A Glimpse into the Vastness: Unraveling the Geographical Map of Russia
Related Articles: A Glimpse into the Vastness: Unraveling the Geographical Map of Russia
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Glimpse into the Vastness: Unraveling the Geographical Map of Russia. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Glimpse into the Vastness: Unraveling the Geographical Map of Russia
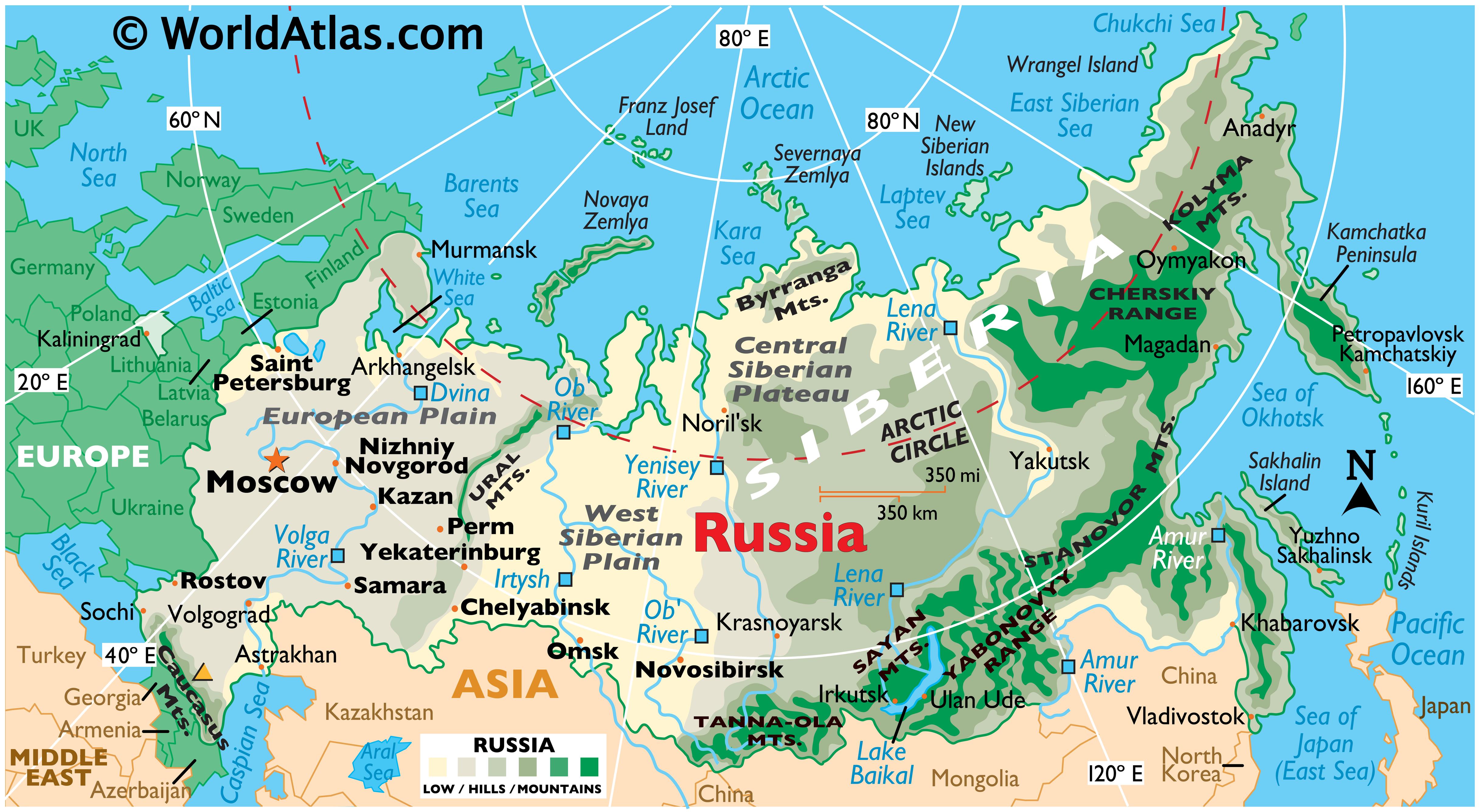
Russia, the largest country in the world by landmass, sprawls across a vast expanse of Eurasia. Its geographical map is a tapestry woven with diverse landscapes, climates, and resources, shaping its history, culture, and global significance. Understanding this map unveils a complex and fascinating world, revealing the intricate interplay of geography and human civilization.
A Land of Extremes: Diverse Landscapes and Climates
The geographical map of Russia is defined by its sheer scale and its remarkable diversity. Stretching from the Baltic Sea in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east, it encompasses 11 time zones and a vast array of landscapes.
-
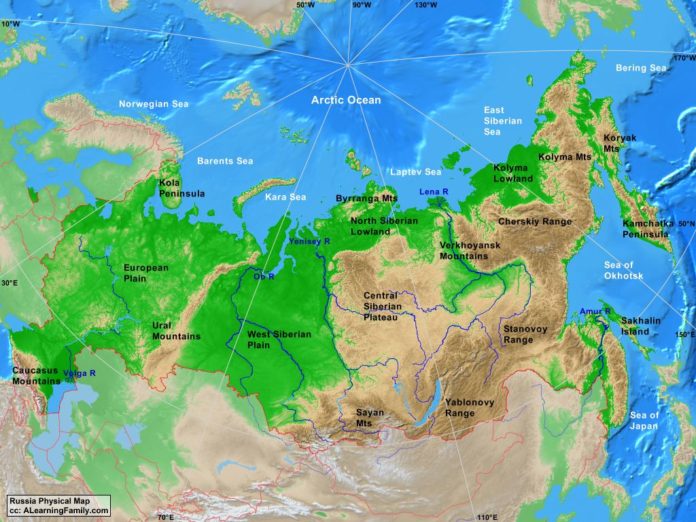
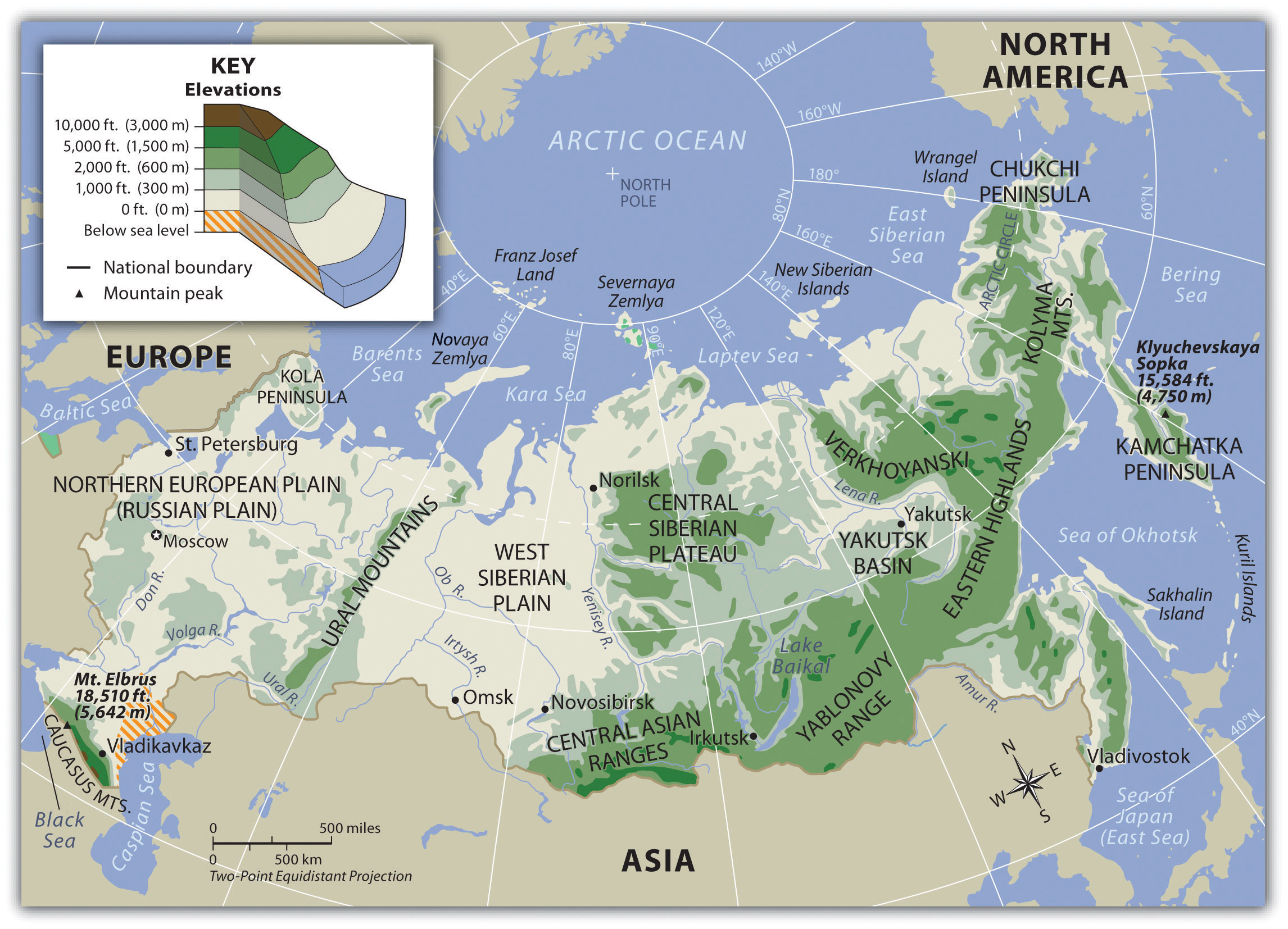
European Russia: The western portion, known as European Russia, is characterized by rolling plains, fertile black earth, and a temperate climate. This region is home to the vast East European Plain, a major agricultural hub, and the Ural Mountains, a natural boundary marking the transition to Asia.
-
Siberia: To the east, Siberia stretches across a vast expanse, encompassing a diverse range of landscapes. From the Siberian Plain, a frozen tundra, to the towering Altai Mountains, Siberia offers a glimpse into the harsh beauty of the Arctic. The Yenisey, Ob, and Lena rivers, among the largest in the world, flow through this region, showcasing the power of nature.
-
The Far East: The easternmost region of Russia, the Far East, is a land of contrasts. It boasts the rugged Kamchatka Peninsula, home to active volcanoes and geysers, and the vast Amur River basin, rich in biodiversity. This region also includes the Kuril Islands, a chain of volcanic islands disputed with Japan.
This geographical diversity translates into a wide range of climates. While European Russia experiences a temperate climate with distinct seasons, Siberia is known for its harsh winters and permafrost. The Far East, meanwhile, is influenced by the Pacific Ocean, resulting in a humid monsoon climate.
The Power of Resources: A Wealth of Natural Treasures
The geographical map of Russia reveals a wealth of natural resources, playing a crucial role in its economy and global influence.
-
Energy Resources: Russia is a global leader in oil and natural gas production, with vast reserves located in Siberia and the Arctic. These resources drive its energy sector and fuel its economy.
-
Mineral Resources: Russia possesses abundant mineral resources, including diamonds, gold, iron ore, and nickel. These resources contribute significantly to its industrial development and international trade.
-
Forest Resources: Russia boasts the largest forest reserves in the world, covering vast swathes of Siberia and the Far East. These forests are a source of timber, pulp, and paper, and play a vital role in regulating the global climate.
-
Water Resources: The vast network of rivers and lakes across Russia provides a crucial resource for transportation, agriculture, and hydroelectric power generation. The Volga River, the longest in Europe, plays a significant role in the country’s economic development.
The Impact of Geography: Shaping History and Culture
The geographical map of Russia has profoundly shaped its history, culture, and national identity.
-
A Land of Expansion: The vast expanse of Russia has historically encouraged expansion, with its borders shifting over centuries. The country’s vast territories have facilitated trade, cultural exchange, and military conquest.
-
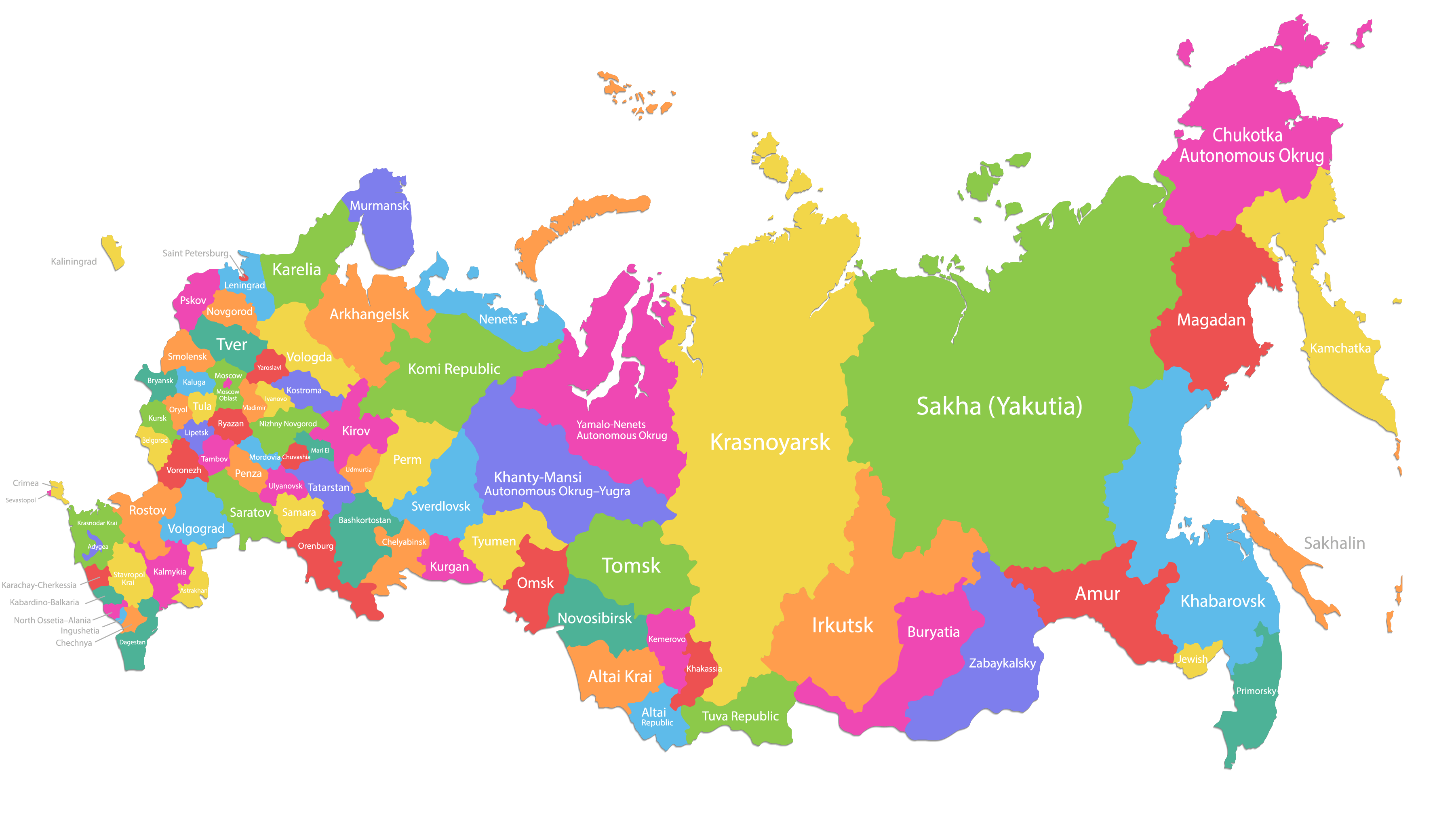
A Diverse Population: The diverse landscapes and climates have contributed to the development of distinct regional cultures and ethnicities. From the Cossacks of the steppes to the indigenous peoples of the Arctic, Russia is a melting pot of cultures.
-
A Sense of Isolation: The vast distances and challenging terrain have historically contributed to a sense of isolation and self-sufficiency. This has fostered a strong sense of national identity and resilience.
Navigating the Map: Understanding the Importance of Geography
Understanding the geographical map of Russia is crucial for comprehending its role in global affairs.
-
Geopolitical Significance: Russia’s vast size, strategic location, and abundant resources make it a major geopolitical player. Its borders touch 14 countries, including major powers like China and the United States, making it a key factor in regional and global security.
-
Economic Powerhouse: Russia’s vast natural resources, particularly oil and gas, have propelled it to become a major economic power. Its energy exports are crucial for many countries, giving it significant leverage in international affairs.
-
Climate Change Impacts: Russia’s vast territory and diverse climates make it particularly vulnerable to the effects of climate change. Melting permafrost, rising sea levels, and extreme weather events pose significant challenges for its infrastructure, economy, and people.
FAQs by Geographical Map of Russia
Q: What are the major geographical features of Russia?
A: Russia’s major geographical features include the East European Plain, the Ural Mountains, the Siberian Plain, the Altai Mountains, the Yenisey, Ob, and Lena rivers, the Kamchatka Peninsula, and the Amur River basin.
Q: What are the main climate zones in Russia?
A: Russia encompasses a wide range of climates, from temperate in European Russia to arctic in Siberia and humid monsoon in the Far East.
Q: What are the most important natural resources in Russia?
A: Russia is rich in natural resources, including oil, natural gas, diamonds, gold, iron ore, nickel, and vast forest reserves.
Q: How has geography influenced Russian history and culture?
A: The vast expanse of Russia has encouraged expansion, while its diverse landscapes and climates have contributed to distinct regional cultures and ethnicities.
Q: What are the geopolitical implications of Russia’s geographical location?
A: Russia’s strategic location and abundant resources make it a major geopolitical player, with its borders touching 14 countries, including major powers like China and the United States.
Tips by Geographical Map of Russia
- Use a variety of sources: Explore atlases, online maps, and geographical texts to gain a comprehensive understanding of Russia’s geography.
- Focus on key features: Pay attention to the major geographical features, including mountains, rivers, and plains, as they shape the country’s landscape and resources.
- Consider historical context: Understand how geographical factors have shaped Russia’s history, culture, and national identity.
- Explore regional differences: Recognize the diversity of landscapes and climates across Russia and how they impact different regions.
- Connect geography to global affairs: Analyze how Russia’s geographical location and resources influence its role in international relations.
Conclusion by Geographical Map of Russia
The geographical map of Russia is a testament to the power of nature, shaping its diverse landscapes, climates, and resources. This vast expanse has played a crucial role in shaping its history, culture, and global significance. Understanding this map unlocks a deeper appreciation of Russia’s unique character and its place in the world. By recognizing the interplay of geography and human civilization, we gain valuable insights into the complexities of this vast and fascinating nation.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Glimpse into the Vastness: Unraveling the Geographical Map of Russia. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!