of intricate design, a complex symphony of interconnected systems working in harmony. Within this intricate network, the muscular system plays a pivotal role, enabling movement, maintaining posture, and supporting vital bodily functions. Understanding the map of muscles, the intricate arrangement of these tissues, provides a deeper appreciation for the body’s capabilities and the importance of maintaining muscular health.
The Muscular System: A Symphony of Movement
The muscular system is comprised of over 600 individual muscles, each with a specific function and contribution to overall movement. These muscles can be broadly categorized into three types:
-
Skeletal Muscles: These are the muscles responsible for voluntary movement, attached to bones via tendons. They allow for a wide range of motion, from walking and running to complex movements like playing an instrument or typing.
-
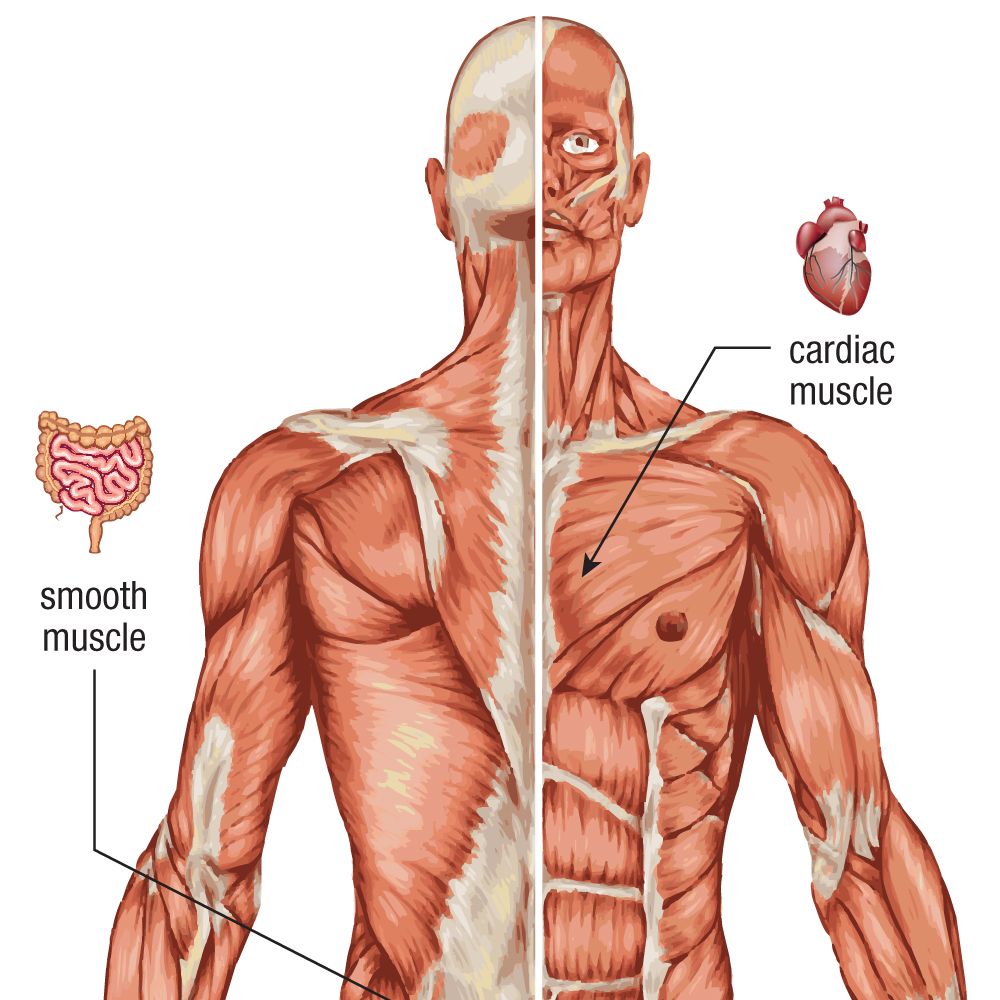
Smooth Muscles: Found in the walls of internal organs like the stomach, intestines, and blood vessels, smooth muscles are responsible for involuntary movements such as digestion and blood flow regulation.
-
Cardiac Muscle: This specialized muscle tissue forms the heart, responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. Its rhythmic contractions are essential for life.
Mapping the Muscular Network: A Guide to the Body’s Power
The map of muscles, a visual representation of the body’s muscular system, provides a comprehensive understanding of the location, function, and interconnectedness of individual muscles. It serves as a valuable tool for various fields, including:
-
Anatomy and Physiology: Students and professionals in the medical field rely on muscle maps to learn about the structure and function of the human body.
-
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation: Therapists use muscle maps to identify muscle imbalances, assess injuries, and develop tailored rehabilitation programs.
-
Exercise and Fitness: Understanding muscle anatomy helps personal trainers and fitness enthusiasts design effective workout routines targeting specific muscle groups.
-
Artistic Anatomy: Artists and sculptors utilize muscle maps to depict realistic human figures, understanding the underlying structure that shapes the body.
Exploring the Map: A Regional Approach
The human body can be divided into different regions, each with a unique set of muscles responsible for specific movements. Examining these regions provides a detailed understanding of the muscular network:
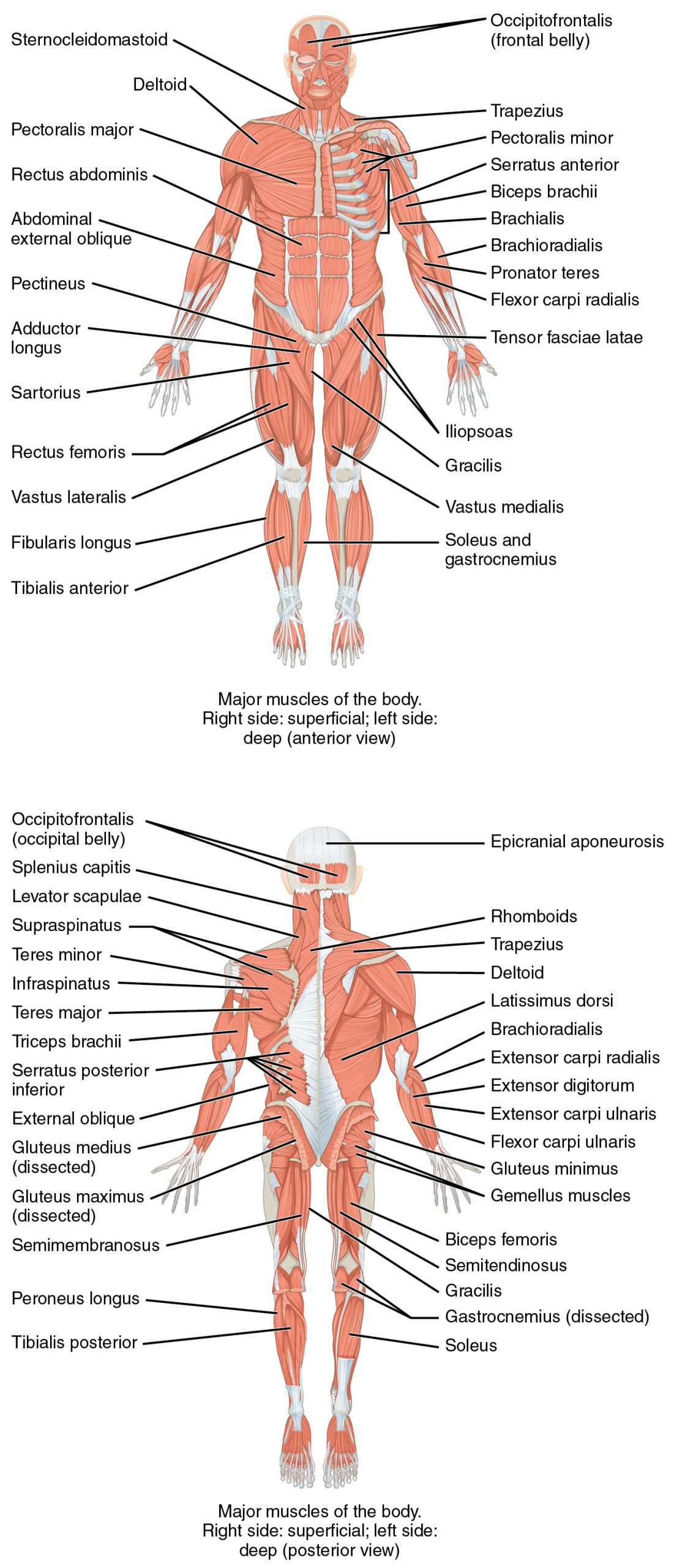
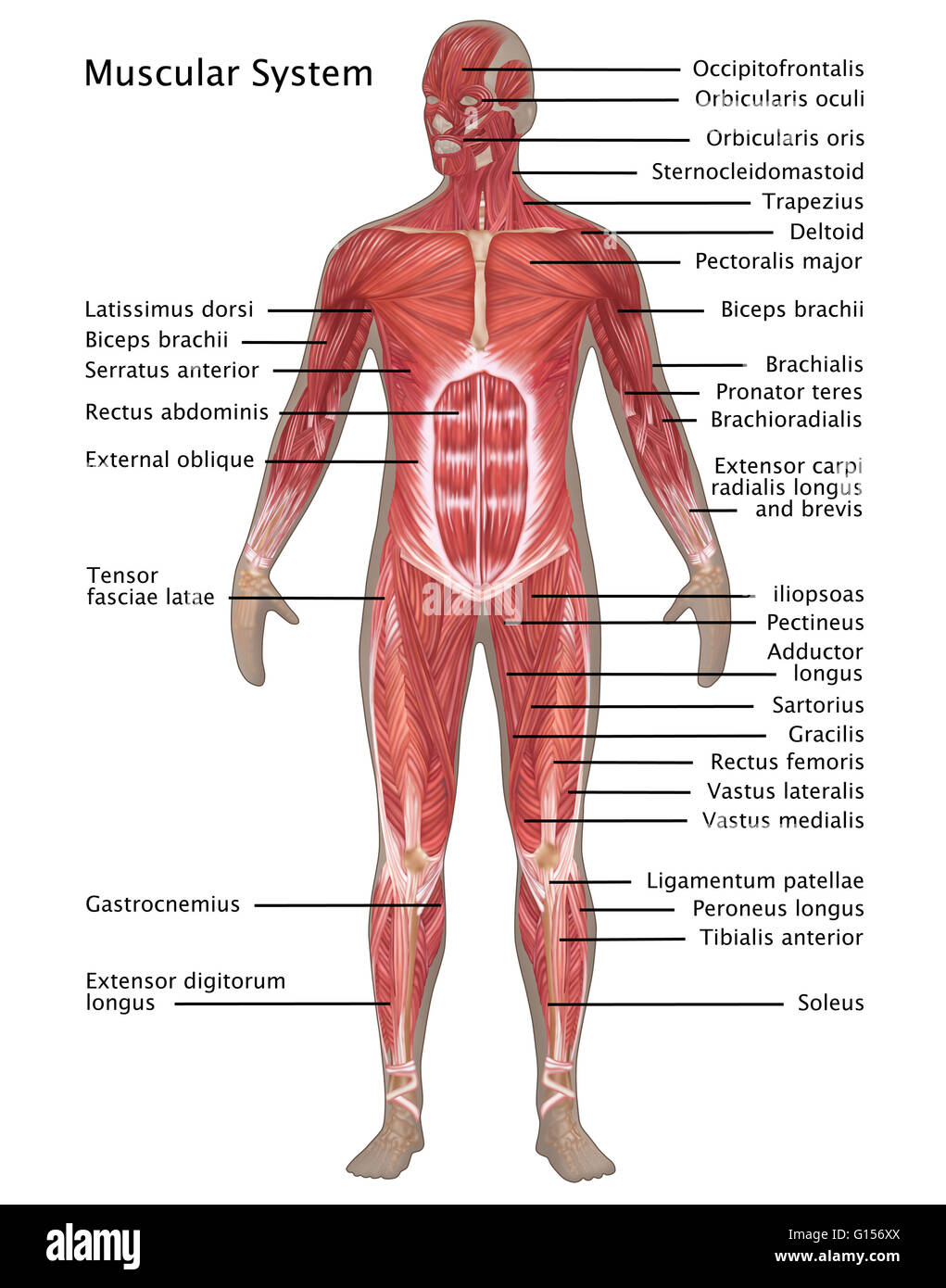
Head and Neck: Muscles in this region control facial expressions, eye movements, chewing, and head movements. Key muscles include the masseter, temporalis, sternocleidomastoid, and trapezius.
Thorax: Muscles in the chest and back play a crucial role in breathing, posture, and upper limb movement. Major muscles include the pectoralis major, latissimus dorsi, intercostals, and diaphragm.
Abdomen: Muscles in the abdomen provide core stability, support internal organs, and contribute to trunk rotation and flexion. Important muscles include the rectus abdominis, obliques, and transverse abdominis.
Upper Limb: Muscles in the arms, forearms, and hands enable a wide range of movements, from gripping and lifting to fine motor skills like writing. Key muscles include the biceps brachii, triceps brachii, deltoid, and flexor/extensor muscles of the wrist and fingers.
Lower Limb: Muscles in the legs and feet are responsible for locomotion, balance, and supporting body weight. Major muscles include the quadriceps femoris, hamstrings, gluteus maximus, gastrocnemius, and soleus.
Understanding Muscle Function: A Deeper Dive
Each muscle in the body has a specific function, contributing to overall movement and bodily function. Understanding these functions is essential for:
-
Optimizing Exercise: Targeted exercises can strengthen specific muscles, improving performance and reducing injury risk.
-
Preventing Muscle Imbalances: Identifying and addressing muscle imbalances can help maintain proper posture and reduce pain.
-
Understanding Injury Mechanisms: Understanding muscle function aids in diagnosing and treating injuries, optimizing recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about the Map of Muscles
Q: What is the significance of understanding muscle anatomy?
A: Understanding muscle anatomy is crucial for various reasons, including:
- Effective Exercise: Targeted exercises can be designed to strengthen specific muscle groups, improving performance and reducing injury risk.
- Injury Prevention: Knowing muscle function helps identify potential imbalances and weaknesses, enabling preventative measures.
- Rehabilitation: Understanding muscle anatomy aids in developing personalized rehabilitation programs for injuries.
Q: How can I learn more about the map of muscles?
A: There are various resources available to learn about muscle anatomy, including:
- Anatomy Textbooks: These provide detailed descriptions and illustrations of the muscular system.
- Online Resources: Websites and educational platforms offer interactive muscle maps and explanations.
- Anatomical Charts: Visual aids displaying the location and function of muscles.
Q: How can I improve my understanding of muscle function?
A: To enhance your understanding of muscle function:
- Study Anatomy: Focus on learning the names, locations, and functions of individual muscles.
- Engage in Exercise: Observe how different muscles work during various movements.
- Seek Professional Guidance: Consult with a physical therapist or personal trainer for personalized advice.
Tips for Understanding and Using the Map of Muscles
- Start with the basics: Begin by learning the names and locations of major muscle groups.
- Use visual aids: Anatomical charts, diagrams, and interactive resources can enhance understanding.
- Connect muscle function to movement: Observe how different muscles work together during everyday activities.
- Seek professional guidance: Consult with healthcare professionals or fitness experts for personalized advice.
Conclusion: The Map of Muscles – A Gateway to Understanding the Body’s Power
The map of muscles is a powerful tool for understanding the intricate workings of the human body. By exploring this map, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complex and interconnected nature of the muscular system, its role in movement, posture, and overall health. Whether you are a student of anatomy, a fitness enthusiast, or simply curious about the human body, understanding the map of muscles provides valuable insights into the power and resilience of this remarkable system.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through the Body’s Muscular Network: Understanding the Map of Muscles. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!