A Journey Across the Italian Landscape: Understanding the Topography of Italy
Related Articles: A Journey Across the Italian Landscape: Understanding the Topography of Italy
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Journey Across the Italian Landscape: Understanding the Topography of Italy. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Across the Italian Landscape: Understanding the Topography of Italy
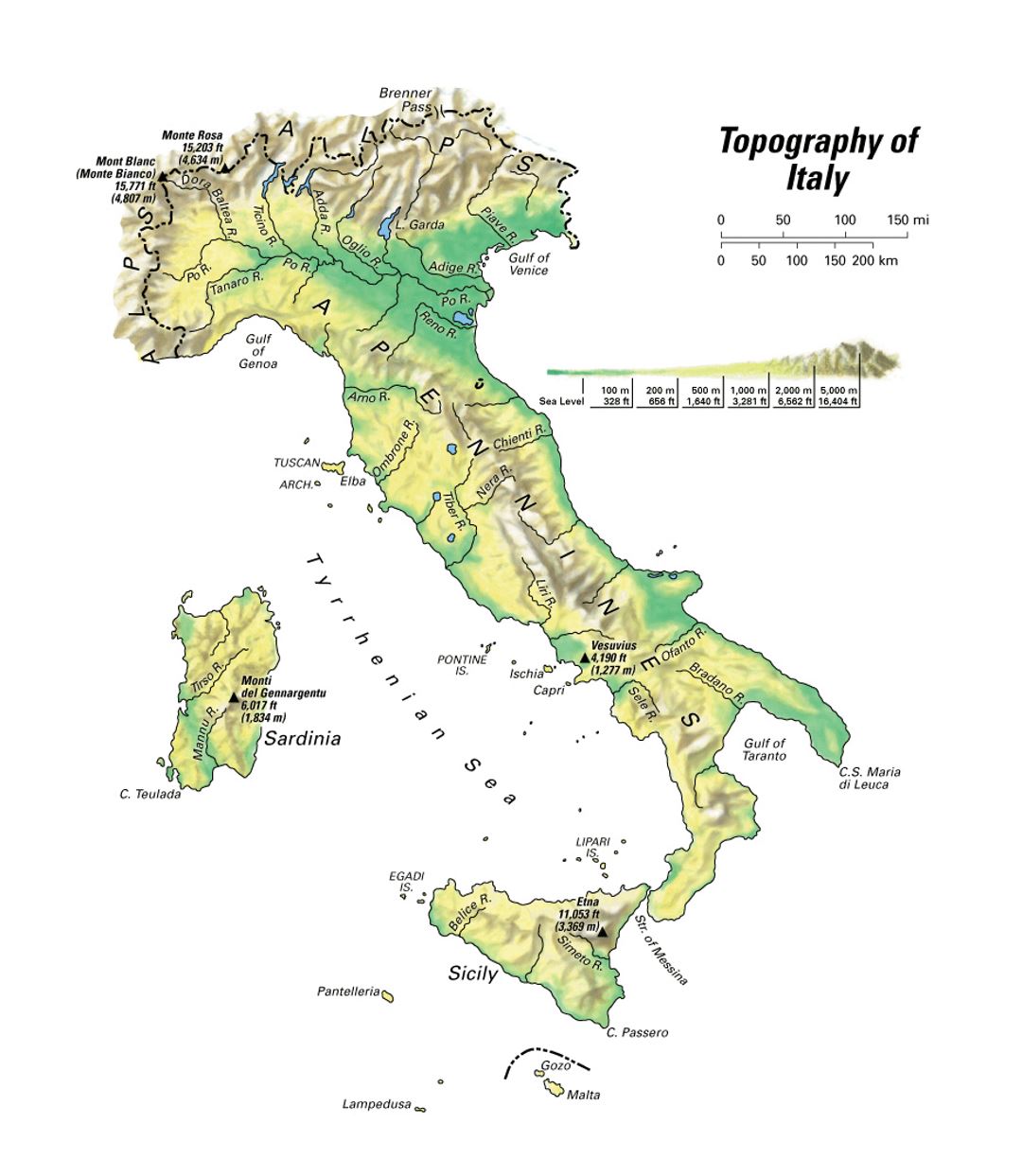
The Italian peninsula, a boot-shaped landmass jutting into the Mediterranean Sea, is a land of dramatic contrasts. From the snow-capped peaks of the Alps to the sun-drenched beaches of the Mediterranean coast, from the rolling hills of Tuscany to the volcanic landscapes of Sicily, Italy’s topography is as diverse as its history and culture. Understanding the intricate interplay of mountains, plains, and coastlines is crucial for appreciating the country’s unique character and its rich tapestry of human activity.
A Land Shaped by Tectonics and Time:
Italy’s topography is a testament to the powerful forces of plate tectonics that have shaped the Earth’s surface over millions of years. The collision of the African and Eurasian plates resulted in the uplift of the Alps, the Apennines, and the Sicilian-Calabrian arc, creating the backbone of the Italian peninsula. These mountain ranges, with their rugged peaks and deep valleys, dominate the landscape, influencing everything from climate and agriculture to transportation and settlement patterns.
The Majestic Alps:
The Alps, a majestic chain of mountains spanning across several European countries, define Italy’s northern border. The Italian Alps, a formidable presence in the north-west, are characterized by their towering peaks, including Mont Blanc, the highest mountain in Western Europe. The region is a paradise for hikers, skiers, and climbers, offering stunning views and challenging adventures. The Alps also play a crucial role in Italy’s water cycle, acting as a natural reservoir, feeding numerous rivers and lakes.
The Apennine Spine:
Running the length of the Italian peninsula, the Apennines form a continuous mountain range, stretching from the Ligurian Alps in the north to the tip of Calabria in the south. The Apennines are less imposing than the Alps, but they are no less significant in shaping Italy’s landscape. They divide the peninsula into two distinct regions: the wetter, more fertile plains to the east and the drier, more arid regions to the west. The Apennines are also home to numerous volcanic peaks, including Mount Vesuvius, the only active volcano on mainland Europe, and Mount Etna, Europe’s largest active volcano, located on the island of Sicily.
The Fertile Plains:
Between the mountain ranges, Italy boasts extensive plains, some of the most fertile in Europe. The Po Valley, stretching across northern Italy, is the largest plain in the country and a vital agricultural region. The fertile soils of the Po Valley support a wide range of crops, from wheat and rice to grapes and olives. Other notable plains include the Padana Plain, the Campanian Plain, and the Apulian Plain, each contributing significantly to Italy’s agricultural output.
The Mediterranean Coastline:
Italy’s coastline, stretching over 7,600 kilometers, is a defining feature of the country. The Mediterranean Sea, with its warm waters and sunny skies, has profoundly influenced Italian culture and economy. The coastline is dotted with picturesque towns and cities, bustling ports, and pristine beaches that attract millions of tourists every year. The Adriatic Sea, to the east, is known for its calm waters and sandy beaches, while the Tyrrhenian Sea, to the west, is characterized by its rugged coastline and volcanic islands.
The Islands of Italy:
Italy’s diverse topography extends beyond the mainland, encompassing a number of islands in the Mediterranean Sea. Sicily, the largest island in the Mediterranean, is a land of contrasts, with its volcanic Mount Etna, fertile plains, and rugged coastline. Sardinia, the second largest island, is known for its pristine beaches, rugged mountains, and ancient archaeological sites. Other notable islands include Elba, Capri, and Ischia, each with its own unique charm and character.
The Impact of Topography on Human Activity:
Italy’s varied topography has had a profound impact on human activity throughout history. The mountains have served as natural barriers, shaping settlement patterns and influencing the development of different cultures. The fertile plains have provided sustenance and supported large populations, while the coastlines have facilitated trade and cultural exchange.
Agriculture and Food:
Italy’s diverse topography has given rise to a rich agricultural tradition. The fertile plains are ideal for growing a wide range of crops, including wheat, rice, grapes, and olives. The mountain slopes are suitable for grazing livestock, while the coastal areas are home to fishing communities. This diversity of agricultural resources has shaped Italy’s culinary heritage, making it one of the most celebrated food cultures in the world.
Transportation and Infrastructure:
Italy’s mountainous terrain has presented challenges for transportation and infrastructure development. The Alps have traditionally been a barrier to travel, but tunnels and passes have been built over the centuries to connect the north and south. The Apennines, while less imposing, have also presented obstacles, leading to the development of a network of winding roads and railways.
Tourism and Recreation:
Italy’s stunning landscapes have made it one of the world’s most popular tourist destinations. The Alps attract skiers and hikers, while the beaches of the Mediterranean coast draw sun-seekers and beach lovers. The rolling hills of Tuscany and the volcanic landscapes of Sicily offer unique and captivating experiences. Italy’s rich cultural heritage, combined with its breathtaking scenery, makes it a truly unforgettable travel destination.
Understanding the Importance of the Italian Topographic Map:
A topographic map of Italy is an invaluable tool for understanding the country’s complex and diverse landscape. It provides a detailed representation of the terrain, including elevations, slopes, rivers, and lakes. This information is essential for a wide range of applications, including:
- Navigation and Planning: Topographic maps are essential for hikers, climbers, and other outdoor enthusiasts, providing them with the necessary information for navigating the terrain and planning their routes.
- Infrastructure Development: Engineers and planners rely on topographic maps to assess the feasibility of infrastructure projects, such as roads, railways, and dams.
- Environmental Studies: Scientists use topographic maps to study the impact of human activities on the environment, such as deforestation, pollution, and climate change.
- Disaster Management: Topographic maps are crucial for disaster management, providing information on flood risks, earthquake zones, and other hazards.
- Tourism and Recreation: Tourists and recreational users can use topographic maps to plan their trips, identify points of interest, and explore the diverse landscapes of Italy.
FAQs about Topographic Maps of Italy:
Q: What are the key features of a topographic map of Italy?
A: A topographic map of Italy typically includes:
- Contour lines: Lines connecting points of equal elevation, providing a visual representation of the terrain’s shape.
- Elevation data: Numerical values indicating the height of different points on the map.
- Hydrographic features: Rivers, lakes, and other water bodies, showing their location and course.
- Cultural features: Cities, towns, roads, railways, and other human-made structures.
- Vegetation: Forests, grasslands, and other vegetation types, providing information on the natural environment.
Q: Where can I find a topographic map of Italy?
A: Topographic maps of Italy are available from a variety of sources, including:
- Government agencies: The Italian National Geographic Institute (IGN) provides detailed topographic maps of the country.
- Online retailers: Websites such as Amazon and eBay offer a wide range of topographic maps, both printed and digital.
- Outdoor stores: Specialty stores that cater to hikers, climbers, and other outdoor enthusiasts often carry topographic maps.
Q: What are the benefits of using a topographic map of Italy?
A: Using a topographic map of Italy offers several benefits, including:
- Enhanced understanding of the terrain: Topographic maps provide a detailed and accurate representation of the landscape, allowing users to visualize the terrain and understand its complexities.
- Improved navigation and planning: Topographic maps provide essential information for navigating the terrain, planning routes, and identifying points of interest.
- Increased safety: Topographic maps can help users avoid hazards, such as steep slopes, cliffs, and water bodies, enhancing their safety during outdoor activities.
- Enhanced environmental awareness: Topographic maps provide information on the natural environment, fostering an appreciation for the beauty and diversity of Italy’s landscapes.
Tips for Using a Topographic Map of Italy:
- Familiarize yourself with the map legend: The legend explains the symbols and colors used on the map, providing essential information for interpreting the data.
- Understand the scale: The scale indicates the ratio between the distance on the map and the actual distance on the ground.
- Use a compass and GPS: These tools can help you navigate the terrain and pinpoint your location on the map.
- Plan your route carefully: Consider the terrain, weather conditions, and your own abilities when planning your route.
- Carry a map and compass even if you have a GPS: GPS devices can malfunction, and a map and compass are essential backup tools.
Conclusion:
The topographic map of Italy is a powerful tool for understanding the country’s diverse and captivating landscape. It provides a detailed representation of the terrain, highlighting the intricate interplay of mountains, plains, and coastlines that have shaped Italy’s history, culture, and economy. Whether you are a hiker, a planner, a scientist, or simply someone who appreciates the beauty of the Italian landscape, a topographic map is an essential resource for exploring this fascinating country.
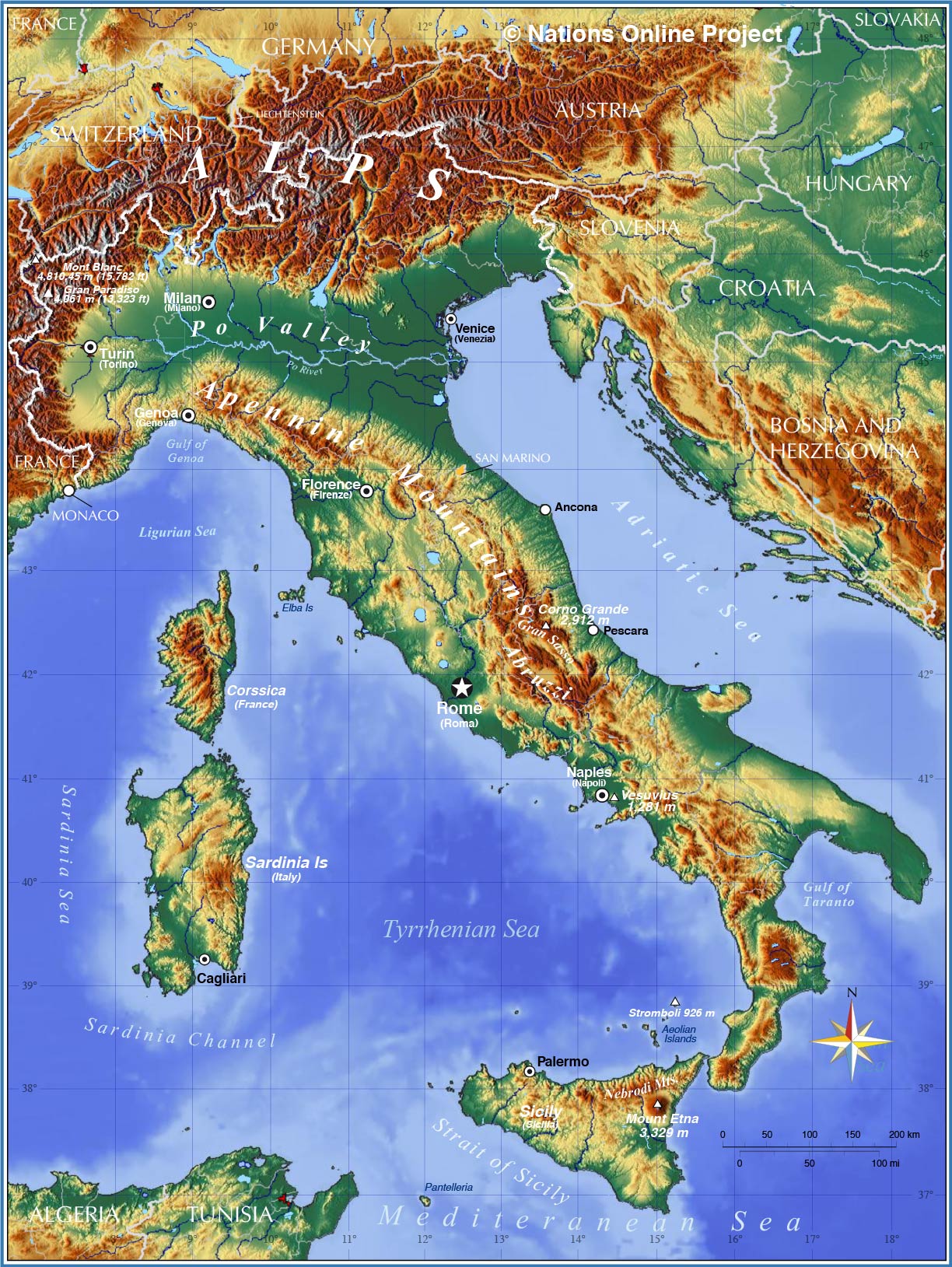

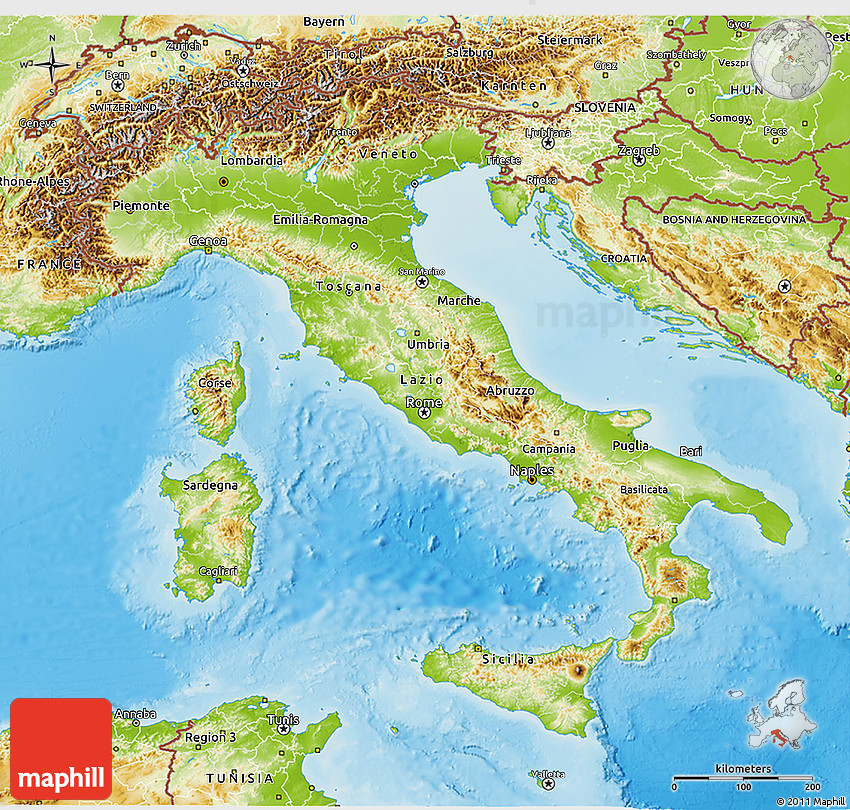





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Across the Italian Landscape: Understanding the Topography of Italy. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!