A Comprehensive Exploration of Niger: Geography, People, and Challenges
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Exploration of Niger: Geography, People, and Challenges
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Exploration of Niger: Geography, People, and Challenges. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Exploration of Niger: Geography, People, and Challenges

Niger, a landlocked country in West Africa, often evokes images of vast deserts and hardy nomadic peoples. While this depiction holds some truth, it only scratches the surface of a nation rich in history, cultural diversity, and natural beauty. This article delves into the geography, people, and challenges of Niger, providing a comprehensive overview of this often-overlooked African nation.
Geography: A Tapestry of Deserts and Savannas
Niger’s landscape is dominated by the Sahara Desert, covering approximately 80% of its territory. The north is characterized by vast, barren plains, while the south transitions into a semi-arid Sahel region, marked by savannas and grasslands. This geographical divide significantly influences the country’s climate, ecosystems, and human settlements.
The Sahara: The vast Sahara Desert, stretching across northern Niger, is a defining feature of the country. Its scorching temperatures, lack of rainfall, and harsh conditions present a significant challenge for human habitation. However, the Sahara also harbors unique biodiversity, including specialized plants and animals adapted to its extreme environment.
The Sahel: Transitioning southwards, the Sahel region offers a stark contrast to the desert. Here, grasslands and savannas provide a more hospitable environment for agriculture and pastoralism. The Sahel region is home to a diverse range of ecosystems, including the Termit Massif, a unique geological formation known for its biodiversity.
Water Resources: A Precious Commodity
Water is a precious commodity in Niger, where most rivers are seasonal and rainfall is scarce. The Niger River, flowing through the southwestern part of the country, is the most significant water source, providing irrigation for agriculture and drinking water for communities. However, the river’s flow is often erratic, making it difficult to rely on for consistent water supply.
People and Culture: A Tapestry of Diversity
Niger is home to a diverse population, with over 100 ethnic groups, each with its own unique language, customs, and traditions. The Hausa, the largest ethnic group, are primarily found in the south and are known for their vibrant culture and rich history. Other significant groups include the Tuareg, nomadic people known for their distinctive blue clothing and desert survival skills, and the Kanuri, known for their strong agricultural traditions.
Religion and Beliefs: Islam is the dominant religion in Niger, practiced by approximately 95% of the population. However, traditional beliefs and practices continue to play a significant role in many communities, particularly in rural areas.
Economy: Challenges and Opportunities
Niger’s economy is largely dependent on agriculture, with over 80% of the population engaged in farming or livestock herding. The country faces significant challenges, including poverty, food insecurity, and limited access to education and healthcare.
Agriculture: Agriculture is the backbone of Niger’s economy, but it is highly vulnerable to climate change and recurrent droughts. The majority of farmers are smallholders, relying on subsistence farming and rain-fed agriculture. The lack of irrigation infrastructure, access to markets, and post-harvest technologies hinders agricultural development and food security.
Mining: Niger possesses significant mineral resources, including uranium, gold, and iron ore. Mining has the potential to contribute significantly to the country’s economy, but it also faces challenges related to environmental sustainability and community development.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Niger faces numerous challenges, including poverty, food insecurity, and climate change. These issues are interconnected, creating a complex web of challenges that require multifaceted solutions.
Poverty: Niger is one of the poorest countries in the world, with over 40% of its population living below the poverty line. This poverty is exacerbated by limited access to education, healthcare, and employment opportunities.
Food Insecurity: Niger is highly vulnerable to food insecurity, with recurrent droughts and climate change impacting agricultural production. Food insecurity leads to malnutrition, particularly among children, hindering their development and well-being.
Climate Change: Climate change poses a significant threat to Niger, exacerbating existing challenges related to drought, desertification, and food insecurity. The country is experiencing rising temperatures, unpredictable rainfall patterns, and increasing frequency of extreme weather events, impacting agriculture, water resources, and human health.
Education and Healthcare: Access to quality education and healthcare remains a challenge for many Nigeriens, particularly in rural areas. Limited resources, inadequate infrastructure, and cultural barriers hinder access to essential services, contributing to high rates of illiteracy and preventable diseases.
Opportunities for Development:
Despite the challenges, Niger possesses several opportunities for development. The country’s rich mineral resources, vast agricultural potential, and strategic location offer possibilities for economic growth and social progress.
Harnessing Mineral Resources: Developing the country’s mineral resources, particularly uranium, gold, and iron ore, has the potential to boost economic growth and create employment opportunities. However, this requires careful planning and management to ensure environmental sustainability and benefit sharing with local communities.
Promoting Agriculture: Investing in agricultural development, including irrigation infrastructure, improved seed varieties, and access to markets, can enhance food security and create economic opportunities. Empowering smallholder farmers through training, access to credit, and market linkages can significantly contribute to agricultural productivity and rural development.
Developing Tourism: Niger’s unique cultural heritage, stunning landscapes, and diverse wildlife offer potential for developing a sustainable tourism industry. Promoting cultural tourism, eco-tourism, and adventure tourism can generate revenue, create employment opportunities, and promote cultural preservation.
FAQs about Niger:
Q: What is the official language of Niger?
A: The official language of Niger is French. However, over 100 languages are spoken throughout the country, including Hausa, Zarma, Kanuri, and Tuareg.
Q: What is the currency of Niger?
A: The currency of Niger is the West African CFA franc (XOF).
Q: What are the main industries in Niger?
A: The main industries in Niger are agriculture, mining, and livestock herding.
Q: Is Niger a safe country to visit?
A: Niger faces security challenges, particularly in the northern regions, due to the presence of armed groups. It is essential to stay informed about security advisories and travel only to areas considered safe.
Q: What are some of the cultural attractions in Niger?
A: Niger boasts a rich cultural heritage, with vibrant traditions, music, and dance. Some of the cultural attractions include the Grand Mosque of Niamey, the Agadez region, known for its Tuareg culture and architecture, and the Zinder region, famous for its traditional markets and crafts.
Tips for Traveling to Niger:
- Obtain a visa: Most visitors require a visa to enter Niger. It is essential to apply for a visa in advance and ensure its validity.
- Stay informed about security advisories: Check with your government’s travel advisories and stay informed about security situations in Niger.
- Respect local customs: Niger is a Muslim-majority country, and it is essential to dress modestly and respect local customs and traditions.
- Learn basic French: French is the official language, and knowing basic French can be helpful for communication.
- Pack light: Niger’s climate is hot and dry, so pack light clothing and comfortable shoes.
- Drink bottled water: It is essential to drink bottled water to avoid waterborne illnesses.
- Be aware of scams: As in many developing countries, be aware of scams and avoid carrying large amounts of cash.
Conclusion:
Niger is a country of contrasts, facing significant challenges but also possessing immense potential for development. Its rich cultural heritage, diverse landscapes, and resilient people make it a fascinating and rewarding destination for those seeking an authentic African experience. By understanding the country’s geography, people, and challenges, we can gain a deeper appreciation for Niger’s resilience and its potential for a brighter future.




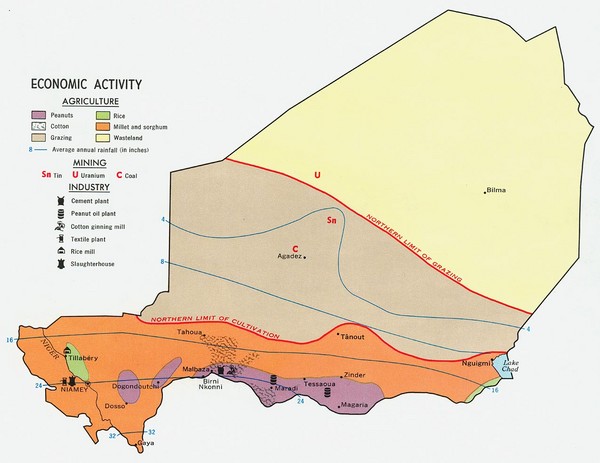

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Exploration of Niger: Geography, People, and Challenges. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!