A Divided Island: Exploring the Geography and History of Haiti and the Dominican Republic
Related Articles: A Divided Island: Exploring the Geography and History of Haiti and the Dominican Republic
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Divided Island: Exploring the Geography and History of Haiti and the Dominican Republic. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Divided Island: Exploring the Geography and History of Haiti and the Dominican Republic

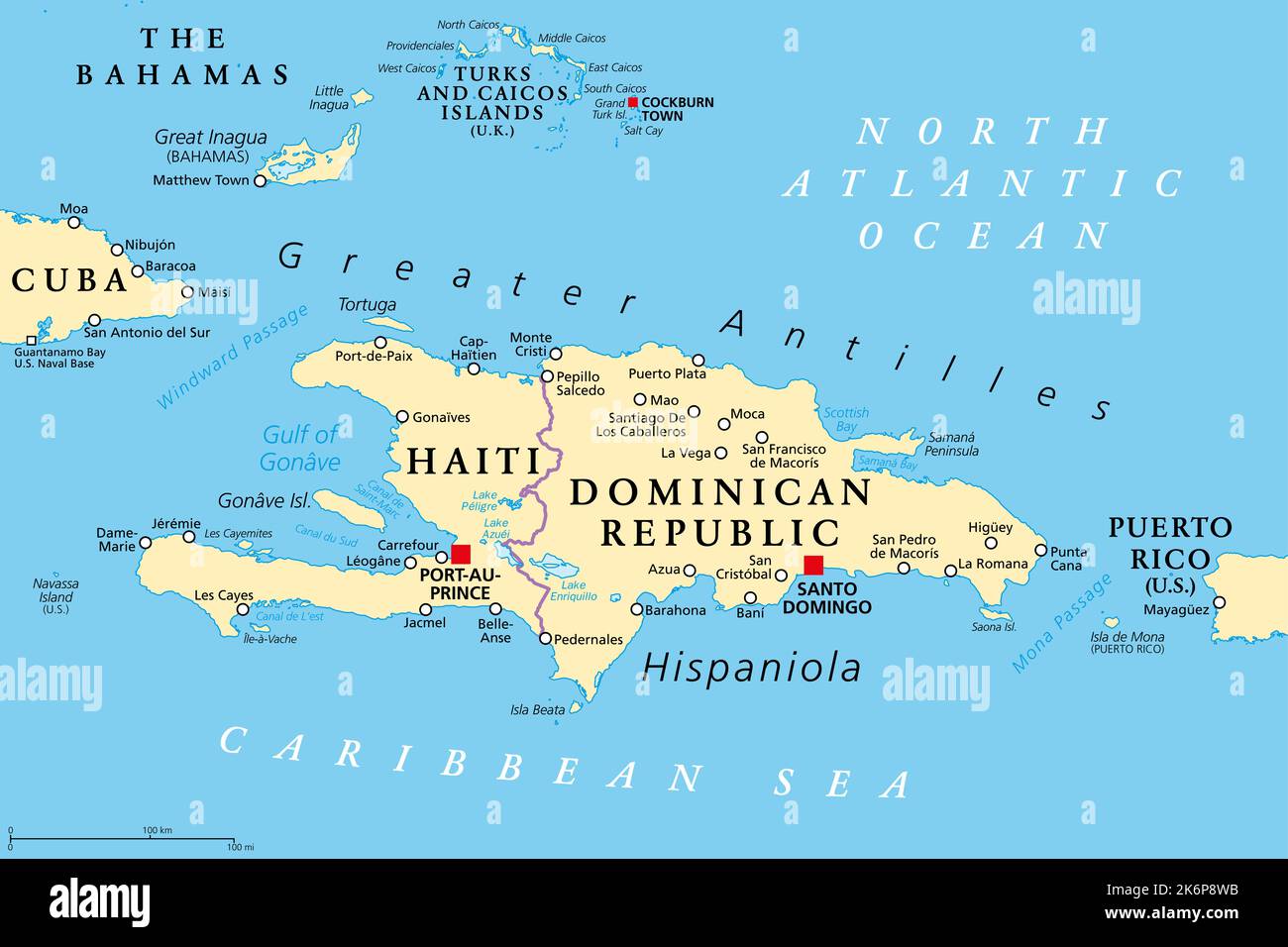
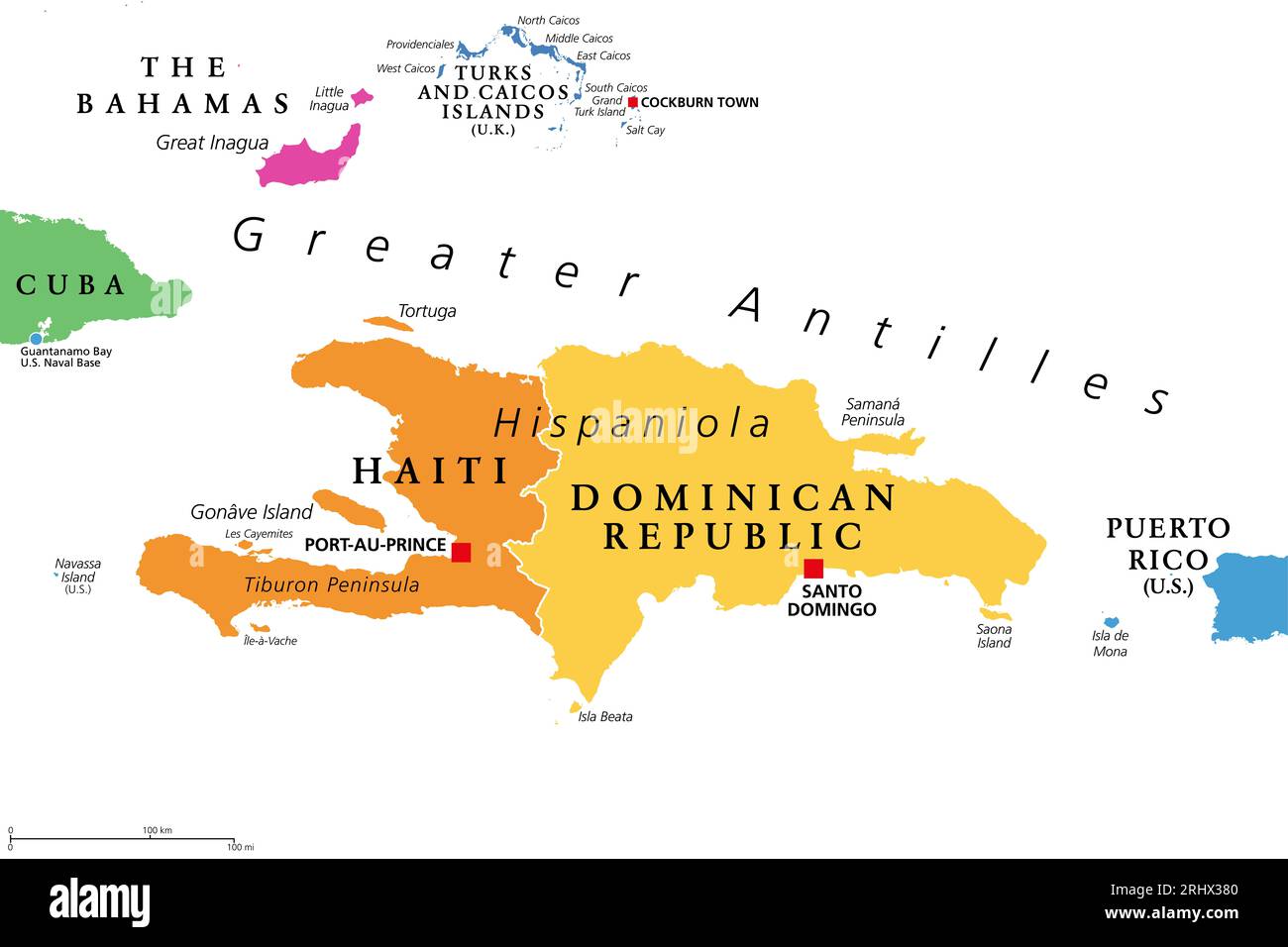
The island of Hispaniola, located in the Caribbean Sea, is home to two distinct nations: Haiti and the Dominican Republic. Though sharing a common island, these countries have vastly different histories, cultures, and landscapes. Understanding the geographic and historical context of Haiti and the Dominican Republic is crucial for appreciating their unique identities and the complexities of their relationship.
Geography: A Shared Landscape with Distinctive Features
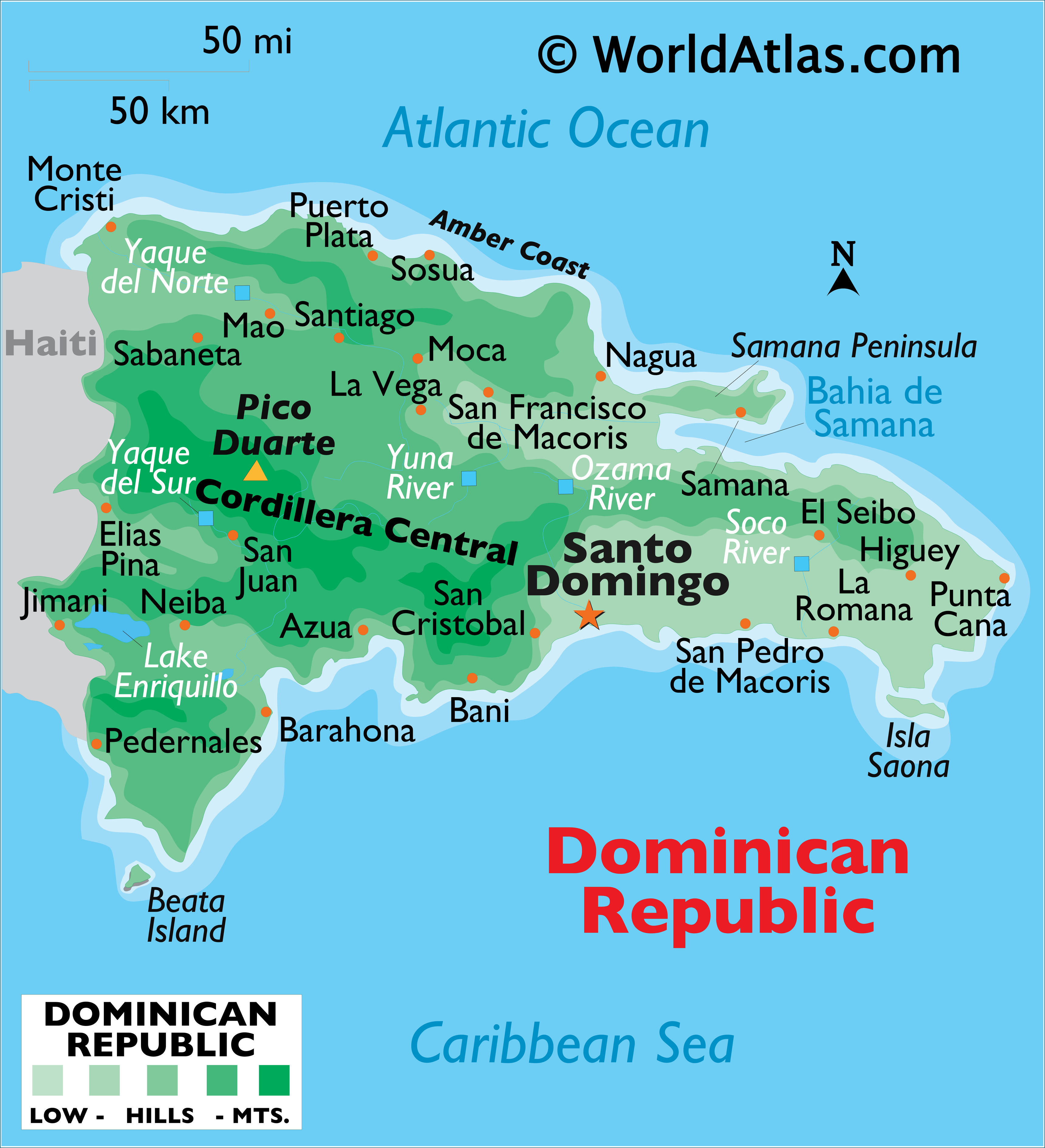
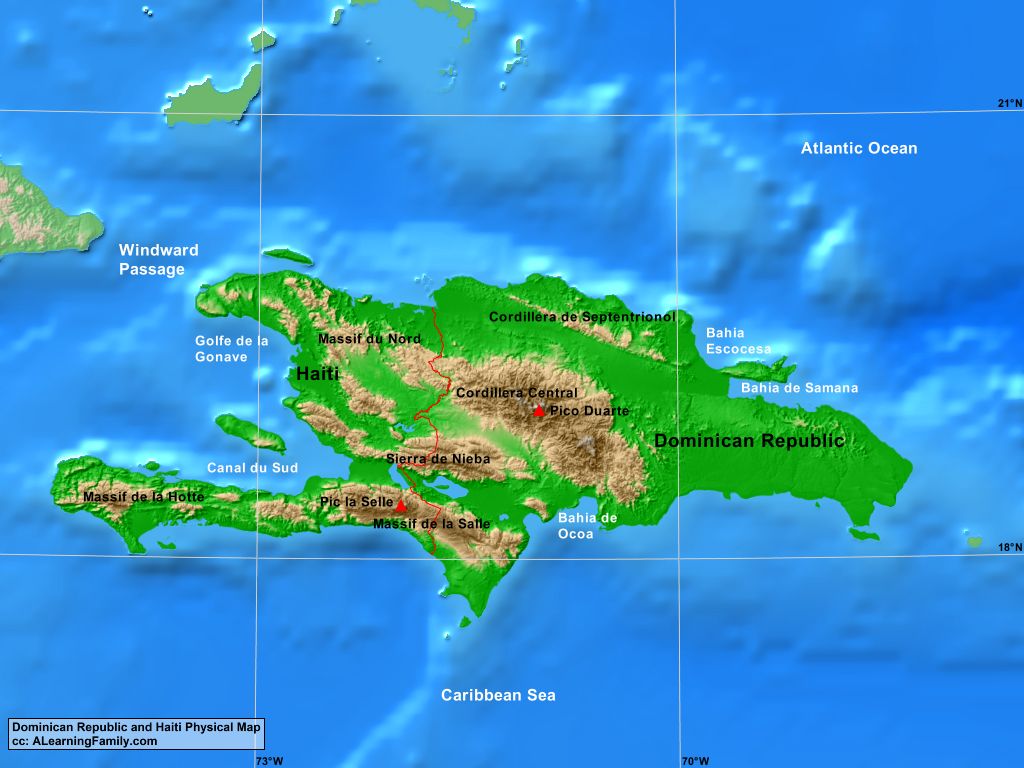
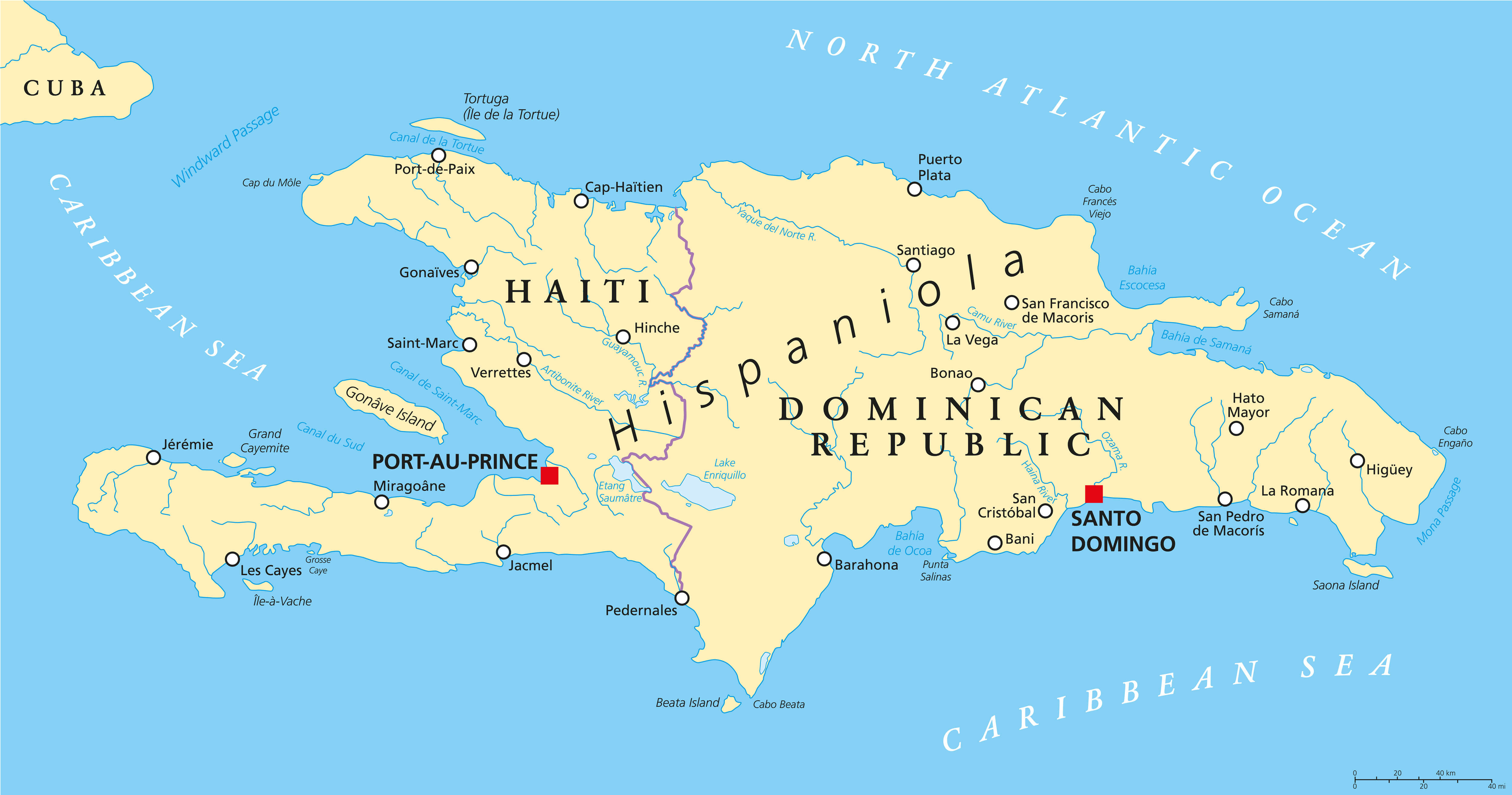
Hispaniola is the second-largest island in the Caribbean, spanning approximately 76,192 square kilometers. Its diverse landscape encompasses lush rainforests, rugged mountain ranges, fertile valleys, and coastal plains. The island’s highest peak, Pico Duarte, reaching 3,175 meters, is located in the Dominican Republic.
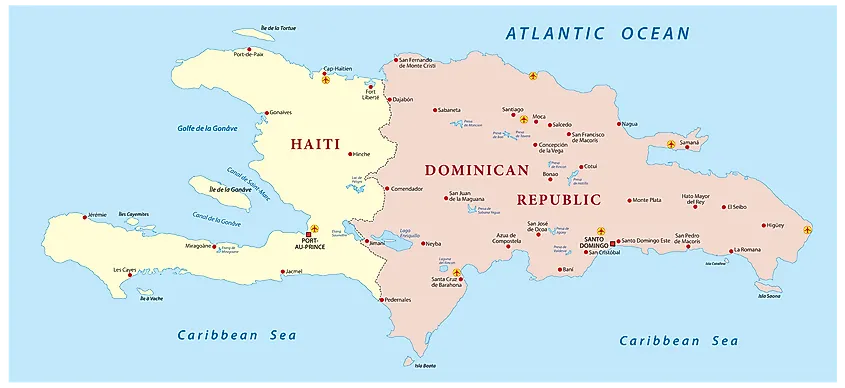
Haiti: Occupying the western third of Hispaniola, Haiti is a mountainous country with a coastline punctuated by numerous bays and inlets. The country is characterized by a complex topography, with the Massif de la Selle, the Massif du Nord, and the Chaîne de la Hotte mountain ranges dominating the interior. Haiti’s landscape is also marked by numerous rivers, including the Artibonite, the longest river in the Caribbean.
Dominican Republic: The Dominican Republic encompasses the eastern two-thirds of Hispaniola, boasting a wide range of landscapes. It features the Cordillera Central mountain range, which includes Pico Duarte, and the Cordillera Septentrional range in the north. The country also possesses extensive coastal plains, particularly in the south, and a variety of ecosystems, including dry forests, mangroves, and coral reefs.
History: Two Nations, Two Paths
The history of Haiti and the Dominican Republic is intertwined, yet marked by significant divergence. Both countries were colonized by Spain in the 15th century, but their destinies took different turns.
Haiti: In 1697, the western third of Hispaniola was ceded to France, becoming Saint-Domingue. The French colony thrived on sugar plantations, fueled by the brutal exploitation of enslaved Africans. In 1791, a slave rebellion erupted, led by figures like Toussaint Louverture, culminating in Haiti’s independence in 1804. This marked the first successful slave revolt in history and the establishment of the first independent Black republic in the world. However, Haiti’s independence was followed by political instability, economic hardship, and foreign interventions, shaping its trajectory for centuries.
Dominican Republic: The eastern part of Hispaniola remained under Spanish control until 1821 when it declared independence. However, this independence was short-lived. In 1822, Haiti annexed the Dominican Republic, initiating a 22-year period of Haitian rule. In 1844, the Dominican Republic regained its independence, establishing itself as a separate nation. Despite its struggles with political turmoil and economic challenges, the Dominican Republic has experienced periods of relative stability and economic growth, particularly in recent decades.
A Shared Island, Divided Identities
The history of colonization, revolution, and independence has shaped the distinct identities of Haiti and the Dominican Republic. While sharing a common island, they have developed unique cultures, languages, and social structures.
Haiti: Haitian culture is rich in music, dance, and art, deeply influenced by its African heritage. Haitian Creole, a French-based Creole language, is the dominant language, reflecting the country’s French colonial past. Haiti’s history of poverty, political instability, and natural disasters has profoundly impacted its social and economic realities.
Dominican Republic: Dominican culture is a vibrant blend of Spanish, African, and indigenous Taino influences. Spanish is the official language, and Dominican music, such as merengue and bachata, enjoys global popularity. The Dominican Republic has experienced economic growth and a growing middle class, although social disparities persist.
The Importance of Understanding the Haiti-Dominican Republic Relationship
The shared history, geography, and cultural influences of Haiti and the Dominican Republic create a complex and dynamic relationship. Understanding the nuances of this relationship is crucial for addressing shared challenges and fostering cooperation.
Challenges:
- Border Disputes: The border between Haiti and the Dominican Republic has been a source of tension and conflict, with disputes over land ownership and migration.
- Economic Disparities: The significant economic disparity between the two countries presents challenges for cooperation and development.
- Environmental Concerns: Both countries face environmental challenges, including deforestation, soil erosion, and climate change, requiring collaborative efforts for sustainable management of shared resources.
Opportunities:
- Economic Cooperation: Collaboration in areas like tourism, agriculture, and trade can benefit both countries, fostering economic growth and development.
- Cultural Exchange: Promoting cultural exchange and understanding can strengthen ties and break down stereotypes.
- Environmental Collaboration: Joint initiatives to address environmental challenges, such as climate change adaptation and biodiversity conservation, can benefit both countries.
FAQs about the Haiti-Dominican Republic Map
Q: What are the main geographical features of Haiti and the Dominican Republic?
A: Both countries feature diverse landscapes, including mountains, coastal plains, and rainforests. Haiti is characterized by its mountainous terrain, while the Dominican Republic boasts the highest peak in the Caribbean, Pico Duarte.
Q: What are the main differences between the histories of Haiti and the Dominican Republic?
A: Haiti’s history is defined by its struggle for independence from French colonial rule and the legacy of slavery, while the Dominican Republic experienced a period of Haitian rule before regaining its independence.
Q: What are the main cultural differences between Haiti and the Dominican Republic?
A: Haitian culture is heavily influenced by its African heritage and French colonial past, while Dominican culture reflects a blend of Spanish, African, and indigenous Taino influences.
Q: What are the main challenges facing the relationship between Haiti and the Dominican Republic?
A: The relationship faces challenges such as border disputes, economic disparities, and environmental concerns.
Q: What are the potential opportunities for cooperation between Haiti and the Dominican Republic?
A: Opportunities for cooperation exist in areas such as economic development, cultural exchange, and environmental protection.
Tips for Understanding the Haiti-Dominican Republic Map
- Study the physical features: Observe the mountain ranges, rivers, and coastlines to understand the geographic context.
- Research the historical events: Explore the colonial history, independence movements, and political developments of both countries.
- Examine the cultural influences: Understand the role of African, European, and indigenous influences on the cultures of Haiti and the Dominican Republic.
- Analyze the economic disparities: Consider the factors contributing to the differences in economic development between the two countries.
- Identify areas of potential cooperation: Explore opportunities for collaboration in areas such as trade, tourism, and environmental protection.
Conclusion
The Haiti-Dominican Republic map is more than just a geographical representation; it is a reflection of a shared history, complex relationship, and diverse cultural identities. Understanding the nuances of this map requires acknowledging the historical context, appreciating the unique features of each country, and recognizing the challenges and opportunities for cooperation. By engaging with this map, we can foster deeper understanding and promote a more collaborative future for both Haiti and the Dominican Republic.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Divided Island: Exploring the Geography and History of Haiti and the Dominican Republic. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!