A Comprehensive Look at Nuclear Power in the United States: Mapping the Landscape
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Look at Nuclear Power in the United States: Mapping the Landscape
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Look at Nuclear Power in the United States: Mapping the Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Look at Nuclear Power in the United States: Mapping the Landscape

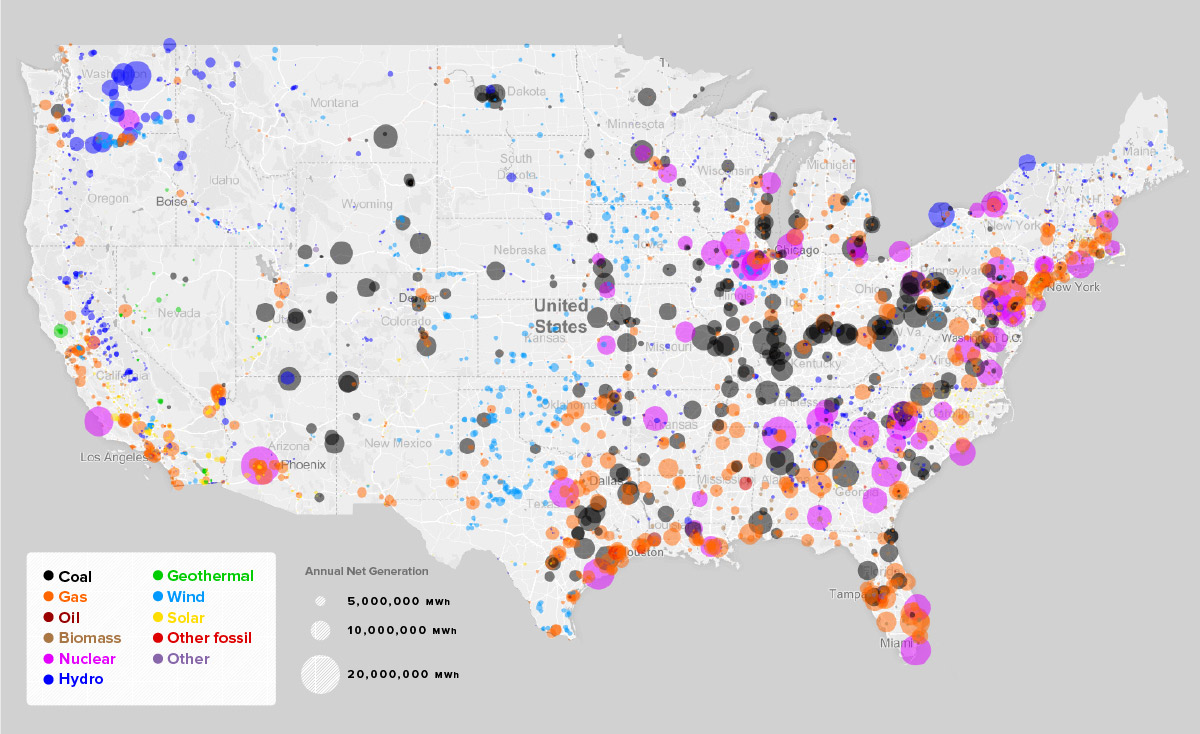
The United States boasts a significant network of nuclear power plants, playing a crucial role in the nation’s energy landscape. This article provides a comprehensive overview of nuclear power plants in the U.S., exploring their geographical distribution, operational details, and the factors influencing their prominence.
Mapping the Nuclear Power Landscape
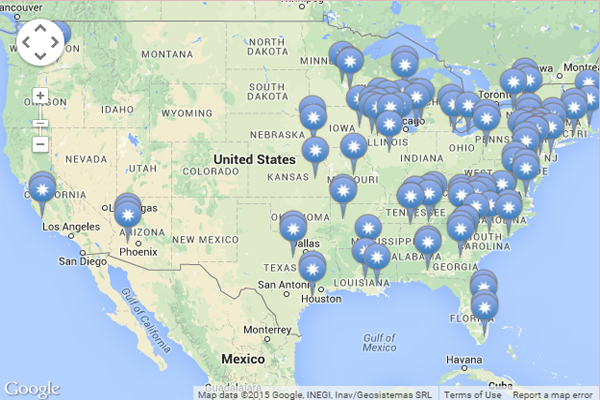
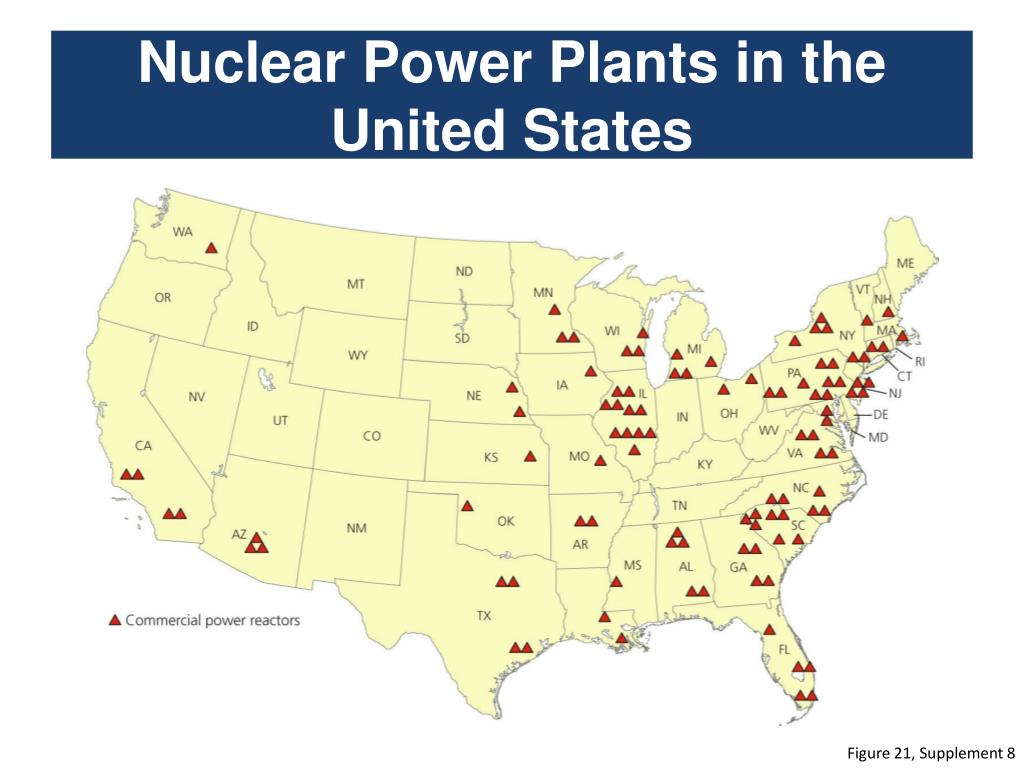
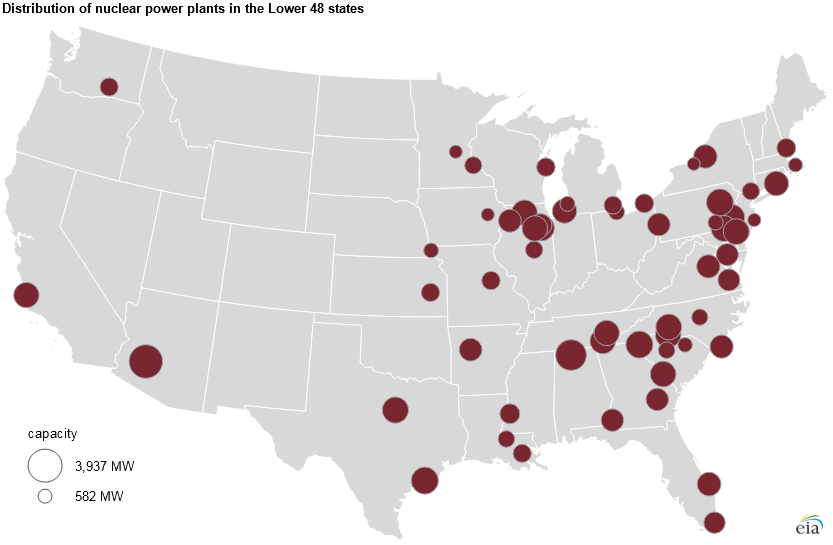
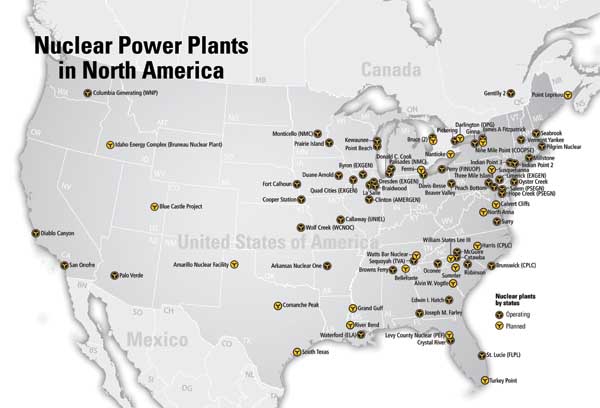
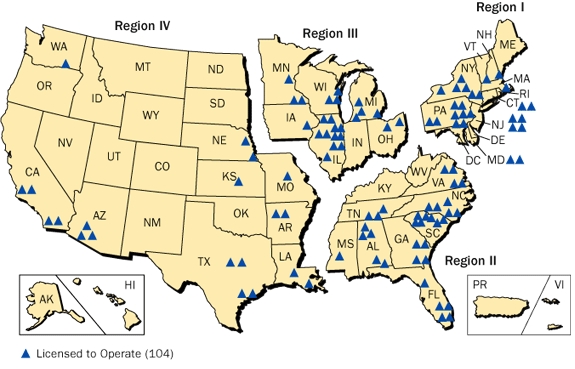
A visual representation of nuclear power plants across the U.S. reveals a distinct pattern. While not evenly distributed, the majority of these facilities are concentrated in specific regions:
- The Eastern Seaboard: States like Pennsylvania, New Jersey, New York, Connecticut, and Massachusetts are home to a significant number of nuclear power plants. This concentration is attributed to factors such as proximity to major population centers and access to water sources for cooling.
- The Midwest: States like Illinois, Ohio, Michigan, and Wisconsin also house a considerable number of nuclear plants. The region’s industrial base and historical reliance on coal-fired power plants contributed to the development of nuclear power.
- The Southeast: States like Georgia, South Carolina, and North Carolina have seen a recent surge in nuclear power development, driven by factors such as favorable regulatory environments and growing energy demand.
- The West Coast: California, Washington, and Oregon, despite their commitment to renewable energy sources, still rely on nuclear power to a significant degree.
Key Factors Influencing Nuclear Plant Location
Several factors influence the location of nuclear power plants, including:
- Proximity to Water Sources: Cooling water is essential for nuclear power plants, making access to large bodies of water like rivers, lakes, or oceans a critical consideration.
- Accessibility to Transportation Networks: Nuclear plants require efficient transportation networks for fuel delivery, waste disposal, and the movement of personnel.
- Seismic Stability: Regions with high seismic activity are generally avoided for nuclear plant construction due to the potential risks associated with earthquakes.
- Population Density: Nuclear power plants are typically located in areas with lower population densities to minimize potential risks in case of accidents.
- Regulatory Environment: States with supportive regulatory frameworks and policies that encourage nuclear power development are more likely to attract nuclear plants.
Understanding the Operation of Nuclear Power Plants
Nuclear power plants operate on the principle of nuclear fission, a process that releases energy from the splitting of uranium atoms. This energy is used to generate steam, which drives turbines to produce electricity. Key components of a nuclear power plant include:
- Reactor Core: The heart of the plant, where nuclear fission takes place.
- Steam Generators: Heat from the reactor core is used to generate steam.
- Turbines: Steam drives turbines to generate electricity.
- Containment Structure: A reinforced structure that encloses the reactor core and protects it from external threats.
- Cooling Systems: Essential for removing heat from the reactor and preventing overheating.
Benefits and Challenges of Nuclear Power
Nuclear power offers several advantages, including:
- Carbon-Free Energy: Nuclear power plants do not emit greenhouse gases, contributing to efforts to combat climate change.
- High Energy Density: Nuclear fuel has a very high energy density, meaning a small amount can produce a significant amount of electricity.
- Baseload Power: Nuclear power plants can operate continuously, providing a reliable source of baseload power.
However, nuclear power also faces challenges:
- Safety Concerns: Accidents at nuclear power plants, such as Chernobyl and Fukushima, have raised public concerns about safety.
- Waste Management: Nuclear waste remains radioactive for thousands of years, posing a challenge for long-term storage and disposal.
- High Construction Costs: Nuclear power plants are expensive to build, requiring significant upfront investment.
- Nuclear Proliferation: The potential for nuclear weapons proliferation is a concern associated with nuclear power.
Addressing Public Concerns and Moving Forward
Public perception of nuclear power remains complex, with concerns about safety and waste management persisting. However, advancements in technology and safety protocols have significantly improved the safety of nuclear power plants. Moreover, ongoing research and development focus on addressing the challenges of waste management and proliferation.
FAQs: Nuclear Power in the United States
Q: How many nuclear power plants are there in the United States?
A: As of 2023, there are 92 operational nuclear power plants in the United States, with a total generating capacity of approximately 100 gigawatts.
Q: What percentage of the U.S. electricity supply comes from nuclear power?
A: Nuclear power currently contributes about 20% of the total electricity generated in the U.S.
Q: How long does it take to build a nuclear power plant?
A: The construction of a nuclear power plant can take 5-10 years, depending on factors such as site location, regulatory approvals, and construction complexities.
Q: What are the different types of nuclear reactors used in the U.S.?
A: The majority of nuclear power plants in the U.S. utilize pressurized water reactors (PWRs). Other types include boiling water reactors (BWRs) and CANDU reactors.
Q: What happens to the nuclear waste generated by power plants?
A: Nuclear waste is currently stored on-site at nuclear power plants. Long-term storage solutions, such as geological repositories, are under development.
Q: What are the future prospects for nuclear power in the U.S.?
A: The future of nuclear power in the U.S. is uncertain, with factors such as public perception, regulatory policies, and the development of advanced reactor technologies playing a significant role.
Tips for Understanding Nuclear Power
- Consult Reliable Sources: Seek information from reputable organizations such as the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC), the World Nuclear Association, and the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA).
- Engage in Informed Discussions: Participate in discussions about nuclear power, sharing information and perspectives based on factual evidence.
- Support Research and Development: Advocate for continued research and development of advanced nuclear technologies to address safety and waste management concerns.
Conclusion
Nuclear power plays a significant role in the U.S. energy landscape, providing a carbon-free and reliable source of electricity. While challenges exist, particularly concerning safety and waste management, advancements in technology and ongoing research hold promise for addressing these concerns. By understanding the complexities of nuclear power and engaging in informed discussions, individuals can contribute to shaping the future of this important energy source.
![U.S. Nuclear Power Plants and Production by State [1650x1275] : MapPorn](https://external-preview.redd.it/IabWt3J8zmHtcCP04mPXZQaKuufPN2t7tvlvUtSatUU.png?width=960u0026crop=smartu0026auto=webpu0026s=35c6857a877c048ddb83a9b7b0f8b2ef93024b3b)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Look at Nuclear Power in the United States: Mapping the Landscape. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!